How to Use AI for Bug Fixing and Code Reviews
This comprehensive guide teaches beginners how to use AI for bug fixing and code reviews. Learn practical techniques using ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot, and free AI tools to identify and fix coding errors efficiently. Discover step-by-step workflows for integrating AI into your development process, understand the limitations and best practices, and explore real examples of AI catching bugs that humans might miss. Whether you're a new programmer or experienced developer, this guide will help you leverage AI to improve code quality and save hours of debugging time.
How to Use AI for Bug Fixing and Code Reviews: A Complete Beginner's Guide
In today's fast-paced development environment, finding and fixing bugs can consume up to 50% of a programmer's time. What if you could reduce that time significantly while improving code quality? Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how developers approach bug fixing and code reviews, making these processes faster, more accurate, and accessible to programmers of all skill levels.
This guide will walk you through practical, beginner-friendly methods to leverage AI for identifying bugs, suggesting fixes, and conducting thorough code reviews. Whether you're writing your first lines of code or managing large projects, these techniques will save you time and help you write better software.
Understanding AI-Powered Bug Detection
Before diving into tools and techniques, let's understand how AI can help with bug detection. Traditional debugging relies on human intuition, print statements, and debugging tools. AI adds a new layer by:
- Analyzing patterns across millions of code repositories
- Identifying common error patterns you might miss
- Suggesting fixes based on similar resolved issues
- Learning from your specific codebase over time
Unlike static analysis tools that follow fixed rules, AI tools understand context and can adapt to different coding styles and patterns. This makes them particularly valuable for catching subtle bugs that traditional tools might overlook.
Getting Started: Essential AI Tools for Bug Fixing
1. GitHub Copilot - Your AI Pair Programmer
GitHub Copilot has evolved from just a code completion tool to a comprehensive programming assistant. For bug fixing, it offers several powerful features:
- Real-time error detection: As you type, Copilot analyzes your code and highlights potential issues
- Fix suggestions: When it detects a bug, it provides specific code suggestions to fix it
- Alternative implementations: Suggests different approaches that might be more robust
To get started with GitHub Copilot for bug fixing:
- Install the Copilot extension in VS Code or your preferred IDE
- Enable the "Copilot Suggestions" in your settings
- Start typing code and watch for yellow/red highlights indicating potential issues
- When you see a suggestion, press Tab to accept it or Ctrl+Enter to see alternatives
For beginners, start with simple projects and gradually increase complexity as you become comfortable with the suggestions.
2. ChatGPT for Code Analysis
While not specifically designed for code review, ChatGPT (especially GPT-4) excels at understanding and analyzing code. Here's how to use it effectively:
Step-by-Step ChatGPT Bug Finding Workflow:
- Prepare your code snippet: Copy the problematic function or class (keep it under 200 lines for best results)
- Craft your prompt: Be specific about what you want analyzed. Example: "Please review this Python function for bugs and suggest fixes. Focus on edge cases and potential runtime errors."
- Include context: Mention the programming language, libraries used, and what the code is supposed to do
- Ask specific questions: Instead of "find bugs," ask "what edge cases might cause this function to fail?"
- Iterate: Based on ChatGPT's response, ask follow-up questions about specific suggestions
Remember that ChatGPT might not have access to your entire codebase context, so provide relevant information about data structures and dependencies.
3. Free AI-Powered Code Review Tools
Several excellent free tools can help you get started without financial commitment:
- SonarQube with AI plugins: Open-source platform with machine learning-based rule suggestions
- CodeRabbit: Free tier for small repositories with AI-powered review comments
- DeepSource: AI-driven analysis with focus on security and performance bugs
- Snyk Code: Free for open source projects with AI-powered vulnerability detection
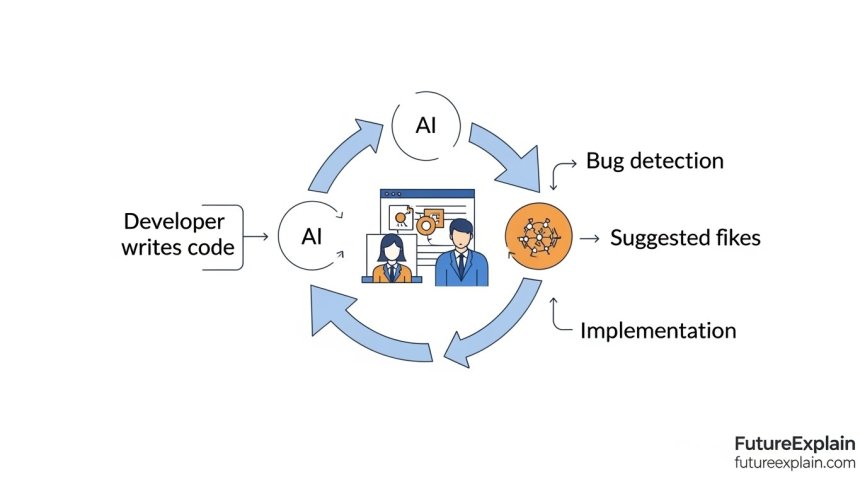
Practical AI Bug Fixing Workflows
Workflow 1: Real-Time AI-Assisted Debugging
This workflow integrates AI directly into your coding process:
- Write code normally in your IDE with AI assistance enabled
- When you encounter an error, highlight the problematic section
- Ask your AI assistant: "What's wrong with this code?" or "How do I fix this error?"
