What Is Workflow Automation? Beginner Explanation
Understand workflow automation easily. This beginner guide explains what it is, how it works, real-life examples, and how it can save you time every day.
Introduction: The Invisible Helper in Your Daily Work
Have you ever felt like you're doing the same digital task over and over? Maybe it's sending a welcome email to every new customer, moving data from a form into a spreadsheet, or approving the same type of request. This repetition isn't just boring; it eats up your time and increases the chance of mistakes. What if you could teach your computer to handle these predictable sequences for you? That's the core idea behind workflow automation, a concept that is transforming how we work, yet remains shrouded in jargon for many.
In this beginner's guide, we'll strip away the complexity. We will explain what workflow automation is in simple terms, how it functions, and why it's becoming an essential skill—not just for tech experts but for students, entrepreneurs, and professionals in every field. By the end, you'll see your daily tasks in a new light and understand how to start making them work for you, instead of the other way around.
What Exactly is a "Workflow"?
Before we can automate a workflow, we need to understand what one is. Think of a workflow as a recipe for a task. It's a repeatable sequence of steps that leads from a starting point to a defined finish line. These steps often involve multiple people, decisions, and tools.
A simple, non-digital example: Making your morning coffee. The workflow might be: 1) Grab mug, 2) Insert coffee pod, 3) Place mug in machine, 4) Press brew button, 5) Add milk, 6) Drink. It's a predictable process you follow every day.
In a digital or business context, workflows are everywhere:
- New Employee Onboarding: HR creates email account → IT sets up laptop → Manager assigns software access → Team lead schedules orientation.
- Content Publishing: Writer drafts article → Editor reviews → Graphic designer adds images → SEO specialist adds tags → Manager approves → Article is published.
- Customer Support Ticket: Customer submits issue → Ticket is created and categorized → Assigned to an agent → Agent responds → Ticket is marked solved → Customer receives satisfaction survey.
These sequences are workflows. They are the backbone of how things get done. Often, they are manual, slow, and prone to bottlenecks (like waiting for someone's approval). This is where automation enters the picture.
Workflow Automation Defined: The Simple Explanation
Workflow automation is the use of software to complete the tasks within a workflow automatically, with little to no human intervention. It's about programming the "recipe" so the computer can execute it.
Instead of you performing each step, you define the rules and triggers once. Then, the automation tool takes over, moving data, sending notifications, creating records, and making simple decisions based on your instructions. The goal isn't to replace human judgment for complex issues but to eliminate the robotic, repetitive parts of our jobs.
It's crucial to distinguish this from general AI vs Automation. While AI involves intelligence and learning, basic workflow automation is about following predefined logic. However, they are converging in powerful ways, which we explore in our guide on Intelligent Automation.

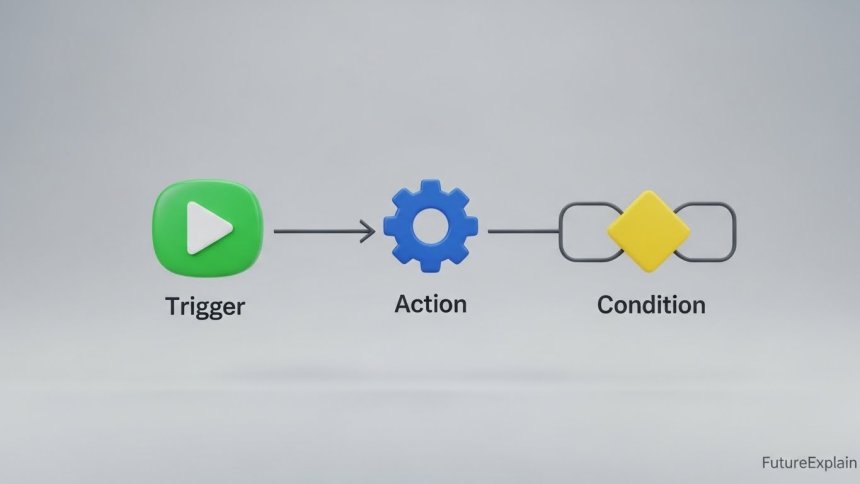
How Does It Actually Work? The Three Key Ingredients
Most workflow automation systems are built on three fundamental components: Triggers, Actions, and Conditions.
