AI-Powered Background Removal and Inpainting Tools
This comprehensive guide explores AI-powered background removal and inpainting tools that are revolutionizing image editing. Learn how these technologies use neural networks to automatically separate subjects from backgrounds and intelligently fill missing image areas. We compare top tools like Remove.bg, Adobe's AI features, and Canva's Magic Edit, provide step-by-step tutorials for beginners, and explain the underlying technology in simple terms. Discover practical applications for e-commerce, photography, content creation, and historical restoration, along with ethical considerations for responsible use. Whether you're a small business owner, content creator, or photography enthusiast, this guide will help you leverage AI image tools to save time and enhance your visual content.
AI-Powered Background Removal and Inpainting Tools: A Complete Beginner's Guide
In today's digital world, visual content is more important than ever—whether for social media, e-commerce, professional presentations, or personal projects. Yet traditional image editing often requires significant time, technical skill, and expensive software. This is where AI-powered background removal and inpainting tools are changing the game. These intelligent applications use artificial intelligence to automate complex editing tasks that once required professional expertise, making sophisticated image manipulation accessible to everyone.
Background removal involves separating a subject from its background, while inpainting refers to filling in missing or unwanted parts of an image with plausible content. Together, these technologies can transform cluttered photos into professional-looking images, restore damaged photographs, and unleash creative possibilities that were previously impractical for non-experts. This guide will explain how these AI tools work, compare the best options available, and show you how to use them effectively—all without needing technical expertise.
We'll explore everything from the basic concepts to practical applications, ensuring you can confidently leverage these powerful tools for your projects. Whether you're a small business owner creating product images, a content creator designing social media graphics, a photographer streamlining your workflow, or simply someone who wants to improve personal photos, this guide will provide the knowledge you need.
What Are AI Background Removal and Inpainting Tools?
At their core, AI background removal and inpainting tools are software applications that use artificial intelligence—specifically computer vision and deep learning algorithms—to analyze and manipulate images. Unlike traditional editing software that requires manual selection and painting, these tools automatically understand image content and make intelligent decisions about what to keep, remove, or recreate.
Background removal tools identify the primary subject in an image and separate it from everything else, creating a transparent background or allowing you to replace it with something new. Think about product photos for an online store: instead of photographing each item against a perfect white background (which requires controlled lighting and setup), you can take pictures in any environment and let AI clean them up automatically. This technology has become increasingly sophisticated, now capable of handling complex edges like hair, fur, and transparent objects with remarkable accuracy.
Inpainting tools, sometimes called "content-aware fill" or "image completion," take this a step further. They analyze the surrounding areas of a missing or unwanted portion of an image and generate new content that blends seamlessly. This can be used to remove unwanted objects (like tourists from vacation photos), repair damaged photographs, or even creatively expand images beyond their original borders. The AI doesn't just copy and paste existing pixels—it understands patterns, textures, and context to generate plausible new content.
What makes these tools particularly revolutionary is their accessibility. While professional graphic designers have used similar techniques for years, they required advanced skills in software like Photoshop. Today's AI tools often work through simple web interfaces or mobile apps, delivering results in seconds with just a few clicks. This democratization of advanced image editing is empowering individuals and businesses of all sizes to create professional-quality visuals without significant investment in training or software.
How Do AI Image Editing Tools Actually Work?
Understanding how these tools work can help you use them more effectively and appreciate the technology behind them. While the algorithms are complex, the basic principles are accessible even to non-technical users.
