Intelligent Automation Explained (AI + Automation Together)
Intelligent automation combines artificial intelligence with traditional automation to create systems that don't just follow rules, but learn, adapt, and make decisions. This comprehensive guide explains how AI technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision transform basic automation into intelligent systems that can handle complex tasks, understand context, and improve over time. You'll learn the key components, real-world applications across industries, implementation steps for beginners, and how this technology is changing businesses and careers. Whether you're a business owner looking to improve efficiency or someone curious about future technology, this guide breaks down intelligent automation in simple, accessible language.
Intelligent Automation Explained: When AI Meets Automation
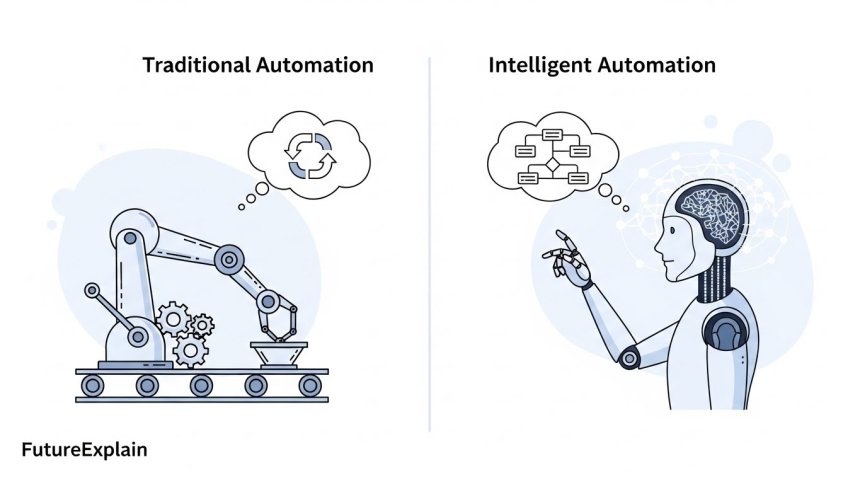
Imagine an automation system that doesn't just follow predetermined instructions, but learns from experience, adapts to changes, and makes decisions like a human would—only faster and without getting tired. This is intelligent automation, the powerful combination of artificial intelligence and traditional automation that's transforming how businesses and individuals work. While traditional automation handles repetitive tasks by following fixed rules, intelligent automation adds thinking capabilities, allowing systems to handle complexity, uncertainty, and variability that would normally require human judgment.
According to IBM's research, intelligent automation represents the next evolution of business process automation, where systems "move beyond rule-based tasks to handle judgment-intensive work" (IBM Research, 2023). This isn't about replacing humans, but about augmenting human capabilities and freeing people from mundane tasks to focus on more creative, strategic work. The global market for intelligent automation is growing rapidly as organizations recognize its potential to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enable new capabilities that weren't previously possible with technology alone.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll break down exactly what intelligent automation is, how it works, where it's being used today, and how you can start understanding or implementing it—even if you're not a technical expert. We'll use simple analogies, real-world examples, and clear explanations to demystify this important technology trend.
What Exactly Is Intelligent Automation?
