Understanding Diffusion Models: Stable Diffusion and Beyond
This comprehensive guide explains diffusion models, the technology behind AI image generators like Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, and Midjourney. We break down how diffusion models work using simple analogies, starting with the basic concept of gradually adding and removing noise to create images. You'll learn about different types of diffusion models, with a focus on Stable Diffusion's unique latent space approach that makes it efficient and accessible. The article compares popular diffusion models, explains key parameters like CFG scale and sampling steps, and provides practical guidance for getting started. We also cover ethical considerations, real-world applications beyond art, and future developments in diffusion model technology for 2024 and beyond.
Understanding Diffusion Models: Stable Diffusion and Beyond
If you've used AI image generators like Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, or Midjourney, you've witnessed the power of diffusion models. These remarkable systems can create stunning, realistic images from simple text descriptions, but how do they actually work? In this comprehensive guide, we'll demystify diffusion models using simple language and clear analogies, making this complex technology accessible to everyone.
Diffusion models represent a breakthrough in generative artificial intelligence, particularly for image creation. Unlike earlier approaches that struggled with consistency and detail, diffusion models can produce high-quality, diverse images that often rival human-created artwork. The key innovation lies in their training process, which teaches AI to reverse a specific type of image degradation—gradually adding noise until an image becomes pure randomness, then learning how to reverse this process.
What Are Diffusion Models? A Simple Analogy
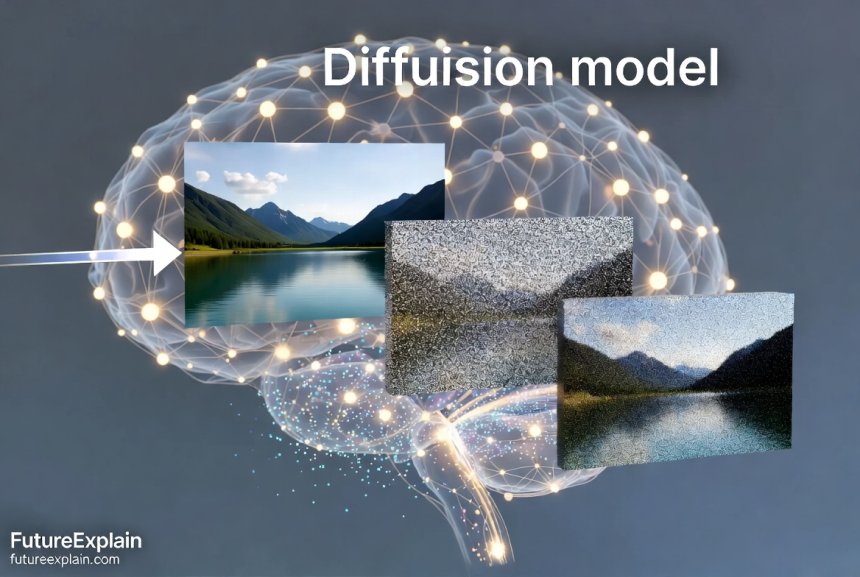
Imagine you have a clear photograph, and you gradually sprinkle sand over it until the original image becomes completely obscured. Now, imagine you could train someone to reverse this process—to carefully remove the sand grains in just the right pattern to reveal the original photograph. This is essentially how diffusion models work, but with mathematical "noise" instead of sand.
Diffusion models learn by observing thousands of examples of this noise-adding process, then figuring out how to reverse it. Once trained, they can start with pure noise and gradually "denoise" it into a coherent image based on your text prompt. This might sound magical, but it's based on sophisticated mathematics and neural network architectures that we'll explore in this guide.
The Two-Phase Process: Forward and Reverse Diffusion
Every diffusion model operates through two main phases:
- Forward Diffusion: Gradually adding noise to training images until they become completely random
- Reverse Diffusion: Learning to remove that noise to reconstruct the original images
The training process exposes the model to millions of images, each undergoing hundreds of steps of gradual noising. The model learns to predict what the image looked like at each previous step, building an understanding of how images are structured and how details relate to each other.