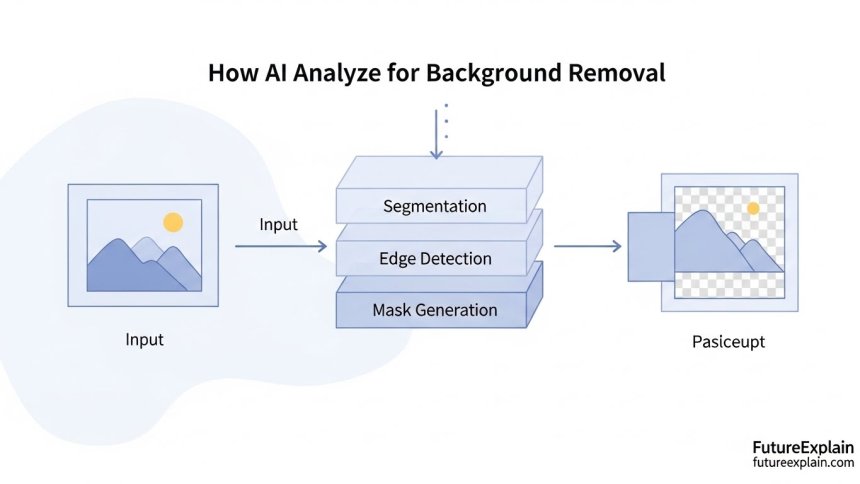
AI background removal tools typically use a type of neural network called a segmentation model. These models have been trained on millions of images where humans have carefully labeled what's "foreground" (the main subject) and "background." Through this training, the AI learns to recognize patterns—like the shape of a person, the contours of a product, or the texture of hair against different backgrounds. When you upload a new image, the AI analyzes it pixel by pixel, making probability calculations about what belongs to the subject versus the background. It then creates a "mask"—an invisible layer that defines what to keep and what to remove.
The most advanced systems use techniques like U-Net architecture, which analyzes images at multiple scales. They look at both fine details (like individual strands of hair) and broader context (like the overall shape of a person) to make accurate decisions. Some tools also use edge detection algorithms to find boundaries between subjects and backgrounds, especially useful for objects with complex outlines.
Inpainting tools employ a different but related approach. They often use generative adversarial networks (GANs), which consist of two competing neural networks. One network (the generator) tries to create plausible content to fill the missing area, while the other (the discriminator) evaluates how realistic that content looks compared to the rest of the image. Through this competition, the system improves its ability to generate convincing results. The AI considers factors like texture continuity, lighting consistency, and pattern completion to make the filled area look natural.
Recent advancements have introduced diffusion models for inpainting, similar to those used in AI image generation tools like Stable Diffusion. These models work by gradually adding structure to randomness, guided by the context of the existing image. They can produce remarkably coherent and creative results, sometimes even extending images in ways that match the original artistic style.
What's particularly impressive is how these systems handle ambiguity. In traditional editing, if you remove a person from in front of a building, you need to manually recreate the building facade behind them. AI inpainting tools analyze the visible parts of the building, understand architectural patterns like windows and bricks, and generate a plausible continuation of that pattern. They don't just copy and paste—they understand and recreate patterns in context.
Top AI Background Removal Tools Compared
With numerous AI background removal tools available, choosing the right one depends on your specific needs, budget, and technical comfort level. Here's a comprehensive comparison of the leading options:
Remove.bg
Perhaps the most well-known dedicated background remover, Remove.bg offers an incredibly simple interface: upload an image, and within seconds you get a result with the background removed. The free version has resolution limits and adds a small watermark, while paid plans offer higher resolutions and batch processing. It excels at people and products but can struggle with very complex edges or transparent objects. The platform also offers an API for developers who want to integrate background removal into their own applications.
Adobe Photoshop with AI Features
While not exclusively a background removal tool, Adobe's recent AI-powered features like Select Subject and Object Selection Tool have revolutionized workflow within the industry-standard software. These tools integrate seamlessly with Photoshop's broader toolkit, allowing for fine-tuning after the AI does the initial work. The Neural Filters also include a Smart Portrait feature that can adjust facial characteristics. The main drawback is the cost and learning curve—Photoshop is a full professional suite, not a single-purpose tool.
Canva's Background Remover
Integrated within the popular Canva design platform, this tool is perfect for users already creating graphics in Canva. It's simple to use and works directly within your design workflow. The free version has some limitations, but premium users get unlimited access. Since it's part of a larger design ecosystem, you can immediately use your background-free image in presentations, social media graphics, or other designs without exporting and re-importing.
Fiverr's Background Removal Service
This represents a different approach: instead of using an automated tool, you're hiring human professionals through the Fiverr platform. While not AI-powered in the same way, many providers on Fiverr use AI tools as part of their workflow. This option makes sense for complex projects where you want human oversight, batch jobs you don't have time for, or when you need absolute perfection for critical images like product catalogs.
