What Is Automation? A Beginner’s Guide
Learn what automation really means in plain language. This guide explains how it works, different types, real-world examples, and how you can start using it to save time.
Introduction: The Magic of Getting Things Done Automatically
Imagine a world where your coffee brews itself as your alarm goes off, your important emails are sorted before you even open your laptop, and the tedious data entry at work happens flawlessly in the background. This isn't science fiction; it's the power of automation in action. In our fast-paced digital age, automation has moved from factory floors to our offices and homes, becoming a key tool for efficiency.
But what exactly is automation? If the term sounds technical or intimidating, you're not alone. Many people associate it only with giant robotic arms or complex computer code. In reality, automation is a simple and incredibly practical concept that anyone can understand and use. This beginner's guide will demystify automation, showing you how it works, why it matters, and how you can harness its power to save time and simplify your life. If you're new to the topic, you might want to first check out our article on AI vs Automation to see how these two powerful concepts relate and differ.
What Is Automation? A Simple Definition
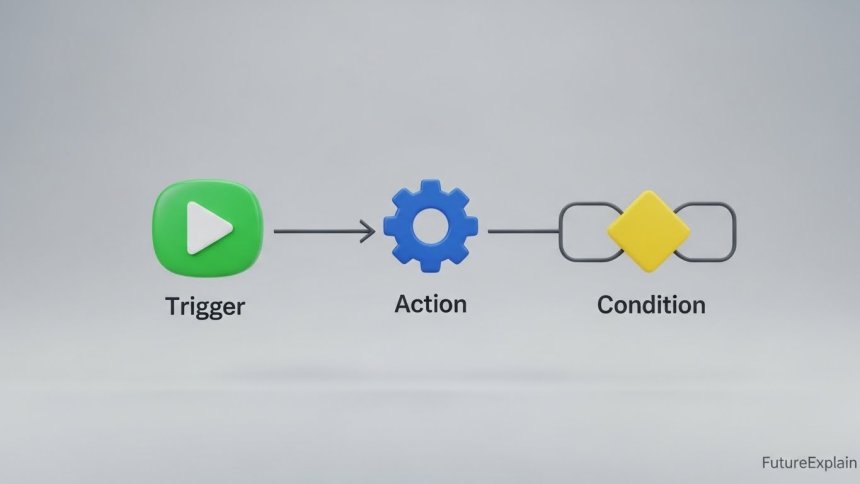
At its core, automation is the use of technology to perform tasks with minimal human input. It's about setting up systems—whether they are physical machines or software programs—to follow a set of predefined rules and carry out a process from start to finish on their own[citation:10].
Think of it like a domino chain. You set up the first domino (create the rules or instructions), and then give it a nudge (start the process). After that, the entire chain falls in a predictable, repeated sequence without you needing to touch each piece. Automation works on a similar principle: "Do this, then that, under these conditions." The goal is to handle repetitive, time-consuming, or error-prone work so humans can focus on activities that require creativity, judgment, and problem-solving[citation:10].
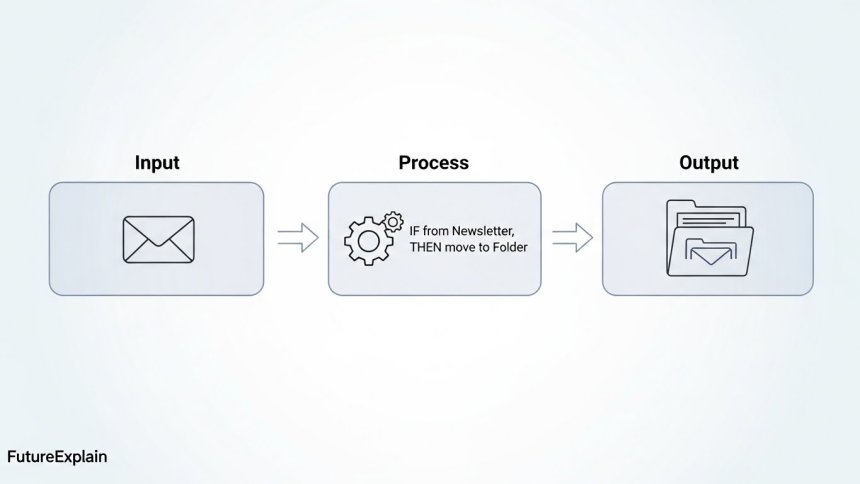
The Key Ingredients of Any Automated System
While automated systems can look very different, most share three common components:
- Input: This is the trigger or the data that starts the process. It could be a new email arriving in an inbox, a sensor detecting an object on a conveyor belt, or a specific time of day.
- Process: This is the set of rules or actions the system follows. It's the "if this, then that" logic. For example, "IF an email arrives from 'newsletter@example.com,' THEN move it to the 'Newsletters' folder."
- Output: This is the result or action taken. The email is moved, the robot arm welds a car part, or a report is generated and sent to your manager.