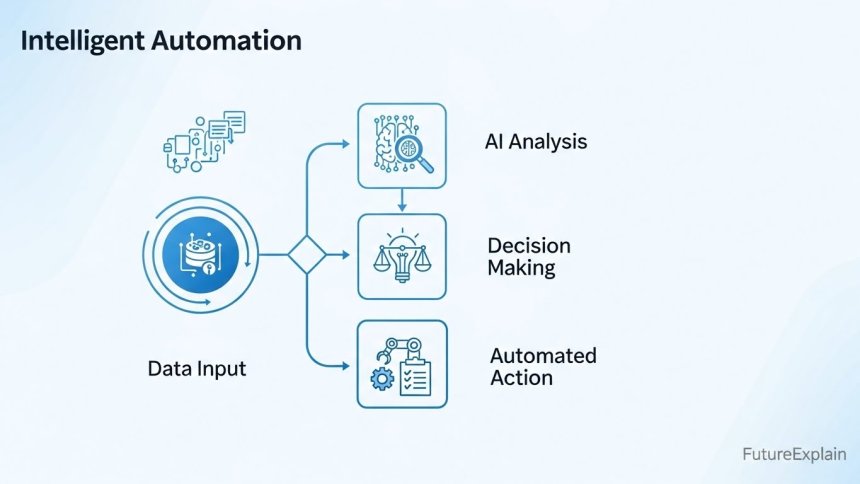
Intelligent automation (IA) is the integration of artificial intelligence technologies with automation tools to create systems that can perform tasks, make decisions, and improve their performance over time without constant human intervention. Think of it as giving automation a brain—not just arms that can do repetitive work, but eyes to see, ears to hear, and cognitive abilities to understand and decide.
The core idea is simple: traditional automation excels at doing the same thing over and over perfectly, but it struggles when anything changes. Add AI capabilities, and suddenly the system can handle variations, learn from examples, understand natural language, recognize patterns, and make judgment calls. This combination creates what industry experts call "cognitive automation"—systems that mimic human cognitive functions within automated workflows.
Three key characteristics distinguish intelligent automation from basic automation:
- Learning capability: IA systems improve their performance based on data and experience
- Adaptability: They can handle variations and changes in their environment
- Decision-making: They can make choices based on rules, patterns, and context
The Building Blocks: How AI Supercharges Automation
To understand how intelligent automation works, let's look at the key AI technologies that make automation "intelligent":
1. Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics
Machine learning allows automation systems to recognize patterns in data and make predictions or decisions based on those patterns. Instead of being programmed with explicit rules for every scenario, ML-powered automation learns from historical examples. For instance, an intelligent document processing system can learn to extract information from invoices even when they come in different formats, because it has been trained on thousands of example invoices.
Predictive analytics takes this further by forecasting future outcomes. An intelligent inventory management system might analyze sales patterns, seasonality, supplier lead times, and even weather forecasts to automatically reorder stock at optimal times, avoiding both shortages and overstock situations.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables automation systems to understand, interpret, and generate human language. This is what allows intelligent chatbots to have meaningful conversations, or document automation systems to comprehend the content of emails, reports, and forms. Unlike basic automation that might look for specific keywords, NLP-powered systems understand context, sentiment, and intent.
For example, an intelligent customer service automation can read incoming emails, understand what the customer is asking (even if phrased differently than expected), retrieve relevant information, and compose a appropriate response—all without human intervention for routine inquiries.
3. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Computer vision gives automation systems "eyes" to interpret visual information. This enables automation to work with images, videos, and visual interfaces. From quality inspection on manufacturing lines to automatically processing scanned documents, computer vision allows automation to handle tasks that previously required human visual perception.
Retailers use intelligent automation with computer vision to monitor shelf stock levels, while healthcare providers use it to help analyze medical images alongside human experts.
4. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Enhanced with AI
RPA forms the "doing" part of intelligent automation—the digital robots that interact with applications and systems. When enhanced with AI capabilities, these robots become much more versatile. Basic RPA can only follow strict rules, but AI-enhanced RPA can handle exceptions, make judgment calls, and adapt to interface changes.
According to UiPath's documentation on intelligent automation, "AI capabilities transform RPA from a tool that automates repetitive tasks to a platform that automates entire business processes, including those requiring perception, understanding, and decision-making" (UiPath, 2023).
Intelligent Automation in Action: Real-World Examples
Understanding intelligent automation becomes much easier when we look at how it's actually being used across different industries. These examples show the practical application of the concepts we've discussed.
Financial Services: Fraud Detection and Prevention
Banks and financial institutions use intelligent automation to monitor transactions in real-time for potential fraud. Traditional rule-based systems might flag transactions above a certain amount or from unusual locations, but intelligent systems analyze hundreds of factors simultaneously: your typical spending patterns, time of day, merchant type, device used, and even your typing patterns during login.