How Stable Diffusion Revolutionized AI Image Generation
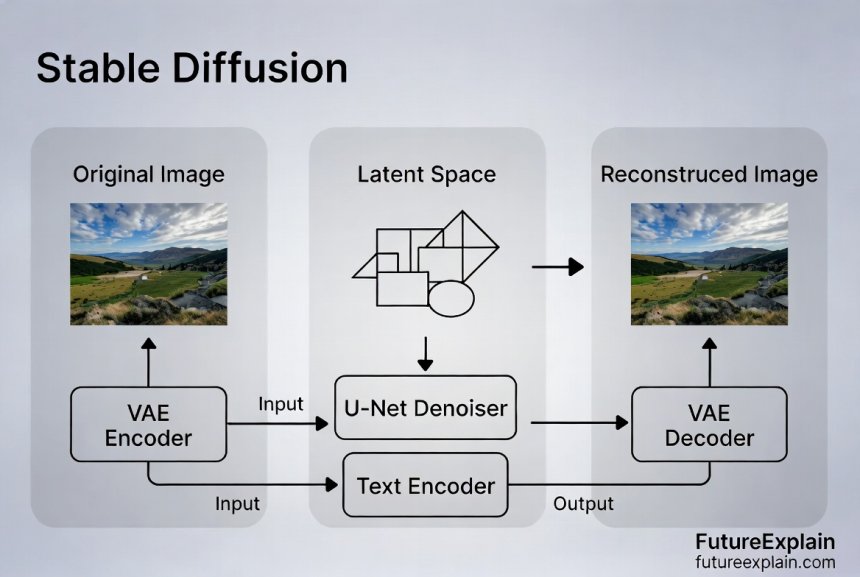
Stable Diffusion, released in 2022 by Stability AI, brought diffusion models to the mainstream by solving two critical challenges: speed and accessibility. Previous diffusion models required expensive hardware and took minutes to generate a single image. Stable Diffusion's innovation was operating in "latent space"—a compressed representation of images—making it fast enough to run on consumer graphics cards.
The Three Key Components of Stable Diffusion
Stable Diffusion combines three neural networks working together:
- VAE (Variational Autoencoder): Compresses images into latent space and decompresses them back
- U-Net: The denoising engine that predicts and removes noise in latent space
- CLIP Text Encoder: Converts text prompts into numerical representations the model understands
This architecture allows Stable Diffusion to generate 512x512 pixel images in seconds rather than minutes, making it practical for widespread use. The latent space approach also means the model works with data that's 48 times smaller than the final image, dramatically reducing computational requirements.
Different Types of Diffusion Models Explained
Not all diffusion models are created equal. Here are the main types you'll encounter:
1. Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM)
The original diffusion model architecture introduced in 2020. DDPMs use a fixed schedule for adding and removing noise, with each step carefully calibrated. They produce high-quality results but are relatively slow compared to newer approaches.
2. Latent Diffusion Models (Stable Diffusion)
As discussed above, these models operate in compressed latent space, offering a balance of quality and speed. Stable Diffusion is the most famous example, but there are many variants and fine-tuned versions available.
3. Guided Diffusion Models
These models incorporate additional guidance during generation, often using classifiers or CLIP embeddings to steer the image toward specific characteristics. This allows for better control over the output based on text prompts.
4. Cascaded Diffusion Models
These use multiple diffusion models in sequence—one to generate a low-resolution image, then others to progressively increase resolution and add details. This approach can produce extremely high-resolution images.
Key Parameters: What Do They Actually Do?
When using diffusion models, you'll encounter several important parameters that control the generation process:
CFG Scale (Classifier-Free Guidance)
This controls how closely the generated image follows your text prompt. Lower values (1-3) give the model more creative freedom, while higher values (7-15) enforce stricter adherence to the prompt. Values around 7-9 typically offer a good balance.
Sampling Steps
The number of denoising iterations. More steps generally mean higher quality but longer generation time. Most models produce good results with 20-50 steps, with diminishing returns beyond that.
Sampler/Scheduler
Different mathematical approaches to the denoising process. Popular options include:
- DDIM: Fast but can produce less detailed results
- PLMS: Balanced quality and speed
- DPM Solver++: High quality with fewer steps
- Karras schedulers: Specialized for high-quality outputs
Seed Value
A starting point for the random noise. Using the same seed with the same prompt and settings will produce the same image, allowing for reproducibility.
Comparing Popular Diffusion Models in 2024
Here's how the major diffusion models compare as of 2024:
Stable Diffusion Variants
- SD 1.5: Most widely supported, largest ecosystem of fine-tuned models
- SD 2.0/2.1: Improved prompt understanding but more restrictive licensing
- SDXL: Higher resolution (1024x1024), better composition, but requires more VRAM
- SDXL Turbo: Real-time generation (1-4 steps) with maintained quality
Proprietary Models
- DALL-E 3: Excellent prompt understanding, integrated with ChatGPT
- Midjourney: Exceptional artistic style, strong community features
- Adobe Firefly: Focus on commercial safety, integration with Creative Cloud
Open Source Alternatives
- Kandinsky: Strong performance, developed by Russian researchers
- DeepFloyd IF: Excellent text rendering, multi-stage architecture
- Playground v2: Balanced quality and speed, good for beginners
Practical Applications Beyond Art Generation
While most people associate diffusion models with creating artwork, their applications extend far beyond this:
Scientific Visualization
Researchers use diffusion models to generate realistic simulations of scientific phenomena, create visualizations of molecular structures, or produce training data for other AI systems. For example, astronomers can generate synthetic telescope images to test analysis algorithms.
