Ethics of AI-Generated Media: Copyright and Attribution
This comprehensive guide explores the ethical landscape of AI-generated media, focusing on copyright laws and proper attribution practices. We explain current legal frameworks in simple terms, including the U.S. Copyright Office's stance on AI authorship and international perspectives. You'll learn practical strategies for labeling AI content responsibly, navigating different platforms' terms of service, and protecting your own creative rights. The article includes real-world examples, step-by-step attribution guidelines, and discussions on emerging regulations like the EU AI Act. Whether you're a content creator, business owner, or curious beginner, this guide provides clear, actionable advice for using AI media tools ethically and legally in 2024.

Ethics of AI-Generated Media: Copyright and Attribution
As AI image generators, video creators, and audio tools become more accessible, a crucial question emerges: who owns what these systems create? The ethics of AI-generated media sit at the intersection of technology, law, and creative practice. This comprehensive guide will help you navigate copyright laws, understand proper attribution methods, and develop responsible practices for using AI media tools in 2024.
AI-generated content is transforming creative industries, but it's also creating unprecedented ethical and legal challenges. From commercial artwork to social media posts, understanding the rules and responsibilities surrounding AI media is essential for anyone creating or using this technology. Let's start with the fundamental question: can AI-generated content be copyrighted?
Understanding Copyright Law and AI Authorship
Copyright law was designed to protect original works created by human authors. When AI systems generate images, music, or text, they challenge this foundational principle. According to the U.S. Copyright Office's 2023 guidance, works created entirely by AI without human authorship cannot be copyrighted. However, works that include substantial human creative input—like significant editing, arrangement, or modification of AI outputs—may qualify for protection.
The landmark case of Thaler v. Perlmutter (2023) established that AI cannot be listed as an author on copyright registrations. This decision underscores that copyright protection requires human creativity. Yet, as the Copyright Office notes, this doesn't mean all AI-assisted works are unprotected. If a human provides creative direction, selects specific outputs, and modifies them significantly, the resulting work may be copyrightable as a human-AI collaboration.
Internationally, perspectives vary. The European Union's approach through the AI Act (expected to be fully implemented by 2024-2025) focuses on transparency requirements rather than copyright status. The Act mandates that AI-generated content must be labeled as such, particularly for deepfakes and synthetic media that could deceive viewers. Meanwhile, countries like Japan have taken more permissive stances, allowing broader use of AI in creative works.
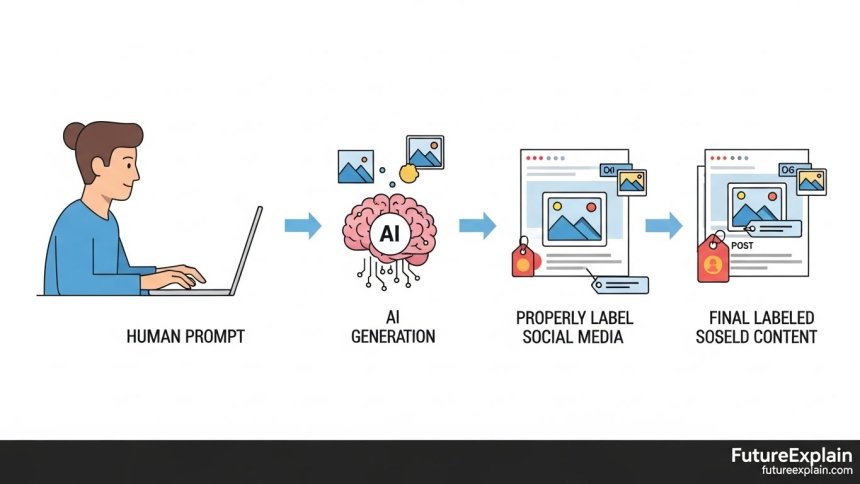
Practical Attribution: How to Label AI-Generated Content
Regardless of legal requirements, ethical creators should disclose when they use AI tools. Proper attribution builds trust with your audience and respects the broader creative community. Here's a practical guide to labeling AI content across different platforms:
1. Social Media Best Practices
Most major platforms are developing policies for AI-generated content. As of 2024, here are the emerging standards:
- Instagram and Facebook: Meta recommends using tags like "AI-generated" or disclosing in captions when content is created with AI, especially if it could be mistaken for reality
- YouTube: Requires disclosure for synthetic content that appears realistic, particularly for political or sensitive topics
- TikTok Has implemented AI labeling tools that creators can use when posting content
- Twitter/X: Community notes and manual disclosure are common practices
The key principle is transparency. When in doubt, add a simple disclosure like: "Created with AI tools" or "AI-generated image." For commercial work, more detailed attribution may be necessary.
2. Professional and Commercial Contexts
When using AI-generated media commercially, your obligations increase. Consider these guidelines:
- Include AI tool attribution in project credits when appropriate
- Document your creative process, including prompts and edits
- Review client contracts for AI usage clauses
- Consider adding AI disclosure statements to websites or portfolios
Terms of Service: What Different AI Tools Allow
Not all AI tools are created equal when it comes to ownership and usage rights. Here's a breakdown of major platforms' policies as of 2024:
Open-Source Models (Stable Diffusion, etc.)