- 1. Trigger: This is the event that starts the workflow. It's the "when this happens..." part. Examples: A new row is added to a Google Sheet. A form is submitted on your website. An email arrives with a specific subject line. A payment is received.
- 2. Actions: These are the tasks performed automatically after the trigger. The "then do this..." part. Examples: Send a welcome email. Create a task in a project management tool like Trello. Post a message to a Slack channel. Update a database record.
- 3. Conditions (Optional but Powerful): These are the "if/then" rules that add logic. They make your workflow smart. Example: IF the form submission says "Priority: High," THEN send an immediate SMS alert to the manager. OTHERWISE, just log it in the daily report.
By chaining these triggers, actions, and conditions together, you build an automated workflow. Modern tools let you do this with drag-and-drop interfaces, no coding required. For a hands-on approach, see our Automation How-To guides.
Real-Life Examples You Can Relate To
Let's make this concrete with scenarios you might encounter.
Example 1: The Social Media Manager
Manual Workflow: Every Monday, you spend an hour drafting posts, finding images, and manually scheduling them for the week on Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter.
Automated Workflow: You use a tool like Buffer or Hootsuite. You draft all posts in one place on Friday. The tool automatically publishes them at the scheduled times and days across all platforms. Trigger: Scheduled time. Action: Publish post to connected social accounts.
Example 2: The Freelancer or Consultant
Manual Workflow: A client emails you about a new project. You reply with your standard proposal document, then manually create an invoice in another program if they agree, and finally track the payment in a spreadsheet.
Automated Workflow: Using a tool like Zapier or a CRM, you set this up: Trigger: "New Deal" marked in CRM. Actions: 1) Auto-send a personalized proposal from a template. 2) If client signs (via e-signature), automatically generate and send an invoice via QuickBooks. 3) When payment is marked "Paid," move the client to a "Completed Projects" list and auto-send a thank-you email requesting a testimonial.
Example 3: The Student or Researcher
Manual Workflow: You find an interesting academic paper online. You save the PDF to a folder, then manually enter the citation details into your reference manager (like Zotero or Mendeley), and maybe copy the link into a separate notes document.
Automated Workflow: Browser extensions for reference managers can often automate this. Trigger: You click the extension button on the paper's webpage. Actions: The tool automatically grabs the title, authors, journal, DOI, and saves the PDF to your designated library folder, with all metadata attached. It's one click instead of ten minutes of typing.
These examples show how automation fits into various lives. For more everyday tips, check out Automation Made Easy.
The Tangible Benefits: Why Bother Automating?
The advantages go far beyond just "saving time."
- Time Liberation: This is the most obvious benefit. Automating a 15-minute daily task saves you over 60 hours a year. That's time for strategic thinking, creativity, or simply less stress.
- Reduced Errors: Humans get tired and make typos, forget steps, or send emails to the wrong person. A properly configured workflow performs the same way, every single time.
- Improved Visibility & Accountability: Automated workflows create logs. You can see the status of any process instantly. Who approved it? When was the email sent? This transparency is gold for teamwork and client trust.
- Faster Processes: Work doesn't get stuck in someone's inbox over the weekend. Automation works 24/7, speeding up everything from customer response times to internal approvals.
- Enhanced Employee & Customer Experience: Employees are freed from soul-crushing repetition. Customers get instant confirmations and consistent service. Everyone wins.
- Scalability: Handling 10 customers or 10,000 becomes a matter of server capacity, not hiring an army of people to do manual data entry. Your systems grow with you.
For small businesses, this scalability is critical. Explore more in our article on AI for Small Businesses.

Types of Workflow Automation: From Simple to Smart
Not all automation is created equal. It exists on a spectrum.
1. Basic Task Automation
This automates a single, simple task. Setting up an email filter to label incoming messages is task automation. It's a great starting point, as covered in our Personal Productivity section.
2. Process Automation (Robotic Process Automation - RPA)
This mimics how a human would interact with multiple software applications to complete a process. For example, an RPA "bot" might log into a web portal, download a report, open Excel, reformat the data, and email it to a list. It's excellent for bridging gaps between systems that don't natively talk to each other.