Mobile Apps: PhotoRoom, Retouch, and Others
For smartphone users, numerous mobile apps bring background removal to your device. PhotoRoom is particularly popular for e-commerce sellers, offering templates and scenes to place your product against after background removal. Retouch specializes in object removal and minor repairs. These apps often use simplified versions of the algorithms found in desktop tools, optimized for mobile processors. They're convenient for quick edits on the go but may have limitations with very high-resolution images.
When choosing a tool, consider your primary use case. For occasional use with simple subjects, free online tools may suffice. For e-commerce businesses processing hundreds of product images, a paid service with batch processing and API access is worth the investment. Design professionals will benefit from integrated solutions within comprehensive software like Photoshop or Affinity Photo.
Leading AI Inpainting Solutions
AI inpainting tools have seen rapid advancement, with several standout options available for different user needs:
Adobe Photoshop Content-Aware Fill
The industry standard for professional inpainting, Adobe's Content-Aware Fill has become increasingly sophisticated with AI enhancements. It now offers multiple modes (Surface, Creation, and Color Adaptation) and allows you to select which areas of the image should inform the fill. The latest versions use Adobe's Sensei AI to better understand image content and context. While powerful, it requires a Photoshop subscription and substantial learning to use all its capabilities effectively.
Stable Diffusion Inpainting
For users comfortable with more technical tools, Stable Diffusion—the open-source AI image generation model—includes powerful inpainting capabilities. Through interfaces like Automatic1111's WebUI or ComfyUI, you can mask areas of an image and prompt the AI to fill them with specific content. This approach offers tremendous creative control but has a steeper learning curve. It's particularly powerful for creative and conceptual work where you want to add elements that weren't in the original image.
Canva's Magic Edit
Part of Canva's suite of AI tools, Magic Edit allows users to select an area of an image and replace it with something new using text prompts. While not strictly traditional inpainting (which focuses on seamless continuation), it represents a related AI image manipulation capability. It's remarkably accessible for non-technical users and integrates smoothly with Canva's design workflow. The results can be mixed depending on the complexity of the request, but it's improving rapidly.
Luminar Neo with AI Augmented Sky and Object Removal
Luminar Neo takes a specialized approach with tools like AI Augmented Sky (which can dramatically replace skies while maintaining realistic lighting on landscapes) and object removal that cleanly fills the resulting space. It's particularly strong for photographers working with natural scenes. The software is available as a standalone product or plugin for other photo editors, making it accessible to photographers at different technical levels.
Web-Based Tools: Cleanup.pictures, Inpaint Online
For quick, simple jobs without installing software, web-based tools offer convenience. Cleanup.pictures provides a straightforward interface for removing objects from photos, while Inpaint Online handles both object removal and basic restoration. These are excellent for occasional users who need to clean up a photo quickly. They typically have file size limitations in their free versions and may offer subscription plans for heavier use.
The right inpainting tool depends on whether you need precision restoration (leaning toward Photoshop), creative expansion (considering Stable Diffusion), or quick fixes (web tools). Many users eventually work with multiple tools for different purposes.
Step-by-Step Tutorials for Beginners
Let's walk through practical examples using different types of tools. These tutorials assume no prior expertise with image editing.
Tutorial 1: Removing Backgrounds for E-commerce Products
If you're selling products online, clean, consistent product images can significantly impact sales. Here's how to create them using AI tools:
Step 1: Capture Your Product Photo
Take a well-lit photo of your product. Natural, diffused light works best. Place the product on a surface with some contrast to the product itself (a dark product on a light surface, or vice versa) but don't worry about perfection—the AI will handle the hard part.
Step 2: Choose Your Tool
For beginners, I recommend starting with Remove.bg or Canva's background remover. Both have simple drag-and-drop interfaces.
Step 3: Upload and Process
Drag your image into the tool's interface. Most will process automatically within seconds. If the tool offers different modes (like "person" vs. "product"), choose the appropriate one.