Medical Imaging
Diffusion models can enhance low-quality medical scans, generate synthetic medical images for training purposes (while preserving patient privacy), or help visualize disease progression. They're particularly valuable for rare conditions where real images are scarce.
Product Design and Prototyping
Designers can quickly generate product concepts, packaging designs, or architectural visualizations. Diffusion models can create hundreds of variations in minutes, accelerating the ideation phase dramatically.
Education and Training
Educators can create custom illustrations for teaching materials, historical reconstructions, or scientific diagrams tailored to specific lesson plans. This makes abstract concepts more accessible to visual learners.
Content Creation at Scale
Businesses can generate product images, marketing materials, or social media content efficiently. When combined with automation tools, diffusion models can produce thousands of variations for A/B testing or personalized marketing.
Getting Started with Diffusion Models: A Beginner's Roadmap
If you're new to diffusion models, here's a practical path to get started:
Step 1: Try Web Interfaces
Begin with user-friendly web platforms that don't require installation:
- Hugging Face Spaces: Free community-hosted versions of various models
- Playground AI: Generous free tier with multiple models
- Lexica.art: Specialized for Stable Diffusion with prompt library
Step 2: Learn Prompt Engineering
Effective prompts make all the difference. Learn to include:
- Subject: What you want to see
- Style: Artistic style or medium (photorealistic, oil painting, etc.)
- Details: Specific elements, lighting, composition
- Quality indicators: "4K, detailed, professional"
Check out our guide on prompt engineering best practices for more detailed techniques.
Step 3: Experiment with Local Installation
For more control and privacy, install Stable Diffusion locally:
- Automatic1111: Most popular web UI for Stable Diffusion
- ComfyUI: Node-based interface for advanced workflows
- InvokeAI: Professional-focused interface with good organization
Step 4: Explore Fine-Tuned Models
Once comfortable with the basics, try community-created models on platforms like Civitai that are specialized for particular styles (anime, realistic portraits, fantasy art, etc.).
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Use
As with any powerful technology, diffusion models come with important ethical considerations:
Copyright and Attribution
Diffusion models are trained on millions of images, often without explicit permission from creators. While courts are still determining the legal status of AI-generated images, it's important to:
- Disclose when images are AI-generated
- Respect artist opt-out requests (many models now exclude opted-out artists)
- Consider the ethical implications of generating images in a particular artist's style
Deepfakes and Misinformation
Diffusion models can create realistic fake images and videos. Always:
- Clearly label AI-generated content when sharing
- Never use AI to create deceptive or harmful content
- Support initiatives for AI content detection and watermarking
Bias and Representation
Like all AI systems, diffusion models reflect biases in their training data. They may:
- Over-represent certain demographics
- Perpetuate stereotypes
- Struggle with non-Western cultural elements
Be mindful of these limitations and consider using tools like bias mitigation techniques when creating content for diverse audiences.
Environmental Impact
Training large diffusion models requires significant computational resources. When possible:
- Use existing models rather than training from scratch
- Optimize inference settings to reduce energy use
- Consider the carbon footprint of extensive image generation
The Future of Diffusion Models: 2024 and Beyond
Diffusion model technology is evolving rapidly. Here are key developments to watch:
1. Faster Sampling Methods
New approaches like Consistency Models and Rectified Flows promise to reduce generation time from dozens of steps to just 1-2 steps while maintaining quality.
2. Improved Controllability
Advancements in conditioning techniques allow more precise control over composition, style transfer, and specific attributes without complex prompt engineering.
3. Multimodal Integration
Combining diffusion models with other modalities like multimodal AI systems for coherent generation across text, image, audio, and video.
4. Specialized Enterprise Applications
Industry-specific diffusion models for medicine, engineering, architecture, and scientific research with domain-specific training and validation.
5. Real-time and Interactive Generation
Models that can generate and edit images in real-time as you type or sketch, enabling truly interactive creative tools.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Even experienced users face challenges with diffusion models. Here are solutions to common problems:
Problem: Images Don't Match the Prompt
Solution: Improve your prompt engineering, increase CFG scale, or try a different model better suited to your subject matter. Sometimes adding negative prompts (what you don't want) helps clarify your intent.