Open-source AI models typically grant broad usage rights, but come with important caveats:
- You generally own outputs you generate
- Commercial use is usually permitted
- Attribution requirements vary by license
- You're responsible for ensuring your use doesn't violate other laws
The CreativeML Open RAIL-M license used by many open models allows commercial use but restricts certain harmful applications. Always check the specific license for any model you use.
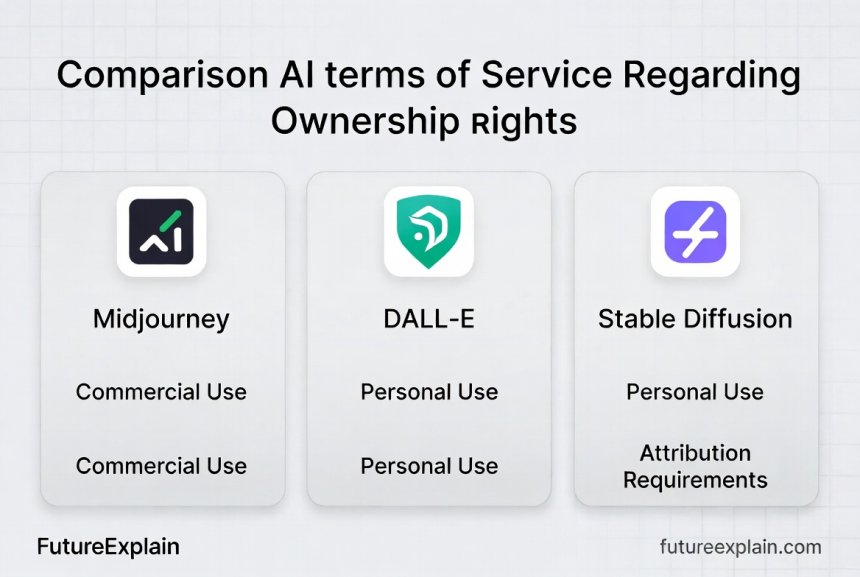
Commercial Platforms (Midjourney, DALL-E, etc.)
Subscription-based services have more complex terms:
- Midjourney: Subscribers own assets they create, subject to content policy restrictions. The company retains certain usage rights for service improvement.
- DALL-E/OpenAI: Users get full usage rights to generated content, including commercial rights. Attribution to OpenAI is appreciated but not required.
- Adobe Firefly: Designed for commercial safety, Firefly grants broad commercial rights and addresses training data ethics through Adobe's Content Authenticity Initiative.
Specialized Tools (Runway, ElevenLabs, etc.)
Niche AI tools for video, voice, and music have their own considerations:
- RunwayML: Generated content can be used commercially, but specific restrictions apply to certain features
- ElevenLabs: Voice generation outputs require careful consideration of voice rights and disclosure
- AI music tools: Often have the strictest limitations due to music industry licensing complexities
Training Data Ethics: The Source Matters
Beyond output ownership, ethical considerations extend to how AI models are trained. Many popular AI image generators were trained on datasets scraped from the web without explicit permission from creators. This raises important questions:
1. Opt-Out Mechanisms
Some platforms now offer opt-out systems for creators who don't want their work used in AI training:
- Robots.txt directives for web crawling
- Platform-specific opt-out forms (like Stability AI's upcoming system)
- Metadata tagging standards like "NoAI" tags
As a user, you can support ethical training practices by choosing tools that use licensed or ethically sourced training data.
2. Ethical Alternatives
Several initiatives promote more ethical approaches:
- Adobe Firefly: Trained on Adobe Stock and public domain content with appropriate rights
- Shutterstock AI: Compensates contributors whose work is used in training
- Open-source ethical datasets: Community efforts to create properly licensed training data
By supporting these initiatives, you contribute to a more sustainable AI ecosystem.
Real-World Case Studies
Let's examine how copyright and attribution play out in actual scenarios:
Case Study 1: AI-Assisted Book Illustrations
An author uses Midjourney to generate illustrations for their self-published children's book. They:
- Significantly edit each image in Photoshop
- Combine multiple AI outputs into original compositions
- Add hand-drawn elements to each illustration
Ethical approach: The author includes an "AI-assisted" note in the credits, documents their creative process, and ensures the final work reflects substantial human creativity that likely qualifies for copyright protection.
Case Study 2: Social Media Marketing Agency
A marketing agency uses DALL-E to create campaign images for clients. They:
- Use AI for initial concepts but hire human artists for final versions
- Disclose AI usage in internal documents and client communications
- Review each platform's policies before posting
Ethical approach: Transparency with clients about tools used, proper labeling on social posts, and respecting platform-specific guidelines.
