Securing Your AI App: Basics of Model and Data Security
This comprehensive guide explains AI application security in simple terms for beginners and non-technical users. Learn how to protect your AI models, secure sensitive data, implement proper access controls, and prevent common security threats. We cover practical steps for securing AI APIs, managing model versions, encrypting training data, and complying with regulations. Whether you're building a small AI tool or deploying enterprise applications, this guide provides actionable security foundations without overwhelming technical complexity. Includes checklists, real-world examples, and cost-effective solutions for businesses of all sizes.

Securing Your AI App: Basics of Model and Data Security
As artificial intelligence becomes more accessible, security concerns grow equally important. Whether you're building a customer service chatbot, an image generation tool, or a predictive analytics platform, securing your AI application is no longer optional—it's essential. This guide breaks down AI security into simple, actionable concepts that anyone can understand and implement.
Many beginners assume AI security is too complex or only for large enterprises. The truth is that basic security measures are accessible to everyone and can prevent catastrophic data breaches, model theft, and privacy violations. According to the OWASP ML Security Top 10 framework, many AI security issues stem from fundamental oversights that are easily preventable with proper planning.
Why AI Security Is Different (And Why It Matters)
Traditional application security focuses on protecting code and user data. AI applications add two critical layers: the model itself and the training data. Both require specialized protection approaches.
Your AI model represents significant intellectual property and computational investment. A stolen model can be replicated, reverse-engineered, or used maliciously. Meanwhile, training data often contains sensitive information—customer details, proprietary business data, or personal identifiers—that requires protection under regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Consider a healthcare AI that predicts patient outcomes. The model might be valuable, but the patient data used to train it is protected health information (PHI) requiring stringent security. Similarly, a financial fraud detection model uses transaction data that must remain confidential.
The Three Pillars of AI Application Security
1. Data Security: Protecting What Feeds Your AI
Training data is the foundation of any AI system. Securing it involves multiple layers of protection throughout its lifecycle.
Data at Rest Encryption: Always encrypt stored training data. Modern cloud platforms offer simple encryption options that don't require deep technical knowledge. For example, when storing data in Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage, enable server-side encryption with a single click.
Data in Transit Protection: When data moves between systems—from collection points to storage, or from storage to training environments—use TLS/SSL encryption. This is the same technology that secures website connections (HTTPS). Most modern APIs and data transfer tools include this by default.
Data Minimization Principle: Only collect and retain data necessary for your AI's purpose. This reduces your security burden and compliance requirements. Before adding a new data field, ask: "Is this essential for model training?" If not, don't collect it.
Access Controls for Data: Implement the principle of least privilege. Team members should only access data necessary for their specific roles. Use role-based access controls (RBAC) available in most cloud platforms and database systems.
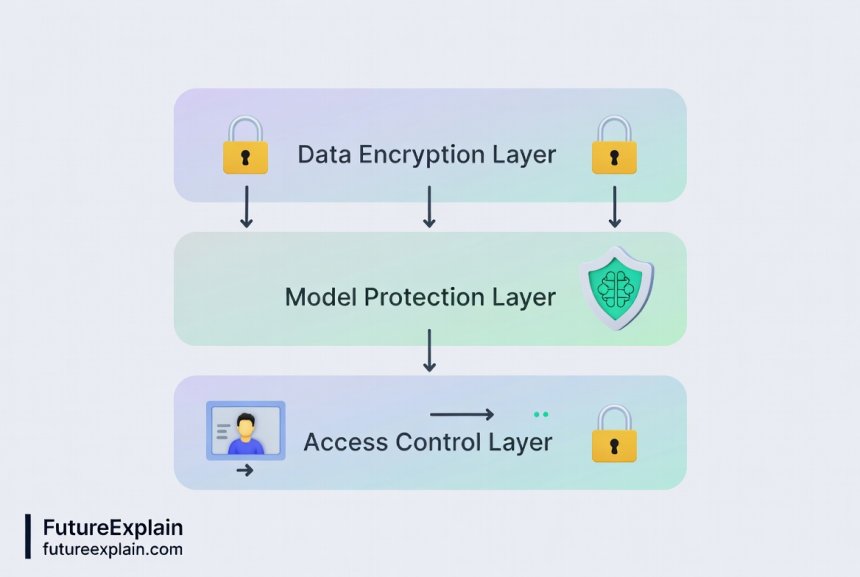
2. Model Security: Protecting Your AI Brain
Your trained model represents weeks or months of computational work and unique business logic. Protecting it requires specific strategies.