Step 4: Review and Adjust
Examine the edges of your product. Zoom in to check for areas where the AI might have made mistakes—sometimes it removes parts of the product or leaves bits of background. Many tools offer simple editing interfaces to fix these issues with brush tools.
Step 5: Download or Export
Once satisfied, download your image. For e-commerce, PNG format with transparent background is standard. You can now place your product against any background in your store template.
Pro Tip: If you have multiple products, look for tools with batch processing. You can often upload dozens of images at once, saving enormous time compared to manual editing.
Tutorial 2: Removing Unwanted Objects from Photos
We've all taken great photos ruined by unwanted elements—a tourist in the background, power lines across a beautiful sky, or temporary construction. Here's how to clean them up:
Step 1: Select the Right Tool
For this task, you'll want an inpainting tool rather than just background removal. Adobe Photoshop's Content-Aware Fill is powerful if you have access. For free options, try Cleanup.pictures or Inpaint Online.
Step 2: Identify What to Remove
Look at your image and decide what needs to go. Simple objects against consistent backgrounds (like a trash can on a lawn) are easiest. Complex objects overlapping your main subject (like someone standing in front of a person you want to keep) are more challenging.
Step 3: Mark the Area
Using the tool's selection brush, carefully mark the object you want to remove. Most tools work better if you include a little of the surrounding area, not just the object itself. This gives the AI more context for what should replace it.
Step 4: Let the AI Work
Process the image. The AI will analyze the surrounding pixels and generate content to fill the selected area.
Step 5: Evaluate and Refine
Examine the result closely. Does the filled area look natural? Sometimes the AI creates slightly repetitive patterns or doesn't perfectly match lighting. Many tools allow you to run the process again on the same area for a different result, or manually touch up with cloning tools.
Step 6: Save Your Cleaned Image
Once you're happy with the result, save a new version of your image. Always keep the original in case you need to start over or try a different approach.
With practice, you'll develop an eye for what different AI tools handle well and when you might need to combine AI with manual touch-ups.
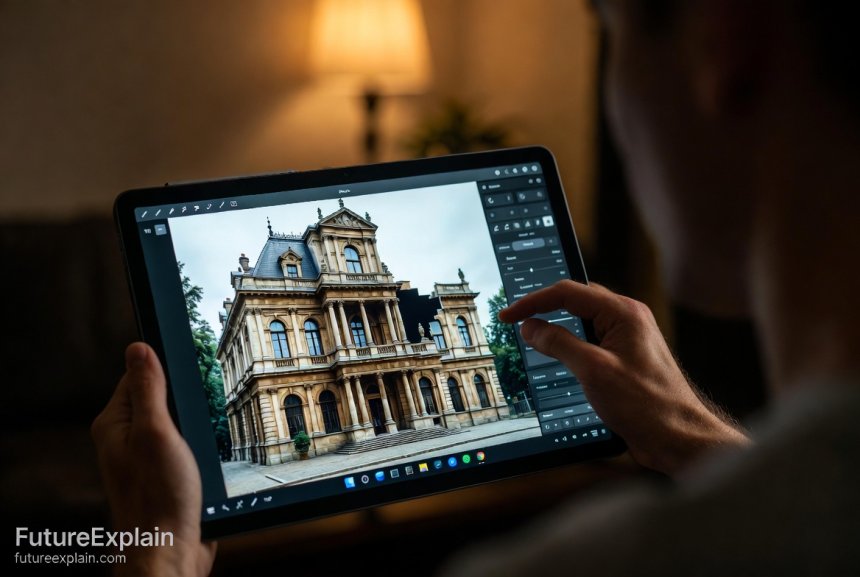

Practical Applications Across Industries
AI background removal and inpainting tools aren't just for individual photo editing—they're transforming workflows across numerous fields. Understanding these applications can help you identify opportunities in your own work or business.
E-commerce and Product Photography
Online retailers face constant pressure to produce high-quality product images at scale. AI tools allow them to photograph products in any environment (saving studio costs and time) and automatically generate clean, consistent images. Some advanced systems can even create 360-degree product views from a limited set of photos by intelligently generating the missing angles. For marketplaces like Amazon or Etsy that have specific image requirements, these tools ensure compliance without manual labor.