3. Business Process Automation (BPA)
This is a more holistic, strategic approach. It looks at entire business processes (like "Order-to-Cash" or "Lead-to-Customer") and uses a combination of automation, integration, and sometimes human-in-the-loop steps to optimize the whole chain. This is the realm of dedicated Business Automation platforms.
4. Intelligent Automation (IA)
This is where workflow automation meets Artificial Intelligence. IA adds cognitive abilities like reading documents (OCR), understanding language (NLP), making predictions, and learning from outcomes. For instance, an IA system could read an invoice, extract the amount and due date, predict the best time to pay it for cash flow, and then schedule the payment. We dive deeper into this synergy in our article on Intelligent Automation Explained.
Getting Started: Your First Automated Workflow
Feeling inspired? Here’s a simple, safe first project anyone can try.
Goal: Automatically save email attachments to Google Drive.
Tools: Gmail and Google Drive (both free). You can use a connector like Zapier (free tier) or Google's own native features.
- Identify the Trigger: "When I receive an email in Gmail with an attachment."
- Define the Action: "Save the attachment to a specific folder in my Google Drive."
- Set it up: In Zapier, you would create a "Zap." Choose Gmail as the trigger app and select "New Email with Attachment." Connect your Gmail account. Then, choose Google Drive as the action app and select "Upload File." Connect your Drive and specify the folder.
- Test it: Send yourself an email with a test attachment. Watch the magic happen.
This small win demonstrates the power. You’ve just eliminated a future manual task. For more beginner-friendly tools, we have a curated list in Best Automation Tools for Non-Technical Users.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Starting out, you might hit some roadblocks. Here’s how to navigate them.
- Overcomplication: Start small. Don't try to automate your entire business on day one. Pick one annoying, repetitive task.
- Fear of Change: Involve your team early. Frame automation as a tool to remove drudgery, not a threat to jobs. Focus on the "time back" they'll gain.
- Process Isn't Clear: You can't automate a messy process. If your current manual workflow is chaotic, mapping it out on paper first is a crucial step. Sometimes, automation forces you to become more organized—a hidden benefit!
- Choosing the Wrong Tool: Begin with broad, user-friendly platforms like Zapier, Make, or Microsoft Power Automate. They connect to hundreds of apps and are designed for non-coders. Avoid expensive, specialized enterprise software until you have a clear need.
The Future of Workflow Automation
The trend is clear: automation is becoming more accessible, more intelligent, and more integrated. We are moving towards a future where describing a desired workflow in plain English could set it up (thanks to AI). Automation will be less of a separate "project" and more of a built-in feature of every software tool we use.
This evolution will significantly impact the Future of Work. The focus for professionals will shift from performing processes to designing, monitoring, and improving them. Understanding the principles of workflow automation is therefore a foundational skill for the future of automation in offices and businesses.
Conclusion: Your Work, Augmented
Workflow automation is not about cold, robotic replacement. It's about augmentation. It's about creating a digital ally that handles the predictable, so you can focus on the unpredictable—the strategy, the creativity, the human connection, and the complex problem-solving that machines cannot replicate.
By understanding the simple trigger-action-condition model, you now have a lens to view your own work. Look for the recipes, the repeatable sequences. Start with one. Automate it. Reclaim your time and mental energy. As you explore, remember that this is a journey toward working smarter, a key part of preparing for an AI-driven future. The tools are here, and they are waiting for your instructions.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
265
Like
265
 Dislike
2
Dislike
2
 Love
45
Love
45
 Funny
8
Funny
8
 Angry
1
Angry
1
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
32
Wow
32















This is a foundational article. Will be coming back to it as I learn more. Bookmarked.
Thanks for not making it sound like magic. It's logic and tools. Makes me feel like I can actually do it.
The "types of workflow automation" section helped me categorize what we already do and what we should aim for. We are heavy on basic task, need to move to process.
The scalability point for small businesses is everything. We are growing, and manual processes are starting to crack. This article is our roadmap.
Simple, powerful, actionable. More content like this, please.
Read this and the "AI vs Automation" piece. Now I finally get the difference. One follows rules, the other can learn. But they work best together.