- Review suggestions and understand why they work
- Test the fix before committing changes
This approach is particularly effective for syntax errors, type mismatches, and common logical errors.
Workflow 2: Batch Code Review with AI
For reviewing larger code changes or entire files:
- Prepare your changes in a separate branch or local copy
- Use AI review tools like GitHub Copilot Chat or dedicated review platforms
- Ask specific review questions: "Are there any security vulnerabilities in this authentication code?"
- Categorize findings by severity: critical bugs, improvements, style issues
- Implement fixes gradually, starting with the most critical issues
This workflow works well for pull requests and regular code maintenance.
Workflow 3: Learning from AI-Suggested Fixes
Beyond just fixing bugs, you can use AI suggestions to improve your coding skills:
- When AI suggests a fix, don't just accept it blindly
- Analyze why the suggested fix works better
- Research the pattern if it's unfamiliar to you
- Add to your knowledge base of common bug patterns and fixes
- Apply the learning to prevent similar bugs in future code
Common Bug Patterns AI Excels At Detecting
AI tools are particularly good at identifying certain types of bugs:
1. Null Reference and Boundary Issues
AI can track variable initialization and usage patterns to catch potential null reference errors before they cause runtime crashes. For example:
- Variables that might be used before initialization
- Array indices that could go out of bounds
- Missing null checks for function returns
2. Resource Leaks and Cleanup Issues
Memory leaks, unclosed file handles, and database connections left open are common issues that AI can help identify by analyzing resource acquisition and release patterns.
3. Security Vulnerabilities
AI trained on security bug patterns can identify:
- SQL injection possibilities
- Cross-site scripting vulnerabilities
- Insecure direct object references
- Weak cryptography implementations
4. Performance Anti-patterns
Inefficient algorithms, unnecessary computations, and suboptimal data structures can be flagged by AI analyzing code patterns against known performance best practices.
Advanced Techniques: Training AI on Your Codebase
While pre-trained AI models are useful, you can achieve better results by customizing them for your specific codebase:
1. Contextual Learning with GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot learns from your coding patterns over time. To accelerate this learning:
- Keep your codebase organized and consistent
- Use clear naming conventions
- Accept suggestions that match your style
- Reject suggestions that don't fit your patterns
2. Creating Custom Rules with SonarQube
For teams with specific quality requirements, you can train SonarQube's AI to recognize patterns unique to your projects:
- Identify common bug patterns in your historical data
- Create custom rules based on these patterns
- Train the model with examples and counter-examples
- Continuously refine based on new bug discoveries
3. Building Your Own AI Assistant with OpenAI API
For advanced users, you can create a specialized bug-finding assistant:
- Collect examples of bugs from your codebase
- Fine-tune a model on these examples
- Create a custom interface for your team
- Continuously update with new bug patterns

Limitations and When to Trust (or Question) AI Suggestions
While AI tools are powerful, they're not infallible. Understanding their limitations is crucial for effective use:
Common Limitations of AI Bug Detection:
- Context blindness: AI might not understand your specific business logic
- False positives: Sometimes flags correct code as problematic
- False negatives: Might miss complex, domain-specific bugs
- Security concerns: Be careful about sending proprietary code to cloud services
- Over-reliance risk: Can hinder learning if used as a crutch
Best Practices for Critical Review:
- Always understand why a fix works before implementing it
- Test thoroughly after applying AI suggestions
- Maintain human review for critical systems
- Use multiple tools to cross-verify findings
- Keep learning traditional debugging skills alongside AI tools
Integrating AI Bug Fixing into Team Workflows
For teams adopting AI tools, consider these integration strategies:
1. Establish Team Guidelines
- Which AI tools are approved for use
- When to use AI vs. human review
- How to document AI-assisted fixes
- Security protocols for code sharing
2. Create a Blended Review Process
Combine AI and human review effectively:
- AI performs initial scan for obvious issues
- Human reviewer focuses on complex logic and business rules
- AI checks for consistency and style compliance
- Final human approval for critical changes
3. Track Effectiveness Metrics
Measure how AI is helping your team:
- Bugs caught earlier in development cycle
- Time saved on debugging and review
- Code quality metrics improvement
- Team satisfaction with AI assistance
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Example 1: Catching a Subtle Race Condition
A developer was building a multi-threaded application and wrote code that seemed correct. GitHub Copilot highlighted a potential race condition in resource access that wasn't obvious during manual review. The AI suggested adding proper synchronization, preventing what could have been a difficult-to-reproduce bug in production.