Model Encryption: Encrypt model files both at rest and during transfer. When deploying models to production environments, ensure they're stored encrypted. Many model serving platforms like TensorFlow Serving or TorchServe support built-in encryption.
API Security for Model Endpoints: Most AI applications expose models via APIs. Secure these endpoints with authentication (API keys, OAuth tokens), rate limiting to prevent abuse, and input validation to block malicious queries. Tools like FastAPI with security dependencies make this accessible even for beginners.
Model Watermarking: For particularly valuable models, consider digital watermarking—embedding identifiable patterns that help prove ownership if the model is stolen. Research from institutions like the University of Maryland shows practical watermarking techniques that don't affect model performance.
Version Control and Integrity Checks: Use version control systems (like Git) for model code and track model versions with checksums. This allows detection of unauthorized modifications. Tools like MLflow or Weights & Biases provide user-friendly versioning interfaces.
3. Infrastructure Security: The Foundation Layer
Even with perfect data and model security, weak infrastructure can create vulnerabilities.
Secure Cloud Configuration: Most AI applications run on cloud platforms. Ensure proper configuration of cloud resources: private networks where possible, firewall rules restricting unnecessary access, and regular security group reviews. Cloud providers offer "security center" tools that identify misconfigurations.
Container Security: If using Docker containers for deployment, follow container security best practices: use minimal base images, regularly update dependencies, scan images for vulnerabilities, and run containers with non-root users.
Monitoring and Logging: Implement comprehensive logging of all AI system activities: data access, model predictions, API calls, and user interactions. Centralized logging with alerting helps detect anomalies early. Cloud-native solutions like AWS CloudWatch or Google Cloud Logging provide accessible interfaces.
Common AI Security Threats and How to Prevent Them
Data Poisoning Attacks
Attackers intentionally feed malicious data during training to manipulate model behavior. For example, subtly altering product images could cause an e-commerce recommendation system to favor certain items.
Prevention Strategies:
- Implement data validation pipelines that check for anomalies before training
- Use diverse data sources to reduce dependency on any single stream
- Regularly retest model performance against validation datasets
- Consider federated learning approaches that keep data decentralized
Model Inversion Attacks
Attackers use model outputs to reconstruct sensitive training data. Research from Cornell University demonstrated that with enough API queries, attackers could reconstruct faces from facial recognition models.
Prevention Strategies:
- Limit prediction API outputs to only necessary information
- Add noise to predictions (differential privacy techniques)
- Implement query rate limiting and monitoring
- Regularly audit which data could be reconstructed from outputs
Adversarial Examples
Specially crafted inputs designed to cause incorrect model predictions. A classic example: adding subtle noise to a stop sign image causes an autonomous vehicle system to misclassify it.
Prevention Strategies:
- Train models with adversarial examples to improve robustness
- Implement input validation and sanitization
- Use ensemble methods combining multiple models
- Monitor for unusual input patterns that might indicate attacks
Model Stealing
Attackers query your model extensively to create a copy. This is particularly concerning for proprietary models representing significant R&D investment.
Prevention Strategies:
- Implement strict API authentication and rate limiting
- Consider model watermarking for ownership proof
- Use model distillation to create simpler, less valuable public versions
- Monitor query patterns for excessive similar requests
Practical Security Checklist for AI Applications
Use this actionable checklist regardless of your technical expertise level:
Before Development Begins
- Conduct a security risk assessment specific to your AI use case
- Identify regulatory requirements (GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, etc.)
