Explainability & Interpretability for Non-Experts
This beginner-friendly guide explains AI explainability and interpretability without technical jargon. You'll learn the crucial difference between these concepts and why they matter for everyday AI use. We cover real examples where transparent AI decisions are essential—from loan approvals to medical diagnoses—and show how to recognize when you need explanations from AI systems. The article includes practical steps for requesting understandable AI outputs, compares how different AI tools provide explanations, and discusses the balance between accuracy and transparency. You'll also learn about current regulations requiring AI transparency and how to be an informed user of AI technology.

Explainability & Interpretability for Non-Experts
When artificial intelligence makes decisions that affect our lives—whether it's recommending a movie, approving a loan, or suggesting a medical treatment—we naturally want to understand why. This desire for understanding leads us to two crucial concepts in AI: explainability and interpretability. While these terms might sound technical, they're actually about something very human: the need for clarity and trust.
Imagine you're denied a loan by an AI system. Would you be satisfied with simply being told "the computer said no"? Probably not. You'd want to know which factors influenced that decision. This is where explainable AI comes in—it's AI that can provide understandable reasons for its actions.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll break down these concepts into simple, non-technical language. Whether you're a student learning about AI, a business owner using AI tools, or simply someone curious about how AI decisions are made, this article will give you the knowledge to understand—and ask for—transparent AI systems.
What Are Explainability and Interpretability? (In Simple Terms)
Let's start with clear definitions that don't require a computer science degree:
Interpretability refers to how easily a human can understand how an AI system works. Think of it like being able to look under the hood of a car. Some AI models are naturally interpretable because they follow simple rules we can understand. For example, a system that says "If income is above $50,000 and credit score is above 700, approve the loan" is highly interpretable.
Explainability, on the other hand, is about getting the AI to provide reasons for its specific decisions. Even if the AI is complex, explainability techniques can generate understandable explanations after the fact. It's like asking a chess master why they made a particular move—they might not be able to explain their entire thought process, but they can give you specific reasons for that move.
The key difference: interpretability is about understanding the system's overall logic, while explainability is about understanding individual decisions.

Why Should Non-Experts Care About This?
You might wonder why these concepts matter if you're not building AI systems. Here are several important reasons:
- Fairness and Bias Detection: Without explanations, we can't tell if an AI system is making unfair decisions. For example, if a hiring AI consistently rejects candidates from certain backgrounds, explanations help us identify and fix this bias.
- Trust and Adoption: People are more likely to use AI systems they understand and trust. If your doctor uses an AI diagnostic tool, you'd want to know why it suggested a particular treatment.
- Accountability: When AI makes mistakes (and it does), we need to understand why to fix the system and determine responsibility.
- Legal Compliance: Increasingly, regulations like the EU's AI Act require certain AI systems to provide explanations for their decisions, especially in high-stakes areas like finance, healthcare, and criminal justice.
- Learning and Improvement: Explanations help humans learn from AI systems and vice versa. A doctor might learn new diagnostic patterns from an AI's explanations.
Real-World Examples Where Transparency Matters
Let's look at concrete situations where AI explainability is crucial:
1. Healthcare Decisions
When an AI system suggests a cancer diagnosis or recommends a specific treatment, doctors need to understand the reasoning. They can't simply accept "the AI says so"—they need to verify the logic matches medical knowledge. For instance, an explainable AI system might say: "I identified a 3mm nodule in the upper right lung with irregular borders, which matches 87% of malignant cases in my training data. The patient's smoking history increases the risk probability by 15%." This allows the doctor to evaluate the reasoning.
2. Financial Services
If you're denied a loan, credit card, or insurance, regulations often require the institution to provide reasons. An explainable AI system might generate: "Application denied due to: 1) Credit utilization ratio of 85% (threshold is 30%), 2) Two late payments in the last 6 months, 3) Insufficient credit history length (8 months)." This is far more helpful than a simple denial.
