Top Image-Generation Tools in 2024: A Practical Guide
A practical, beginner-friendly guide to the top image-generation tools in 2024. Compare features, use-cases, pricing, and prompt tips to choose the right tool for hobbyists, creators, and small businesses.
Summary
This practical guide explains the leading AI image-generation tools available in 2024 and helps beginners choose the right one for their needs. It compares popular services (including hosted models and open-source options), explains how each tool fits into common workflows, covers pricing and privacy trade-offs, and gives concrete prompt tips and example use-cases. The article is aimed at hobbyists, content creators, educators, and small-business owners who want to use AI images safely and effectively without needing deep technical skills. Readers will learn how to evaluate models for quality, speed, cost, and control; how to prepare prompts and build simple iterative workflows; and what ethical and copyright considerations to keep in mind. The guide also links to related beginner resources in the FutureExplain series for further learning.
Top Image-Generation Tools in 2024: A Practical Guide
Purpose: This article helps beginners and non-technical users understand, compare, and choose AI image-generation tools in 2024. It focuses on real use-cases, practical workflows, prompt tips, and ethical considerations.
Why AI image tools matter now
AI image-generation tools have matured significantly. They let people create concept art, marketing images, mockups, and social posts quickly — without hiring a designer. For beginners and small teams, these tools can save time and provide creative starting points. However, choosing a tool requires understanding trade-offs: image quality, speed, cost, control, and legal/ethical limits.
How to use this guide
Read the comparison section to match tool features to your needs. Use the workflow and prompt sections to get practical results fast. If you need foundations, review what-is-artificial-intelligence-a-complete-beginners-guide or the tool primer in top-ai-tools-for-beginners-to-boost-productivity.
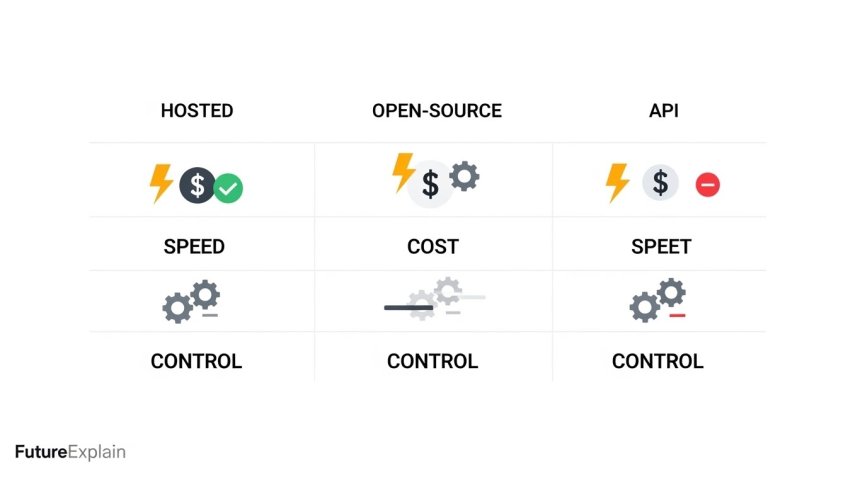
Categories of image-generation tools
- Hosted web services: Provide simple web UIs (good for non-technical users).
- API services: Let developers integrate image generation into apps.
- Open-source models: Run locally or on cloud (better control, no vendor lock-in).
- Hybrid tools: Combine image generation with editing (inpainting, upscaling).
Popular tools to evaluate in 2024
Below are the common choices and what beginners should consider.
1. Midjourney (hosted)
Who it's for: Creators seeking high-quality stylised images quickly.
- Strengths: Distinctive artistic styles, strong community, Discord-based workflow.
- Limitations: Less granular control for photorealism; subscription-based pricing.
- Use-cases: Concept art, moodboards, social visuals.
2. DALL·E family (hosted by major providers)
Who it's for: Users who want balanced photorealistic and creative outputs with an easy web UI.
- Strengths: Photorealism, inpainting, prompt-guided edits.
- Limitations: Usage costs, and some content policies restrict outputs.
- Use-cases: Product mockups, marketing images, simple edits.
3. Stable Diffusion and derivatives (open-source)
Who it's for: Users wanting flexibility, privacy, and lower per-image cost over time.
- Strengths: Local hosting possible, many community checkpoints and UIs, strong plugin ecosystem for fine-control.
- Limitations: Requires technical setup or a managed cloud instance; model quality varies by checkpoint and prompt.
- Use-cases: Custom pipelines, batch generation, commercial use where vendor privacy is a concern.
4. Commercial APIs & platforms (various)
Several cloud vendors offer image APIs combining multiple models. These are useful if you want programmatic image generation integrated into a product with SLA and developer support.
How to choose the right tool — practical checklist
Use this short checklist before committing:
- Quality needs: Do you need photorealism or stylized art?
- Budget: Are you creating a few images or thousands?
- Privacy & ownership: Do you require local processing or full IP ownership?
- Ease of use: Are you comfortable with APIs or prefer a web UI?
- Editing needs: Is inpainting, upscaling, or batch generation important?
Feature comparison (what to compare)
Consider these dimensions when you read product pages or test tools:
- Output quality & style range — how realistic or artistic are results?
- Prompt controls — do they support negative prompts, seeds, or style tokens?
- Editing tools — inpainting, mask editing, upscaling?
- Throughput & speed — how long per image and are there bulk options?
- Cost model — subscriptions, per-image credits, or self-hosted compute costs?
- License & terms — can you use images commercially?
- Safety & content policy — how do they handle copyrighted or sensitive content?
Practical workflow examples
Here are step-by-step beginner workflows for common tasks.