The system learns what's normal for each customer and can detect subtle anomalies that might indicate fraud. When suspicious activity is detected, it can automatically trigger additional verification steps, temporarily limit account capabilities, or alert human investigators—all while allowing legitimate transactions to proceed smoothly. This represents a significant advancement over basic automation, which would either block too many legitimate transactions or miss sophisticated fraud patterns.
Healthcare: Patient Triage and Administrative Automation
Hospitals and clinics are implementing intelligent automation to handle initial patient interactions and administrative tasks. When a patient contacts a healthcare provider, an intelligent system can understand their symptoms described in natural language, ask clarifying questions, check appointment availability, and schedule appropriate consultations.
Behind the scenes, these systems automatically update patient records, process insurance information, and even help with billing. By handling routine administrative tasks and initial triage, intelligent automation frees healthcare professionals to focus on patient care while reducing wait times and administrative errors. Research indicates that such systems can process standard administrative tasks up to 70% faster than manual methods while maintaining higher accuracy rates.
Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance and Quality Control
Modern factories use intelligent automation to monitor equipment health and product quality. Sensors collect data on machine vibration, temperature, power consumption, and output quality. Machine learning algorithms analyze this data to predict when equipment is likely to fail or when product quality is beginning to drift from standards.
The system can then automatically schedule maintenance before breakdowns occur, adjust machine parameters to maintain quality, or even order replacement parts—all without human intervention. This prevents costly downtime and ensures consistent product quality. Unlike basic automation that might simply shut down a machine when parameters exceed fixed limits, intelligent automation can detect subtle patterns that indicate developing problems long before they cause failure.
Retail: Personalized Customer Experiences
E-commerce platforms and physical retailers use intelligent automation to create personalized shopping experiences at scale. By analyzing browsing history, purchase patterns, demographic information, and even real-time behavior, these systems can automatically customize website layouts, recommend products, adjust pricing, and personalize marketing messages for each individual customer.
Intelligent inventory systems automatically manage stock levels across multiple locations, predict demand for different products, and optimize logistics. When a customer service inquiry comes in, the system can automatically pull up their complete history, understand their question, and provide a personalized response or route them to the most appropriate human agent if needed.
The Evolution: From Basic to Intelligent Automation
To fully appreciate intelligent automation, it helps to understand how we got here. Automation has evolved through several distinct phases:
Phase 1: Mechanical Automation (Industrial Revolution)
The first wave of automation involved physical machines replacing manual labor for repetitive tasks. Think assembly lines, conveyor belts, and mechanical looms. These systems followed fixed mechanical processes with no adaptability.
Phase 2: Programmable Automation (Computer Age)
With computers came the ability to program automation systems with more complex instructions. Numerical control machines, early industrial robots, and business software automation allowed for more flexibility through programming, but changes still required manual reprogramming.
Phase 3: Rule-Based Digital Automation (RPA Era)
The rise of Robotic Process Automation brought software robots that could mimic human interactions with digital systems. These could follow complex rules and handle structured digital tasks, but struggled with variability, unstructured data, and exceptions.
Phase 4: Intelligent Automation (Current Era)
Today's intelligent automation combines the execution capabilities of previous automation with AI's cognitive abilities. This creates systems that can handle unstructured information, learn from experience, adapt to changes, and make context-aware decisions. The system doesn't just do what it's told—it figures out what needs to be done based on understanding the situation.
This evolution represents a fundamental shift from automation as a tool that executes human instructions to automation as a partner that understands intent and context.
Key Benefits: Why Intelligent Automation Matters
Organizations adopt intelligent automation for several compelling reasons that go beyond simple efficiency gains:
1. Handling Complexity and Variability
Traditional automation breaks down when faced with variability or exceptions. Intelligent automation thrives on it. Whether it's invoices in different formats, customer inquiries phrased in unique ways, or production variations, intelligent systems can adapt and handle the diversity that characterizes real-world business processes.