Professional Photography and Portraiture
Photographers can use these tools to dramatically reduce post-processing time. Portrait photographers can quickly place subjects against different backgrounds without elaborate green screen setups. Wedding photographers can remove distracting elements from ceremony shots. Real estate photographers can erase temporary objects like trash cans or cars to present properties at their best. The time savings allows photographers to focus more on shooting and client relationships rather than hours at the computer.
Content Creation and Social Media
In the attention economy, striking visuals are currency. Content creators use background removal to create consistent branding across platforms—isolating themselves or products for use in various templates. Inpainting helps create more engaging compositions by removing distractions. YouTube thumbnail creators particularly benefit from these tools to make click-worthy images. The speed of AI tools means creators can produce more content without sacrificing quality.
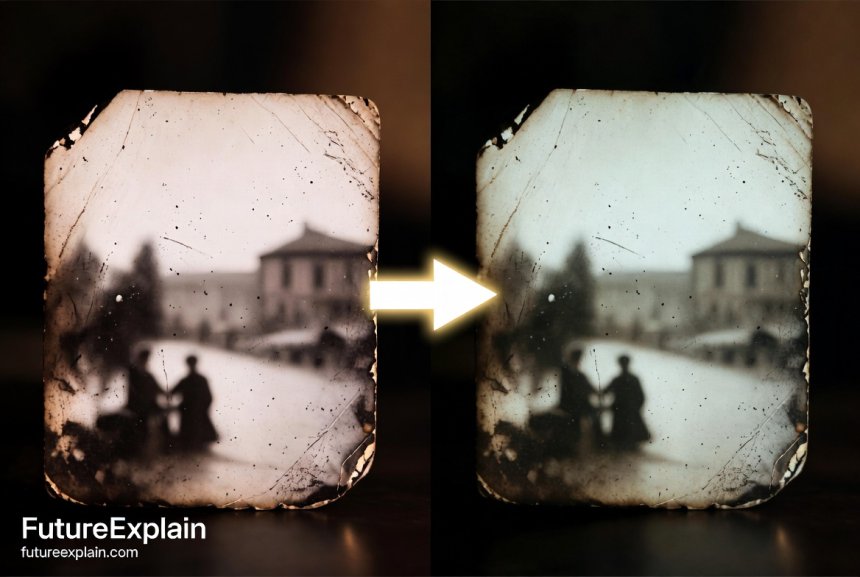
Historical Preservation and Photo Restoration
Museums, archives, and families are using AI inpainting to restore damaged historical photographs. The technology can automatically fill in missing sections of torn photos, reduce scratches and stains, and even colorize black-and-white images with plausible colors. While ethical considerations apply (discussed later), the potential for preserving visual history is significant. Some tools are specifically designed for this purpose, with modes that understand historical photographic processes and materials.
Education and Presentation Materials
Educators and presenters use these tools to create cleaner, more focused visual materials. Removing busy backgrounds from images makes slides less distracting. Creating transparent PNGs of diagrams or objects allows them to be layered effectively in educational content. Students can use these tools for projects and presentations without needing to master complex software.
Interior Design and Architecture
Professionals in these fields use inpainting to visualize changes to spaces. They can remove existing furniture from room photos and replace it with new options. Architects can clean up site photos by removing temporary structures or vehicles to better present their designs. Some tools are developing specialized capabilities for these industries, like understanding perspective and architectural elements.
As these tools continue to improve, we'll see even more specialized applications emerge. The common thread is saving time while increasing creative possibilities—a combination that's valuable across virtually any field that works with images.
Understanding the Technology Behind the Tools
While you don't need to be an AI expert to use these tools, understanding some key concepts can help you get better results and appreciate what's happening when you click "process."
Neural Networks and Training
At the heart of these tools are neural networks—computing systems loosely inspired by biological brains. These networks consist of layers of "neurons" that process information. During training, they're shown millions of example images and gradually adjust their internal parameters to get better at specific tasks, like identifying where a person ends and the background begins.