Automation vs. Artificial Intelligence: What's the Difference?
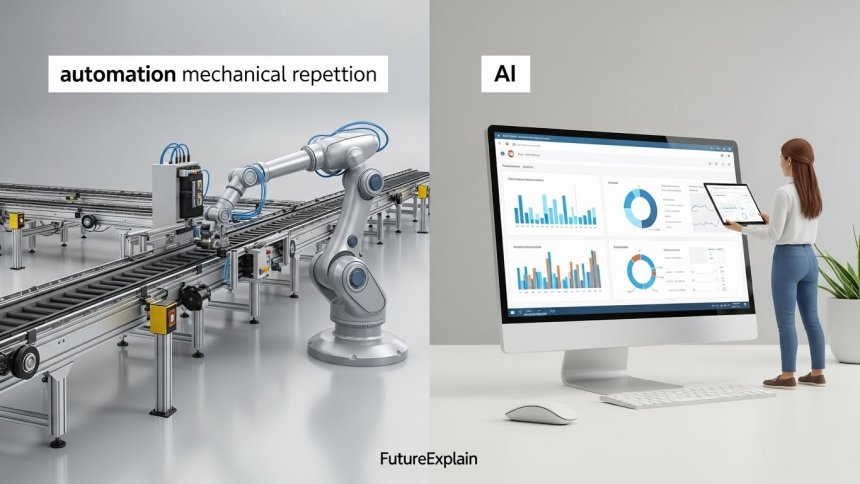
This is a common point of confusion, and understanding the distinction is crucial. While automation and AI (Artificial Intelligence) often work together today, they are fundamentally different concepts.
Automation is rule-based. It excels at doing the same thing, the same way, over and over again. It's incredibly fast and accurate, but it cannot handle surprises or make decisions outside its programmed rules[citation:10]. A classic example is an assembly line robot that tightens a bolt in the exact same spot on every single car that passes by.
Artificial Intelligence is learning-based. AI systems are designed to interpret data, recognize patterns, and make decisions or predictions. They can adapt to new situations. For instance, an AI-powered quality control camera can learn to identify new types of defects it wasn't originally programmed to find[citation:10].
In simple terms: Automation follows instructions. AI figures things out. The most powerful modern systems combine both, in an approach sometimes called "intelligent automation" or "hyperautomation," where AI handles the interpretation and decision-making, and automation executes the resulting actions[citation:10]. You can explore this powerful combination further in our dedicated guide to Intelligent Automation.
The Different Types of Automation: From Factories to Your Phone
Automation isn't one single thing. It comes in many forms, applicable to different areas of work and life. Here are the main types you should know about:
1. Industrial Automation
This is what most people picture: robots in manufacturing plants. Industrial automation uses machinery, control systems, and robots to handle physical production tasks like welding, painting, assembly, and packaging[citation:10]. These systems are the backbone of modern manufacturing, ensuring speed, precision, and consistency that would be impossible for humans to maintain for long periods.
2. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA is like a "software robot" or a digital assistant for your computer. It mimics the actions a human would take on a computer—like clicking, typing, copying, and pasting data between applications[citation:10]. For example, an RPA bot could log into an email account, download all invoice attachments, extract the data, and enter it into an accounting software like QuickBooks, all without a person touching the keyboard. It's perfect for rule-based digital paperwork.
3. Business Process Automation (BPA)
BPA focuses on automating entire multi-step workflows, often involving multiple people and software systems. It's about streamlining complete processes like employee onboarding, customer order fulfillment, or expense report approvals. BPA software (like many CRM or ERP tools) moves tasks and information along a predefined path, sending notifications and escalating issues as needed[citation:10]. To dive deeper into streamlining complete workflows, read our beginner explanation of Workflow Automation.
4. Personal & Home Automation
This is automation in your daily life. It includes smart home devices like thermostats that adjust the temperature based on your schedule, lights that turn on at sunset, or email filters that sort your messages automatically. The goal here is personal convenience and efficiency. For simple ways to start, our article on Automation Made Easy is a great next step.
Real-World Examples of Automation You Might Know
Automation is already all around you. Here are some everyday examples that illustrate how it works:
- Online Bill Pay: You set up a rule with your bank: "Every month on the 5th, pay $50 to the electricity company." The system executes it automatically.
- Social Media Scheduling: Tools like Buffer or Hootsuite let you write a week's worth of posts at once and automatically publish them at the times you specify.
- E-commerce Order Processing: When you click "Buy," automated systems instantly check inventory, process your payment, and send an order confirmation and tracking number. In advanced warehouses, robots may even retrieve your item from a shelf[citation:10].
- Customer Service Chatbots: Many websites use basic automated chatbots to answer frequently asked questions (e.g., "What are your hours?") instantly, without a human agent[citation:10].

Why Automation Matters: The Key Benefits
Why has automation become so widespread? The benefits touch both individuals and large organizations.
- Saves Time and Increases Productivity: This is the most obvious benefit. By handling repetitive tasks, automation frees up hours in your day or your team's week for more valuable work.