2. Continuous Improvement Through Learning
Unlike static automation that performs exactly the same way until reprogrammed, intelligent automation systems improve over time. Every decision, every outcome, and every correction becomes training data that makes the system smarter. This creates a virtuous cycle where performance continuously improves without manual intervention.
3. Better Decision-Making at Scale
Intelligent automation can apply consistent decision-making criteria across thousands or millions of cases, eliminating human inconsistency while handling volume that would be impossible for human teams. This is particularly valuable in areas like loan approvals, insurance claims processing, or quality control where consistency and scalability matter.
4. Enhanced Human-Machine Collaboration
Rather than replacing humans, intelligent automation excels at augmenting human capabilities. It handles routine cognitive work, provides recommendations, surfaces relevant information, and executes tasks—allowing humans to focus on strategic thinking, creativity, complex problem-solving, and emotional intelligence. This creates more satisfying work for people while boosting overall productivity.
5. Resilience and Adaptability
Intelligent systems can detect when normal patterns change and adapt accordingly. During the COVID-19 pandemic, for example, organizations with intelligent automation could quickly adapt to new patterns in customer behavior, supply chain disruptions, and remote work requirements because their systems could learn from the new data rather than requiring complete reprogramming.
Implementation: How to Get Started with Intelligent Automation
For businesses or individuals interested in intelligent automation, here's a practical approach to getting started:
Step 1: Identify Suitable Processes
Look for processes that share these characteristics: high volume, repetitive elements, involvement of structured and unstructured data, requirement for some judgment or decision-making, and currently performed by humans who find the work mundane. Common starting points include invoice processing, customer service triage, employee onboarding, report generation, and data entry tasks.
Step 2: Start with a Pilot Project
Choose one well-defined process for your first intelligent automation project. Ensure it has clear success metrics, manageable scope, and executive sponsorship. The goal is to learn, demonstrate value, and build confidence before scaling.
Step 3: Assemble the Right Team
Successful intelligent automation requires cross-functional collaboration: subject matter experts who understand the current process, automation specialists, data scientists or AI experts, and business leaders. For smaller organizations, many no-code and low-code platforms now make intelligent automation accessible without deep technical expertise.
Step 4: Choose Appropriate Technology
Evaluate platforms based on your specific needs. Key considerations include: ease of integration with existing systems, availability of pre-built AI capabilities (like document understanding or sentiment analysis), scalability, and total cost of ownership. Many cloud platforms offer intelligent automation as a service, reducing the need for upfront infrastructure investment.
Step 5: Implement with Humans in Mind
Design your intelligent automation with human workers as collaborators, not replacements. Involve them in the design process, focus on eliminating tedious work rather than eliminating jobs, and provide training for new roles that leverage human strengths alongside automation.
Challenges and Considerations
While intelligent automation offers tremendous potential, it's important to approach it with eyes wide open to potential challenges:
Data Quality and Availability
Intelligent automation systems depend on data to learn and make decisions. Poor quality data, biased data, or insufficient data can lead to poor outcomes. Organizations need to invest in data governance and ensure they have appropriate, representative data for training their systems.
Explainability and Trust
Some AI techniques, particularly deep learning, can become "black boxes" where it's difficult to understand why a particular decision was made. In regulated industries or for critical decisions, this lack of transparency can be problematic. Techniques for explainable AI are evolving to address this challenge.
Integration Complexity
Intelligent automation often needs to work across multiple legacy systems, each with different interfaces and data formats. Integration challenges can slow implementation and increase costs. Choosing platforms with strong integration capabilities and starting with well-defined interfaces can help mitigate this.
Change Management
Employees may fear job loss or feel threatened by intelligent automation. Successful implementation requires clear communication about how automation will augment rather than replace human workers, along with training and support for transitioning to new roles.