Workflow A — Social media image (fast)
- Pick a hosted tool (e.g., Midjourney or DALL·E).
- Create a short prompt describing scene, mood, color palette, and aspect ratio.
- Generate 4 variations, pick the best, and use the inbuilt upscale or a separate upscaler.
- Optionally refine prompt and re-generate.
Workflow B — Product mockup (control + privacy)
- Use a self-hosted Stable Diffusion checkpoint or a private API.
- Prepare reference images and a clean prompt that includes product details.
- Use inpainting to replace the background or add product labels.
- Run a few iterations, choose a seed, and keep logs of prompts and seeds for reproducibility.
- Refer to models of practice in ai-for-marketing-content-personalization-and-analytics for marketing uses.
Prompt tips for better results
Good prompts are specific, concise, and include style cues. Here are actionable tips:
- Be specific: "A close-up portrait of a young woman, natural light, smiling, 50mm lens look" is better than "woman portrait".
- Use style anchors: Add terms like "photorealistic", "cinematic", "low-poly", or "oil painting".
- Negative prompts: When available, state what to avoid (e.g., "no text", "no watermarks").
- Try seeds: Use seeds if you want reproducible outputs.
- Iterate: Start broad, then refine by adding or removing adjectives.
Editing, upscaling, and finishing steps
Many workflows benefit from editing and final touches:
- Inpainting: Mask areas for the model to change only those regions.
- Background removal: Use AI or manual tools to isolate subjects.
- Upscaling: Use dedicated upscalers (often bundled or available in tools) to increase resolution while preserving detail.
- Color correction: Final fixes in a photo editor improve brand consistency.
Pricing and cost considerations
Costs vary widely. Hosted services charge per image or via subscription; open-source options cost in GPU hours if self-hosted.
- Small volume users: Hosted subscriptions are convenient and predictable.
- High volume users: Self-hosting with cloud spot instances or an on-prem GPU may be cheaper long-term.
- Hidden costs: Consider time for prompt iteration, post-processing, and quality control.
Legal & ethical checklist
Before using AI-generated images commercially, check:
- License terms: Some services claim commercial rights; read terms precisely.
- Copyright risk: Be cautious when generating images in the style of living artists — policies vary and legal questions exist.
- Model provenance: Prefer vendors who document training data sources if ethics are a priority.
- Disclosure: Consider disclosing AI-generated content when transparency matters.
See the ethics series at ethical-ai-explained-why-fairness-and-bias-matter for broader safety guidance.
Accessibility and inclusive design
Ensure images represent diverse people and avoid stereotypes. Use prompts thoughtfully and validate results with diverse reviewers.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
- Overfitting to a single style: Try multiple models or adjust prompts if all images look the same.
- Ignoring post-processing: Raw outputs often need small edits; plan for that time.
- Assuming commercial freedom: Always check license and attribution requirements.
Example use-cases and recommended tools
- Social visuals & marketing: Midjourney or DALL·E for fast, polished images.
- Product mockups: Self-hosted Stable Diffusion with inpainting for control.
- Batch content generation: API-based platforms with credit-based pricing.
- Education and prototyping: Free tiers of hosted tools and open-source models on managed UIs.
How to set up a low-cost experiment
Begin with a 2-week experiment that costs under a small monthly subscription:
- Pick a single use-case (e.g., 10 marketing images).
- Spend one afternoon learning a single tool's prompt controls.
- Generate 20 variations, select the best 5, and polish them in a simple editor.
- Measure outcomes (engagement, time saved) and decide whether to scale.

Prompt library: starter prompts
Use these templates as starting points (replace bracketed tags):
- Photorealistic product: "Photorealistic product photograph of [product], white background, 85mm lens look, soft shadows, high detail."
- Hero marketing image: "Cinematic wide-shot of [subject] in [location], golden hour, shallow depth of field, dramatic lighting, high-resolution."
- Concept art: "Epic fantasy landscape, sunrise, towering cliffs, cinematic composition, oil painting style, high detail."
Further reading and internal loop
To continue learning within FutureExplain, explore related guides:
- how-to-edit-and-enhance-images-with-ai-beginners-walkthrough
- understanding-diffusion-models-stable-diffusion-and-beyond
- ethics-of-ai-generated-media-copyright-and-attribution
- best-free-ai-tools-you-can-use-without-technical-skills
Quick checklist before publishing any AI image
- Confirm license allows intended use.
- Run a simple bias and inclusivity check.
- Ensure no accidental private data is included.
- Keep records of prompts, seeds, and model versions for reproducibility.
Conclusion — a pragmatic approach
AI image tools are powerful but still require thoughtful use. Pick tools that match your quality, cost, and privacy needs, iterate with small pilots, and keep ethical considerations central. With these steps you can add AI-generated images to your workflow safely and effectively.
Next steps
Try a small experiment this week: pick one hosted tool and one open-source option. Create the same prompt in both and compare results. Use the prompt templates above and document time, cost, and quality.
Related reading: For career and skill guidance related to creative AI roles, see ai-careers-explained-beginner-friendly-career-paths and skills-you-should-learn-to-stay-relevant-in-the-ai-era.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0

















Constructive feedback: Could add a short comparison matrix in the article itself.
Short opinion: Very helpful for planning a first pilot.
Praise: Good balance between practical tips and ethics.
Experience: Using a consistent seed helped our iterative designs stay similar across revisions.
Question: For character consistency, how many reference images do you need for fine-tuning?
Hi julianbailey — small LoRA fine-tunes can work with 20–50 curated reference images; quality matters more than quantity.
Constructive feedback: A small FAQ would be nice for quick answers.