The training process is crucial: a network trained primarily on portraits might struggle with product photos, and vice versa. That's why some tools offer different modes or models for different types of images. When you select "person" mode in a background remover, you're telling it to use a neural network specifically optimized for human subjects.
Semantic Segmentation
This is the technical term for what background removal tools do. Instead of just identifying edges or colors, semantic segmentation classifies every pixel in an image according to what object it belongs to. Advanced systems can distinguish between different types of objects—not just "person" vs. "background," but potentially "hair," "skin," "clothing," and different elements of the background itself.
The challenge with semantic segmentation is handling ambiguous boundaries. Where exactly does fluffy hair end and the background begin? Modern systems use probabilistic approaches, assigning confidence scores to each pixel's classification. The algorithms then use this probability map to create smooth, natural-looking edges rather than jagged cuts.
Generative Models for Inpainting
Inpainting represents a different challenge: creating something new rather than just classifying what exists. This is where generative models like GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) and diffusion models come in. These systems learn the underlying "distribution" of natural images—what makes something look like a plausible photograph rather than random pixels.
When filling a missing area, the system doesn't just look at the immediate boundaries. It considers the entire image context. If you're removing a person from in front of a brick wall, the system understands that bricks follow regular patterns, that mortar lines continue in straight lines, and that lighting should be consistent across the filled area. The most advanced systems even understand higher-level concepts: if you remove a window from a building facade, the system knows that what's behind should look like an interior space, not just more bricks.
Real-Time Processing Challenges
The speed of these tools is as impressive as their accuracy. Processing that would have taken minutes or hours on earlier systems now happens in seconds. This is achieved through optimized algorithms, specialized hardware (like GPUs originally developed for gaming), and cloud computing that spreads the work across many processors.
However, there are still trade-offs. The fastest tools often use smaller, less accurate models. Professional tools that offer the highest quality may take longer to process. Understanding this trade-off helps you choose the right tool for your needs: instant results for social media posts versus slower, higher-quality processing for print materials or important product images.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Use
As with any powerful technology, AI image editing tools come with important ethical considerations. Being aware of these helps you use the tools responsibly and avoid unintended consequences.
Authenticity and Misrepresentation
The line between enhancement and deception can be thin. Removing a distracting trash can from a park photo is generally acceptable. Removing evidence of environmental damage from an industrial site photo crosses into unethical territory. In journalism, documentary photography, and scientific imaging, any manipulation that changes the factual content of an image is typically prohibited. Even in commercial contexts, regulations may apply—for example, before-and-after photos in weight loss ads often must disclose if they've been digitally altered.
A good rule of thumb: if the editing changes the truth of what the image represents, consider whether you should do it, and if you do, whether you need to disclose the alteration. This is particularly important in contexts where viewers might make significant decisions based on the image, like real estate purchases or medical before-and-afters.
Privacy Concerns
Background removal can inadvertently reveal information the subject intended to keep private. A photo taken in someone's home might, through background removal, isolate the person but also make certain objects in the background more identifiable to those who know the space. Some tools now include privacy modes that blur or genericize backgrounds rather than removing them entirely when privacy might be a concern.
When editing photos of people, especially for commercial use, ensure you have appropriate permissions. Just because you can remove someone from a background doesn't mean you have the right to use their likeness in your marketing materials.
Bias in AI Systems
AI tools can inherit and amplify biases present in their training data. Some background removal tools have been shown to perform less accurately on people with darker skin tones or certain hair textures. Inpainting tools might generate content that reflects stereotypes based on image context.
As a user, be aware that these systems aren't perfect and may have blind spots. If you notice consistent issues with certain types of images, you might need to use different tools or manual adjustment. Supporting developers who are actively working to reduce bias in their systems also helps move the technology in a positive direction.
Intellectual Property and Copyright
The legal landscape around AI-generated and AI-modified images is still evolving. If you use an AI tool to significantly alter someone else's copyrighted image, you may be creating a derivative work requiring permission. Similarly, if you use these tools as part of a commercial service, ensure your usage complies with the tool's terms of service—some restrict commercial use in their free tiers.