- Document data sources and sensitivity levels
- Define security requirements as part of project specifications
During Development
- Use secure coding practices and dependency scanning
- Implement input validation for all data ingestion points
- Design authentication and authorization from the start
- Encrypt sensitive data in testing environments too
Before Deployment
- Conduct security testing including penetration testing if possible
- Review all access controls and permissions
- Ensure all dependencies are updated and patched
- Configure monitoring and alerting systems
Post-Deployment
- Regularly review access logs for anomalies
- Schedule periodic security assessments
- Keep all components updated with security patches
- Maintain incident response procedures

Implementing Access Controls for AI Systems
Proper access control is one of the most effective yet overlooked security measures. Here's how to implement it practically:
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Define clear roles within your team: Data Scientists (need training data access), DevOps Engineers (need deployment access), Business Users (need prediction API access), and Auditors (need log access). Most cloud platforms provide built-in RBAC systems.
API Key Management: If your AI exposes APIs, use API keys with appropriate permissions. Rotate keys regularly (every 90 days is a good standard), and never hardcode keys in client applications. Use environment variables or secure key management services.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for all administrative access to AI systems. This simple step prevents most credential-based attacks. Cloud platforms make MFA easy to enable.
Just-in-Time Access: For highly sensitive operations (like modifying production models), implement just-in-time access that must be explicitly requested and approved, with automatic expiration after a short period.
Compliance Considerations for AI Applications
Security isn't just about technology—it's also about compliance with regulations that protect users and their data.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): If you serve EU users, GDPR applies. Key requirements for AI include: lawful basis for data processing, data minimization, right to explanation for automated decisions, and data protection by design. The EU AI Act adds specific security requirements for high-risk AI systems.
CCPA/CPRA (California Privacy Rights Act): Similar to GDPR for California residents, with additional transparency requirements about automated decision-making.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): For healthcare AI applications in the US, HIPAA requires specific security controls for protected health information (PHI).
SOC 2 Compliance: Many enterprise customers require SOC 2 certification, which includes specific security controls that should be designed into your AI system from the beginning.
Building compliance into your AI application from the start is far easier than retrofitting it later. Document your security measures as part of compliance requirements.
Cost-Effective Security Solutions for Small Teams
Security doesn't require massive budgets. Here are accessible solutions for teams with limited resources:
Leverage Cloud Provider Security Tools: AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure all offer free tier security services: basic monitoring, vulnerability scanning, and security recommendations. Their paid services often have generous free tiers for small usage.
Open Source Security Tools: Tools like OWASP ZAP for security testing, Trivy for container scanning, and Vault for secret management have free versions suitable for small projects.
Managed Security Services: For critical applications, consider managed security services that start at reasonable monthly rates. These provide 24/7 monitoring without requiring in-house expertise.
Security-as-Code Approaches: Use infrastructure-as-code tools (Terraform, CloudFormation) to define security configurations alongside your application. This ensures consistency and allows security review through code review processes.
Incident Response for AI Security Breaches
Despite best efforts, security incidents can occur. Having a response plan minimizes damage.
Preparation Phase:
- Document contact information for key team members
- Prepare communication templates for different incident types
- Regularly backup critical data and models
- Test your incident response plan annually
Detection and Analysis:
- Monitor for anomalies: unusual data access patterns, unexpected model behavior, or API usage spikes
- Use automated alerting for known attack patterns
- Maintain forensic capabilities: detailed logging that can reconstruct events
Containment and Eradication:
- Isolate affected systems quickly
- Revoke compromised credentials immediately
- Preserve evidence for analysis while containing the threat
- Patch vulnerabilities that were exploited
Recovery and Lessons Learned:
- Restore systems from clean backups
- Communicate transparently with affected users if personal data was compromised
- Conduct post-incident review to improve security
- Update security measures based on lessons learned
Future-Proofing Your AI Security
AI security evolves rapidly. Stay ahead with these forward-looking practices:
Continuous Security Education: AI security threats evolve constantly. Dedicate time for your team to learn about new threats and defenses. Follow resources like the AI Ethics & Safety category for updated information.