Example 2: Security Vulnerability Prevention
In a web application, ChatGPT identified that user input was being directly concatenated into SQL queries. It suggested parameterized queries and provided specific implementation examples, preventing potential SQL injection attacks.
Example 3: Performance Optimization
An AI code review tool analyzed a data processing script and identified that the same calculation was being performed multiple times in a loop. It suggested moving the invariant calculation outside the loop, resulting in a 40% performance improvement.
Getting Started: Your First Week with AI Bug Fixing
Here's a practical plan for your first week with AI-assisted bug fixing:
Day 1-2: Tool Setup
- Install GitHub Copilot or similar tool in your IDE
- Try ChatGPT for simple code questions
- Explore one free code review tool
Day 3-4: Practice on Small Projects
- Use AI while writing new code
- Ask for reviews on simple functions
- Practice understanding AI suggestions
Day 5-7: Integrate into Workflow
- Use AI for actual bug fixing tasks
- Compare AI findings with your own analysis
- Start documenting effective prompts and techniques
Future Trends in AI Bug Detection
The field of AI-assisted programming is rapidly evolving. Here's what to expect in the near future:
- More contextual understanding: AI that understands your entire project, not just snippets
- Proactive bug prevention: Suggestions that prevent bugs before you write problematic code
- Integration with testing: AI that suggests test cases based on code analysis
- Personalized learning: Tools that adapt to your specific skill level and learning style
Conclusion: Embracing AI as a Programming Partner
AI for bug fixing and code reviews represents a significant shift in how we develop software. These tools aren't replacing developers but rather augmenting our capabilities, allowing us to focus on creative problem-solving while AI handles routine error detection and correction.
The key to success is viewing AI as a partner in your development journey. Start with simple integrations, learn the strengths and limitations of different tools, and gradually incorporate more advanced techniques as you become comfortable. Remember that the goal isn't to eliminate human judgment but to enhance it with AI-powered insights.
As you begin using AI for bug fixing, you'll likely find that you not only write better code faster but also develop a deeper understanding of common programming pitfalls and best practices. The learning feedback loop between you and your AI tools can accelerate your growth as a developer in ways that traditional learning methods alone cannot match.
Further Reading
- Code Writing with AI: Copilots, Assistants, and Tools Compared
- Best Automation Tools for Non-Technical Users
- How to Start Learning AI Without a Technical Background
Ready to transform your debugging workflow? Start today with one tool from this guide, and experience how AI can make you a more efficient and effective programmer.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
1420
Like
1420
 Dislike
12
Dislike
12
 Love
340
Love
340
 Funny
45
Funny
45
 Angry
8
Angry
8
 Sad
3
Sad
3
 Wow
210
Wow
210
















The "your first week" plan helped me overcome analysis paralysis. Just starting with one tool made all the difference.
I work in game development. AI tools are catching physics calculation errors and rendering bugs that are hard to spot manually.
The article structure is perfect: theory → tools → workflows → examples → future. More technical articles should follow this format.
How do these tools handle code comments and documentation? Can AI help keep docs in sync with code changes?
Yes! Copilot can generate docstrings and even update comments when you refactor code. It's not perfect but saves a ton of documentation time.
The security vulnerability examples convinced our compliance team. We're now requiring AI review for all auth-related code.
The article doesn't mention cost enough. Some of these tools get expensive fast for larger teams.
Valid concern about costs, Levi. For teams: 1) Start with free tiers to prove value 2) Look at per-developer pricing vs. seat-based 3) Consider open-source alternatives 4) Negotiate enterprise deals for 50+ users 5) Calculate ROI - if a tool saves 5 hours/week per developer at $50/hour, it pays for itself quickly. We'll cover cost optimization in article #53!