3. Content Recommendations
When YouTube recommends videos or Netflix suggests movies, understanding why can improve your experience and help you recognize potential filter bubbles. An explainable recommendation system might say: "Recommended because you watched 3 sci-fi movies this week and rated 'The Martian' 5 stars."
4. Autonomous Vehicles
If a self-driving car suddenly brakes, passengers want to know why. Was it a pedestrian, an animal, or a false alarm? Explanations build trust in the technology.
The Spectrum of AI Transparency
Not all AI systems are equally transparent. They exist on a spectrum:
- Fully Transparent/Interpretable Models: These follow rules humans can easily understand. Examples include decision trees with few branches or linear regression models. They're like simple recipes with clear steps.
- Explainable After the Fact: Complex models (like deep neural networks) that can provide explanations through special techniques. Think of these as brilliant but eccentric experts who can explain their reasoning if asked properly.
- Black Box Models: Systems where even their creators don't fully understand how they reach specific decisions. These are becoming less common as explainability techniques improve.
Interestingly, there's often a trade-off: simpler, more interpretable models might be slightly less accurate than complex black-box models, but they're more trustworthy. The field is working on creating AI that's both highly accurate and explainable.
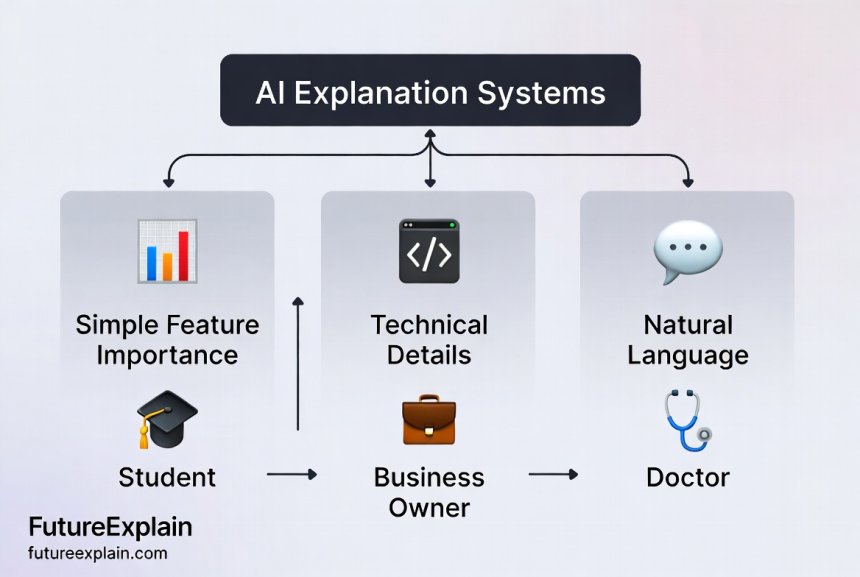
How Different AI Tools Provide Explanations
Various AI systems offer different types of explanations. Here's what you might encounter:
1. Feature Importance
This shows which factors were most important in a decision. For example, a loan approval AI might show: "Income: 40% important, Credit Score: 35% important, Employment History: 25% important." Visual representations often use bar charts or heat maps.
2. Counterfactual Explanations
These answer the question: "What would need to change to get a different outcome?" For a denied loan: "If your credit score were 30 points higher, you would have been approved." These are particularly helpful because they suggest actionable steps.
3. Natural Language Explanations
Some AI systems generate explanations in plain English (or other languages). For example: "I classified this email as spam because it contains phrases commonly found in phishing attempts ('urgent action required,' 'click here to verify') and comes from a domain with poor reputation scores."
4. Local vs. Global Explanations
Local explanations explain a single decision ("Why was THIS loan denied?"). Global explanations explain the overall model behavior ("How does this loan approval system generally work?"). Both are valuable for different purposes.