Ethical Considerations
As automation systems make more decisions, ethical questions arise about accountability, bias, and appropriate use. Organizations need to establish guidelines for ethical automation, regularly audit systems for bias, and maintain human oversight for critical decisions.
The Future of Intelligent Automation
As AI technologies continue to advance, intelligent automation will become even more capable and pervasive. Several trends are shaping its future development:
Hyperautomation
Gartner defines hyperautomation as "the combination of multiple machine learning, packaged software, and automation tools to deliver work." This represents the next evolution—not just automating individual tasks or processes, but orchestrating automation across entire organizations in an integrated, intelligent way.
Autonomous Systems
We're moving toward systems that can operate with minimal human oversight, setting their own goals within defined parameters and figuring out how to achieve them. This represents a shift from automation that executes predefined processes to systems that can discover and optimize processes autonomously.
Democratization Through No-Code/Low-Code Platforms
Tools are becoming more accessible, allowing business users with domain expertise but limited technical skills to create and manage intelligent automation. This democratization will accelerate adoption and innovation as more people can implement automation solutions for their specific needs.
Integration with IoT and Edge Computing
As more devices become connected through the Internet of Things, intelligent automation will extend beyond digital systems to the physical world. Combined with edge computing (processing data closer to where it's generated), this will enable real-time intelligent automation in factories, vehicles, retail stores, and smart cities.
Human-Augmentation Focus
The most successful implementations will focus on enhancing human capabilities rather than replacing them. Future intelligent automation will be designed as collaborative systems that amplify human intelligence, creativity, and emotional intelligence.
Getting Started as an Individual
Even if you're not implementing intelligent automation in an organization, understanding this technology is valuable for career development and personal productivity:
- Learn the basics: Start with our guide on what automation is and how machine learning works
- Experiment with tools: Many platforms offer free tiers for personal use
- Develop relevant skills: Focus on skills that complement automation—critical thinking, creativity, emotional intelligence, and domain expertise
- Stay informed: Follow developments in both AI and automation to understand how they're converging
Intelligent automation represents one of the most significant technological developments of our time, transforming how work gets done across every industry. By understanding its principles, applications, and implications, you position yourself to thrive in an increasingly automated world—whether as an implementer, a collaborator with automated systems, or simply as an informed citizen navigating technological change.
The key insight is that intelligence and automation are no longer separate domains. The most powerful systems combine execution capability with cognitive ability, creating partners that can handle both the routine and the exceptional. As this technology continues to evolve, it will create new opportunities, new business models, and new ways of working that leverage the unique strengths of both humans and machines.
Further Reading
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
1240
Like
1240
 Dislike
12
Dislike
12
 Love
340
Love
340
 Funny
45
Funny
45
 Angry
8
Angry
8
 Sad
5
Sad
5
 Wow
210
Wow
210















We've been using intelligent automation for 2 years now. The biggest lesson? Start with processes that have clear metrics and stakeholder buy-in. Quick wins build momentum.
The article should mention that this isn't just for big companies. We're a 15-person startup using intelligent automation and it's given us capabilities far beyond our size.
We're in hospitality using intelligent automation for guest service requests. Simple requests handled automatically, complex ones routed to appropriate staff. Guests love the speed.
The article mentions edge cases. We learned the hard way that you need to plan for exceptions. Our first automation failed whenever it encountered anything unusual.
Grayson, this is a common learning experience. Best practice is to: 1) Log all exceptions for analysis, 2) Build escalation paths to humans, 3) Gradually expand system capabilities as you encounter more edge cases, 4) Design for graceful failure rather than complete collapse.
We're a retail chain using intelligent automation for inventory management across 50 stores. It's reduced stockouts by 70% and excess inventory by 40%.
The no-code democratization is real but has limits. We hit a complexity wall where we needed developers anyway. It's great for simple automations though.