For content you create yourself, consider how much AI assistance affects your copyright. Most jurisdictions currently treat AI-assisted works similarly to traditionally created works, but significant AI generation might have different status. When in doubt, consult legal advice specific to your use case and jurisdiction.
Environmental Impact
Training and running large AI models requires significant computational resources, which translates to energy consumption. While using these tools for individual images has minimal impact, large-scale commercial use contributes to this footprint. Some companies are working to make their models more efficient or using renewable energy for their data centers.
As a user, you can minimize impact by using local processing when possible (some tools offer desktop versions that don't require cloud processing), avoiding unnecessary reprocessing, and choosing efficient tools. For most individual users, the impact is small compared to other digital activities, but it's worth being mindful as these tools scale.
Responsible use ultimately comes down to intention and transparency. These are powerful tools that can enhance creativity and efficiency, but like any tool, they reflect the ethics of the person wielding them.
The Future of AI Image Editing
The technology behind AI background removal and inpainting is advancing rapidly. Understanding emerging trends can help you prepare for what's coming next.
Real-Time Video Processing
While current tools focus primarily on static images, the next frontier is real-time video. Early implementations already exist for video conferencing (virtual backgrounds) and social media filters, but more sophisticated systems will allow for movie-grade visual effects without green screens. Imagine being able to change locations in a video after filming or remove unwanted objects from moving footage as easily as from photos.
3D and Volumetric Understanding
Current tools work with 2D images, but researchers are developing systems that understand depth and three-dimensional structure. This would allow for more realistic background replacement that accounts for lighting direction and perspective. It could also enable the creation of 3D models from 2D photos through intelligent extrapolation.
Multimodal AI Integration
Future tools will likely combine visual AI with other modalities like natural language processing. You might describe the background you want in words, and the AI will generate it while properly integrating your subject. Or you could ask the AI to "make this product look more premium" and it would adjust lighting, background, and even product presentation based on that instruction.
Personalized AI Models
Rather than one-size-fits-all models, we may see tools that adapt to individual users' styles and needs. A photographer could train a personal AI assistant on their editing preferences, and it would apply similar adjustments to new images. E-commerce businesses might have models fine-tuned for their specific product categories.
Ethical and Authenticity Safeguards
As concerns about deepfakes and misinformation grow, expect to see more tools with built-in authenticity features. These might include digital watermarks indicating AI modification, blockchain-based provenance tracking, or detection systems that can identify AI-altered images. Some platforms might automatically apply these safeguards, while others will offer them as options for users who want to demonstrate the authenticity of their images.
Integration with Broader Workflows
AI image editing won't exist in isolation. We'll see deeper integration with design software, content management systems, e-commerce platforms, and social media. Background removal might happen automatically when you upload a product photo to your online store. Social media platforms might offer inpainting as part of their native editing tools. This seamless integration will make these capabilities even more accessible to non-technical users.
The trajectory is clear: these tools will become faster, more accurate, more versatile, and more integrated into our digital workflows. The challenge will be using them in ways that enhance rather than replace human creativity and judgment.
Getting Started: Your Action Plan
Ready to start using AI background removal and inpainting tools? Here's a practical action plan:
Week 1: Experiment with Free Tools
Begin with no-cost options like Remove.bg's free tier, Canva's free background remover, or web-based inpainting tools. Practice on different types of images: people, products, landscapes. Notice what each tool handles well and where it struggles. Don't worry about perfection—focus on understanding capabilities.
Week 2: Identify Your Primary Use Case
Based on your experimentation, identify what you'll use these tools for most often. Is it cleaning up product photos? Creating social media graphics? Restoring old family photos? This focus will help you choose the right tools and develop relevant skills.
Week 3: Develop a Workflow
Create a step-by-step process for your most common task. For example: "1. Take product photos with consistent lighting. 2. Upload to batch processor. 3. Review automatically processed images. 4. Manually fix any problem edges. 5. Export to folder for website upload." A consistent workflow saves time and improves results.
Week 4: Explore Advanced Features
Once comfortable with basics, explore more advanced capabilities. Many tools offer features like batch processing, API access, or integration with other software. These can dramatically increase efficiency for regular use.