Problem: Poor Composition or Distorted Elements
Solution: Use inpainting/outpainting to fix specific areas, try different aspect ratios, or use control nets for better composition control. SDXL generally has better composition than earlier versions.
Problem: Inconsistent Characters or Styles
Solution: Use reference images with img2img, experiment with model merging, or look into specialized extensions like LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) for consistent character generation.
Problem: Slow Generation Speed
Solution: Optimize settings (reduce steps, use faster samplers), enable xFormers if available, or consider upgrading hardware. Cloud services can also provide faster generation without local hardware investment.
Resources for Further Learning
To continue your journey with diffusion models, explore these resources:
- Online Communities: r/StableDiffusion on Reddit, Stability AI Discord, Hugging Face forums
- Learning Platforms: Hugging Face diffusion course, Fast.ai practical deep learning course
- Technical Documentation: Original DDPM paper, Stable Diffusion technical report, diffusers library documentation
- Creative Inspiration: Lexica prompt library, Civitai model showcase, PromptHero search
Conclusion: The Democratization of Visual Creation
Diffusion models represent one of the most significant advancements in creative technology in recent years. By understanding how they work—from the basic concept of gradual denoising to the sophisticated architectures of models like Stable Diffusion—you can better appreciate both their capabilities and limitations.
As this technology continues to evolve, it's becoming more accessible, controllable, and integrated into creative workflows. Whether you're an artist exploring new tools, a business looking to streamline content creation, or simply curious about how AI generates images, understanding diffusion models empowers you to use this technology effectively and responsibly.
The future of diffusion models isn't just about better image generation—it's about creating tools that augment human creativity, making visual expression more accessible to everyone while pushing the boundaries of what's possible in digital art and design.
Further Reading
If you found this guide helpful, you might also enjoy:
- Top Image-Generation Tools in 2024: A Practical Guide
- How to Edit and Enhance Images with AI (Beginner's Walkthrough)
- Ethics of AI-Generated Media: Copyright and Attribution
"
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
2150
Like
2150
 Dislike
12
Dislike
12
 Love
480
Love
480
 Funny
65
Funny
65
 Angry
8
Angry
8
 Sad
3
Sad
3
 Wow
320
Wow
320

















Just revisiting this as we close out 2025. This article was published at just the right time - right as diffusion models went mainstream. Historical document now!
One year later and I still reference this article. It's become a classic in my bookmarks. When will you do a "Diffusion Models: Two Years Later" update?
Great idea! We're planning a "State of Diffusion Models: 2026 Edition" article for early next year. The technology has evolved so much since this was written. Stay tuned!
The safety vs creativity balance is still being debated, but user-controlled filters seem to be winning. Different tools for different needs.
The beginner roadmap still works! I've guided several new users through it recently. The fundamentals haven't changed, just the specific tools.
Composition control is much better now with newer ControlNet versions and regional prompting. My images finally look how I envision them!
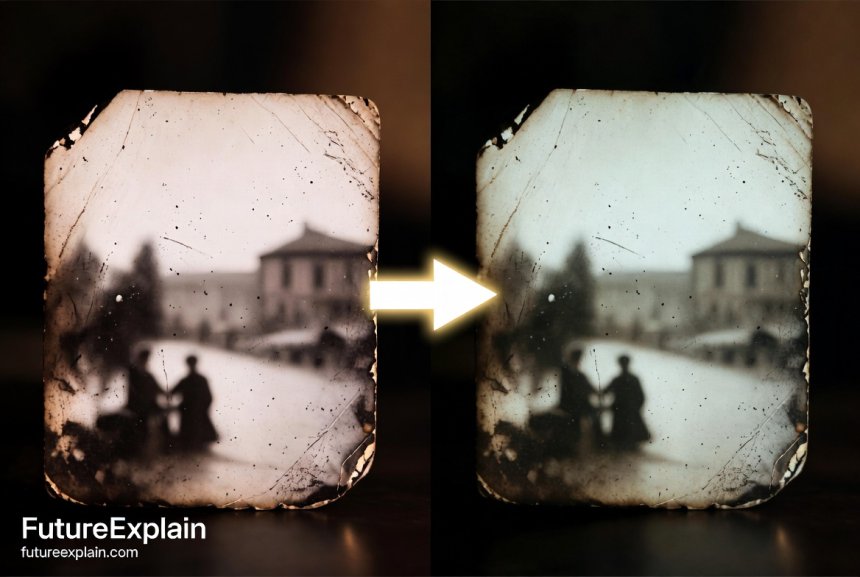
Photo restoration AI has gotten even better. The latest models can handle colorization and damage repair in one pass. Amazing for historical preservation.