Security by Design: Integrate security considerations into every phase of AI development, not as an afterthought. This approach, championed by frameworks like Microsoft's Secure Development Lifecycle, prevents vulnerabilities from being introduced.
Zero Trust Architecture: Implement zero trust principles: verify explicitly, use least privilege access, and assume breach. This is increasingly important as AI systems become more distributed.
Quantum-Resistant Cryptography Planning: While still emerging, quantum computing may eventually break current encryption. Consider future-proofing critical systems with quantum-resistant algorithms for long-term data protection.
Getting Started: Your First 30 Days of AI Security
Feeling overwhelmed? Start with these achievable first steps:
Week 1-2: Assessment
- Inventory your AI assets: models, data repositories, APIs
- Identify sensitive data elements
- Review current access controls and permissions
- Check compliance requirements for your use case
Week 3-4: Basic Protections
- Enable encryption for sensitive data at rest
- Implement API authentication if not already present
- Set up basic logging for critical operations
- Establish regular backup procedures for models and data
Ongoing: Continuous Improvement
- Schedule monthly security reviews
- Subscribe to AI security newsletters or feeds
- Conduct quarterly access permission reviews
- Test restore procedures from backups annually
Remember: Perfect security is impossible, but substantial risk reduction is achievable through consistent, thoughtful measures. Each improvement makes your AI application more resilient.
Conclusion: Security as an Enabler, Not a Barrier
Many developers view security as a constraint on innovation. In reality, robust security enables more ambitious AI applications by building trust with users and stakeholders. A secure AI system can handle sensitive data, serve regulated industries, and scale confidently.
As you build or expand your AI applications, integrate these security fundamentals from the beginning. The extra planning pays dividends in reduced risk, regulatory compliance, and user confidence. For more practical guidance, explore our Business Automation resources or learn about Tool Usage Guides for specific security implementations.
AI security doesn't require becoming a cybersecurity expert overnight. It requires thoughtful application of fundamental principles tailored to AI's unique characteristics. Start where you are, improve incrementally, and make security a continuous part of your AI journey.
Further Reading
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
1240
Like
1240
 Dislike
15
Dislike
15
 Love
320
Love
320
 Funny
45
Funny
45
 Angry
8
Angry
8
 Sad
12
Sad
12
 Wow
210
Wow
210
















What's the biggest security mistake you see beginners make with AI apps? Would help to know what to avoid from day one.
The most common mistake: storing API keys and credentials in code repositories or client-side code. Always use environment variables or secret management services. Second biggest: not implementing any authentication on model endpoints, assuming "it's just an internal tool." Defense in depth is key - start with the basics and build from there!
The adversarial training tip was useful. We've started incorporating adversarial examples into our training pipeline and already see improved robustness.
Practical question: How often should we rotate API keys? The article says "regularly" but what's a good timeframe for a moderately sensitive AI application?
Good question! For most applications: 90 days is a reasonable rotation period. For high-security applications: 30 days. Consider implementing automated key rotation using your cloud provider's key management service. Also rotate immediately if you suspect any compromise. The key is having an automated process so it doesn't become a burden.
The section on security as an enabler resonated. We've used our robust security practices as a selling point to enterprise clients concerned about AI risks.
This article made me realize we need to update our vendor assessment questions. We're now asking AI service providers about their security practices before integrating.
The monitoring and logging section could be expanded. What specific metrics should we monitor for AI security? Failed authentication attempts seem obvious, but what about model behavior anomalies?
Great point! Beyond authentication failures, monitor: prediction confidence score distributions (sudden changes may indicate attacks), input data distributions (for data drift or poisoning), API response times (could indicate resource exhaustion attacks), and model output patterns (for data extraction attempts). Consider tools like Evidently AI or Arize for ML-specific monitoring.