Case Study 3: Non-Profit Educational Content
An educational nonprofit uses Stable Diffusion to create science illustrations for free online courses. They:
- Use openly licensed models and datasets
- Apply Creative Commons licensing to their final materials
- Include clear attribution for both AI tools and source materials
Ethical approach: Leveraging open-source tools for public benefit while maintaining full transparency about content origins.
Step-by-Step: Creating an Ethical AI Media Workflow
Here's a practical framework you can implement today:
Step 1: Pre-Creation Assessment
- Determine your use case (personal, commercial, educational)
- Review relevant platform terms of service
- Check if your subject matter has special considerations (people, trademarks, etc.)
Step 2: Tool Selection
- Choose tools aligned with your ethical priorities
- Consider training data sources and ownership policies
- Evaluate commercial usage rights
Step 3: Creation Process
- Document your prompts and generation process
- Add significant human creative input where possible
- Keep iterations and variations as evidence of creative process
Step 4: Post-Processing and Attribution
- Edit and refine AI outputs substantially
- Add appropriate disclosures and labels
- Follow platform-specific guidelines for AI content
Step 5: Publication and Maintenance
- Publish with clear attribution when required
- Be prepared to explain your process if questioned
- Stay updated on evolving policies and laws
Emerging Regulations and Future Trends
The legal landscape for AI-generated media is evolving rapidly. Here's what to watch:
1. The EU AI Act
Scheduled for full implementation by 2025-2026, this comprehensive regulation includes specific requirements for AI-generated content:
- Mandatory labeling of AI-generated or manipulated content
- Special rules for deepfakes and synthetic media
- Requirements for foundation model transparency
These rules will affect anyone creating or distributing content in European markets.
2. U.S. Legislative Developments
While comprehensive federal legislation is still developing, several trends are emerging:
- State-level regulations (like California's proposed AI disclosure laws)
- Copyright Office ongoing studies and guidance updates
- Federal Trade Commission attention to deceptive AI practices
3. Industry Self-Regulation
Major tech companies are developing their own standards:
- Content authenticity standards (like C2PA)
- Voluntary labeling systems
- Ethical AI development guidelines
Common Questions and Misconceptions
Myth 1: "If I modify AI output, it's automatically copyrighted."
Reality: Only modifications that constitute original human authorship create copyrightable elements. Simple filters or minor adjustments may not be sufficient.
Myth 2: "AI tools own what they create."
Reality: Most tools grant users rights to their outputs, though terms vary. Always check specific terms of service.
Myth 3: "I don't need to disclose AI use for personal projects."
Reality: While legal requirements may not apply, ethical best practices suggest transparency even for personal work.
Myth 4: "All AI training is unethical."
Reality: Ethical approaches exist, including licensed datasets, opt-in systems, and compensation models. The issue is consent and compensation, not AI training itself.
Building an Ethical Practice: Long-Term Strategies
Developing responsible AI media practices is an ongoing process. Consider these long-term strategies:
1. Education and Awareness
- Stay informed about legal developments
- Participate in industry discussions about AI ethics
- Educate clients and collaborators about AI implications
2. Tool Evaluation Framework
Create a checklist for evaluating new AI tools:
- Training data transparency
- Output ownership rights
- Attribution requirements
- Company ethical guidelines
3. Community Engagement
- Support artists and creators in AI discussions
- Participate in developing industry standards
- Share knowledge about ethical practices
Conclusion: The Path Forward
The ethics of AI-generated media represent one of the most important conversations in today's digital landscape. As tools become more powerful and accessible, our responsibility as creators grows correspondingly. By understanding copyright principles, implementing proper attribution practices, and staying informed about evolving standards, we can harness AI's creative potential while respecting the rights and contributions of human creators.
Remember that ethical AI use isn't about restricting creativity but about ensuring that innovation happens responsibly. As the technology continues to evolve, so too will our understanding of how to use it well. The most successful creators in the AI era will be those who combine technical skill with ethical awareness.
For further learning, explore our articles on How to Use AI Responsibly, Ethical AI Explained, and AI Regulation Overview for more detailed guidance on specific aspects of AI ethics and responsibility.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
1245
Like
1245
 Dislike
23
Dislike
23
 Love
345
Love
345
 Funny
45
Funny
45
 Angry
67
Angry
67
 Sad
12
Sad
12
 Wow
289
Wow
289
















This article has changed how I approach AI tools. Instead of seeing them as a black box, I now understand the importance of transparency and responsibility at every step of the process.
The advice about staying updated is so important. I've set up Google alerts for "AI copyright" and "AI regulation" based on this article's recommendation.
The practical attribution examples are gold. I've struggled with how to word AI disclosures—having concrete examples takes the guesswork out of it.
I'm teaching a digital media class, and I'm using this article as required reading. It covers all the important topics in an accessible way for students.
The ethical alternatives section gave me hope. I want to use AI tools but have been uncomfortable with some practices. Knowing there are companies trying to do things right is encouraging.
As a content moderator for a social platform, I see the challenges of AI-generated content daily. Articles like this help educate creators, which makes my job easier. Thank you!