- Reduces Errors: Humans get tired, distracted, or bored when doing repetitive work. Machines don't. An automated system will perform a task the exact same (correct) way every single time, drastically reducing typos, missed steps, and other costly mistakes.
- Improves Consistency and Quality: Whether it's making a product or processing a document, automation ensures every output meets the same standard.
- Operates 24/7: Automated systems don't need sleep, breaks, or holidays. They can run processes overnight, on weekends, and across time zones, accelerating work cycles.
- Cuts Costs: While there's an initial investment, over time, automation reduces labor costs associated with manual tasks and minimizes expenses related to errors and rework.
Considering the Other Side: Challenges and Responsible Use
Like any powerful tool, automation comes with considerations that are important to understand.
The most discussed challenge is job displacement. As tasks become automated, some roles, particularly those centered on routine manual or data-entry work, may evolve or diminish[citation:1][citation:4]. However, history shows that technology also creates new jobs—think of roles like "automation engineer," "RPA developer," or "process analyst." The key for individuals and businesses is adaptation and reskilling, focusing on the uniquely human skills of creativity, strategy, and emotional intelligence that machines lack[citation:1]. For a realistic look at this shift, see our article on How AI Is Changing Jobs.
Other challenges include the initial cost and complexity of setting up robust systems, the potential for over-reliance (where people stop monitoring automated processes), and the need for careful design to avoid automating biased or flawed human processes[citation:4]. The principle of human oversight remains critical; automation should be a tool that augments human work, not a system that operates entirely without accountability[citation:5][citation:6].
How to Get Started with Automation (A Beginner's First Steps)
You don't need a factory or a team of programmers to start benefiting from automation. Here’s how you can dip your toes in:
- Identify the Repetitive: Look for the most tedious, frequent tasks in your day. Do you manually back up files every Friday? Do you sort the same types of emails? Do you copy data from websites into a spreadsheet? These are perfect automation candidates.
- Start Small and Simple: Begin with one task. Use the built-in tools you already have. Set up an email filter. Use the "Rules" feature in your calendar. Create a template for a document you write often.
- Explore "No-Code" and "Low-Code" Tools: A revolution in automation is the rise of user-friendly platforms that let you automate tasks by connecting apps with a visual, drag-and-drop interface—no programming knowledge required. Tools like Zapier, IFTTT, or Microsoft Power Automate can connect your email, calendar, drive, and social media to create powerful "if this, then that" workflows. For a curated list, explore our review of the Best Automation Tools for Non-Technical Users.
- Document and Refine: Once you automate something, check on it periodically. Is it working as intended? Can the rule be improved? Automation is an ongoing process of optimization.
The Future of Automation: What's Next?
Automation continues to evolve. The future points toward more accessible, integrated, and intelligent systems. Trends like "Plug & Produce" solutions are making industrial automation faster to deploy, especially for small businesses[citation:7]. The collaboration between humans and collaborative robots ("cobots") is becoming safer and more sophisticated, with robots handling heavy, repetitive lifting while humans focus on fine assembly[citation:7]. Furthermore, the integration of AI with automation is creating systems that are not just fast, but also adaptable and capable of handling exceptions, pushing the boundaries of what can be automated[citation:7][citation:10].
Conclusion: Your Automation Journey Starts Here
Automation is not a distant, complex technology reserved for engineers. It's a practical approach to working smarter, not harder. By understanding its basic rule-based nature, recognizing its various forms, and starting with small, manageable tasks, you can begin to reclaim time, reduce stress, and boost your own productivity. The goal isn't to remove the human element, but to strategically remove the robotic, repetitive elements from our work, allowing us to focus on what makes us uniquely human.
Ready to learn more? Continue your journey by understanding how automation integrates with AI in our guide to Intelligent Automation, or discover practical ways it can save time in your daily digital life.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
380
Like
380
 Dislike
5
Dislike
5
 Love
120
Love
120
 Funny
25
Funny
25
 Angry
2
Angry
2
 Sad
3
Sad
3
 Wow
65
Wow
65
















The links to related articles are perfectly placed. I went from this to the "Intelligent Automation" piece and now have a complete picture. Excellent content strategy!
After reading this, I audited my workday and found 12 repetitive tasks I could potentially automate. Starting with the easiest ones first as suggested. Feeling empowered!
I run a nonprofit and we're stretched thin. The cost-cutting benefits section convinced me to explore automation for our donor thank-you letters and volunteer scheduling. Every dollar and hour counts!
The watermarked images are a nice professional touch. The split-image visual showing before/after automation really drives the point home effectively.
As someone who manages a remote team across time zones, the "operates 24/7" benefit resonated deeply. We've automated our stand-up reports and it's transformed how we collaborate asynchronously.
This article changed my perspective. I used to see automation as job-threatening, but now I see it as tool that eliminates the boring parts of my work so I can focus on what I actually enjoy.