Practical Guide: How to Ask for AI Explanations
As a non-expert user of AI systems, here's how you can practically seek explanations:
1. Know When to Ask
You don't need explanations for every AI decision. Focus on situations where:
- The decision has significant consequences (health, finance, legal)
- The decision seems surprising or counterintuitive
- You need to learn from the decision
- You suspect potential bias or error
2. Ask the Right Questions
When interacting with AI systems (or the companies that use them), ask questions like:
- "Can you explain why the system made this specific recommendation/decision?"
- "What were the main factors that influenced this outcome?"
- "How confident is the system in this decision?"
- "What would need to change to get a different outcome?"
- "Has this system been tested for bias, and how?"
3. Look for Transparency Features
When choosing AI tools or services, look for:
- Clear documentation about how the system works
- Examples of explanations the system provides
- Information about bias testing and mitigation
- Compliance with relevant regulations (GDPR, AI Act, etc.)
- Options to get human review of AI decisions
4. Understand Common Explanation Formats
Learn to recognize these common explanation formats:
- Percentage scores: "87% confidence this is spam"
- Feature weights: "Income contributed 40% to this decision"
- Comparison examples: "Similar to these 5 approved applications..."
- Rule-based explanations: "Because X and Y, therefore Z"
The Challenges of AI Explainability
While explainability is important, it's not always simple to achieve. Here are some challenges researchers and developers face:
1. The Accuracy-Interpretability Trade-off
Sometimes, the most accurate AI models are also the least interpretable. It's like asking a brilliant but unconventional thinker to explain their thought process—they might struggle to translate their complex reasoning into simple terms.
2. Different Users Need Different Explanations
A data scientist, a doctor, a loan officer, and a regular consumer all need different types of explanations. Creating explanations that work for everyone is challenging.
3. Explanation ≠ Understanding
Just because an AI provides an explanation doesn't mean humans will understand it correctly. Poorly designed explanations can even create false confidence or misunderstanding.
4. Gaming the System
If people know exactly how an AI system works, they might try to manipulate it. For example, if a loan approval system clearly weights income at 40%, someone might temporarily inflate their income report.
5. The "Right to Explanation" vs. Trade Secrets
Companies might resist providing detailed explanations because their AI algorithms are valuable intellectual property. Regulations are still evolving to balance transparency needs with business interests.
Current Regulations and Standards
Governments worldwide are recognizing the importance of AI transparency. Here are key developments:
- EU AI Act (2024): Requires "high-risk" AI systems to provide clear information about their capabilities and limitations, and in some cases, explanations for individual decisions.
- GDPR (EU): Includes a "right to explanation" for automated decisions that significantly affect individuals.
- US Executive Order on AI (2023): Emphasizes the need for transparency and calls for standards development.
- Industry Standards: Organizations like IEEE and ISO are developing standards for AI explainability.
These regulations mean that as a consumer, you have increasing rights to understand AI decisions that affect you.
How to Evaluate an AI System's Transparency
When you encounter an AI system, ask these evaluation questions:
- Clarity of Purpose: Is it clear what the AI system is designed to do?
- Decision Explanation: Can you get explanations for specific decisions?
- Factor Transparency: Are the main decision factors disclosed?
- Limitations: Are the system's limitations and potential errors explained?
- Human Oversight: Is there a way to get human review of AI decisions?
- Bias Information: Has the system been tested for bias, and are results available?
- Update Transparency: Will users be informed if the system changes significantly?
The Future of Explainable AI
The field of explainable AI is rapidly evolving. Here's what we can expect:
- Better Explanation Interfaces: More intuitive ways to explore and understand AI decisions, potentially using virtual reality or interactive visualizations.
- Personalized Explanations: AI systems that adapt their explanations to your knowledge level and needs.
- Standardized Explanation Formats: Common standards so explanations from different systems are comparable.
- Explainability by Design: AI systems built from the ground up to be explainable, rather than having explanations added afterward.
- Educational Integration: AI explanation tools becoming part of education, helping students understand both the subject matter and how AI thinks.