Ongoing: Stay Updated
This field evolves rapidly. Follow a few key blogs or newsletters about AI tools. When you hear about a new capability, test it against your workflow to see if it offers improvements. But avoid constant tool-hopping—sometimes deeper knowledge of one tool yields better results than superficial knowledge of many.
Remember that these are tools to enhance your capabilities, not replace your judgment. The AI handles repetitive, technical tasks so you can focus on creative and strategic decisions. With practice, you'll develop an intuition for when to trust the AI's automatic processing and when to step in with manual adjustments.
Conclusion
AI-powered background removal and inpainting tools represent a significant leap in making sophisticated image editing accessible to everyone. From e-commerce businesses creating professional product images at scale to individuals restoring precious family photos, these technologies are saving time, reducing costs, and unlocking creative possibilities.
The key to success with these tools is understanding both their capabilities and their limitations. They excel at pattern recognition and repetitive tasks but still benefit from human oversight for complex cases and final quality control. As the technology continues to advance, we can expect even more impressive capabilities while (hopefully) addressing current limitations around bias, authenticity, and environmental impact.
Whether you're a complete beginner or someone with some image editing experience, now is an excellent time to explore these tools. Start with the free options, identify your primary use cases, and gradually build your skills. The learning curve is far gentler than traditional image editing software, and the time savings can be substantial.
As you incorporate these tools into your workflow, remember that they're amplifiers of human creativity, not replacements for it. The most compelling images will always be those that combine technical excellence with meaningful content and emotional resonance. AI tools simply give you more time and capability to focus on what makes your visual content uniquely yours.
Further Reading
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
1520
Like
1520
 Dislike
12
Dislike
12
 Love
340
Love
340
 Funny
45
Funny
45
 Angry
8
Angry
8
 Sad
5
Sad
5
 Wow
210
Wow
210
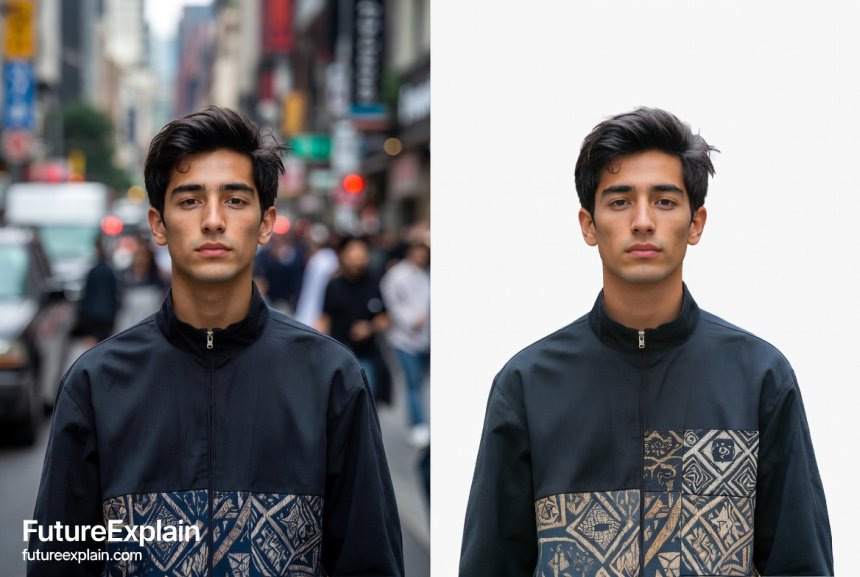


















I appreciate that you didn't just hype the technology. You presented clear limitations (like complex edges) so readers have realistic expectations.
As a beginner, the sheer number of tools was overwhelming. Your guide gave me a logical path to navigate them. Thank you.
The comment about AI not just copying but understanding patterns resonated. It's the difference between a simple tool and an intelligent assistant.
After reading this, I tried the 'week 1' experiment with three different tools. It was the best way to learn their strengths and weaknesses hands-on.
The watermark instruction in the image prompts is a nice touch. Even your examples practice what you preach about attribution.
I run a small marketing agency. This article has convinced me to invest in a team subscription to a robust tool. The ROI on time is clear.