Practical Exercises for Understanding AI Transparency
To better understand these concepts, try these non-technical exercises:
Exercise 1: Explain Your Own Decisions
For a week, practice explaining your own decisions (what to eat, what route to take, what movie to watch). Notice how some decisions are easy to explain ("I chose this route because there's less traffic") while others are harder ("I just had a feeling about that movie"). This helps you understand what we ask of AI systems.
Exercise 2: Analyze Product Recommendations
When Amazon or Netflix recommends something, try to reverse-engineer why. What have you viewed or purchased recently that might explain the recommendation? This helps you think like an explainable AI system.
Exercise 3: Ask for Explanations
Next time you encounter an automated decision (credit application, content moderation, etc.), politely ask for an explanation. Notice what type of explanation you receive and whether it satisfies your curiosity.
Common Myths About AI Explainability
Let's clear up some misconceptions:
Myth 1: "If we can't explain an AI's decisions, we shouldn't use it."
Reality: Sometimes we accept unexplained decisions from humans ("gut feelings"), and sometimes AI accuracy is critical enough to tolerate less explanation. The key is matching the explanation level to the stakes.
Myth 2: "More explanation is always better."
Reality: Too much or poorly organized explanation can overwhelm users. Good explanations are concise and relevant.
Myth 3: "If an AI can explain its decisions, it's completely fair and unbiased."
Reality: Explanations help identify bias but don't eliminate it. A biased AI might provide logical-sounding explanations for biased decisions.
Myth 4: "Only technical people need to understand AI explainability."
Reality: As AI affects more aspects of life, everyone benefits from understanding when and how to ask for explanations.
Connecting to Other AI Concepts
Explainability connects to several other important AI concepts we've covered on FutureExplain:
- AI Ethics & Safety: Explainability is a key component of ethical AI systems.
- AI Myths vs Reality: Understanding what AI can actually explain helps counter myths about AI omniscience.
- Ethical AI Explained: Explanations help detect and address bias.
- Managing Model Bias: Explainability techniques are essential tools for bias management.
Conclusion: Becoming an Informed AI User
AI explainability and interpretability aren't just technical concepts—they're essential for building trustworthy AI systems that serve humanity well. As AI becomes more integrated into our lives, our ability to understand and question AI decisions becomes increasingly important.
Remember that asking "why" isn't being difficult or distrustful—it's being engaged and responsible. Whether you're using AI tools for work, benefiting from AI services as a consumer, or simply trying to understand the technology shaping our world, knowing about explainability empowers you to interact with AI more effectively.
The goal isn't necessarily to understand every technical detail of every AI system. Rather, it's to know when explanations are important, what kinds of explanations to look for, and how to use those explanations to make better decisions and hold systems accountable.
As AI technology continues to evolve, so too will explanation capabilities. By staying informed about these developments, you position yourself not as a passive recipient of AI decisions, but as an active participant in shaping how AI integrates into our society.
Further Reading
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
2450
Like
2450
 Dislike
12
Dislike
12
 Love
567
Love
567
 Funny
89
Funny
89
 Angry
23
Angry
23
 Sad
15
Sad
15
 Wow
345
Wow
345

















The journey from black boxes to transparent AI feels like an important evolution. We're moving toward technology we can understand and trust.
We've added AI explainability training to our employee development program. This article is now required reading!
That's fantastic, Chloe! We should all be advocating for similar training in our organizations.
Regulators are increasingly asking for 'algorithmic impact assessments' - documentation showing how AI systems were tested for fairness and transparency.
The balance between transparency and intellectual property protection will be an ongoing challenge. But consumer demand for explainability is growing.
After reading this, I realize I've been too passive with AI tools. Now I actively seek out explanation features and use them to improve my experience.
We're piloting a system that shows students 'why you got this math problem wrong' with step-by-step reasoning. The educational impact is significant.