AI for E-commerce: Product Images, Recommendations and SEO
This guide explains how artificial intelligence is transforming three core areas of e-commerce: visual content, customer engagement, and visibility. You will learn how AI tools can automatically generate and edit product images, create personalized recommendation systems that boost sales, and optimize website content for search engines. We break down the machine learning concepts behind these technologies—such as generative AI, neural networks, and natural language processing—into simple, non-technical terms. The article provides practical steps for small business owners and marketers to start implementing AI, discusses important ethical considerations like bias and transparency, and explores future trends that will shape the online shopping experience. Whether you're looking to reduce photoshoot costs, increase average order value, or improve your search rankings, this guide offers a clear, actionable roadmap for leveraging AI in your e-commerce strategy.

If you run an online store, you’ve probably heard that artificial intelligence (AI) is a must-have. But what does that actually mean for your day-to-day operations? Beyond the buzzwords, AI is a set of powerful tools that can solve very specific, expensive, and time-consuming problems in e-commerce.
This guide will walk you through how AI is practically applied in three critical areas: creating and managing product visuals, understanding what your customers want to buy next, and making your store visible to search engines. We will demystify the technology in simple terms, show you how it works, and provide a realistic path for getting started.
Understanding the AI Foundation for E-commerce
Before we dive into product images and recommendations, it’s helpful to understand what we mean by "AI" in this context. At its core, AI in e-commerce is about using data and algorithms to automate decisions and create content that would normally require human effort.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad field of creating machines or software that can perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence, such as recognizing patterns, making predictions, or generating content[citation:1]. For online businesses, this isn't about sentient robots; it's about practical software tools.
These tools are often built using two key approaches:
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI where systems learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed for every rule[citation:9]. Think of it as software that gets better at a task the more data it processes. This is the engine behind personalized recommendations and demand forecasting.
- Deep Learning: A more advanced subset of machine learning inspired by the structure of the human brain, using artificial neural networks[citation:3]. These multi-layered networks are excellent at handling complex, unstructured data like images, audio, and text[citation:9]. This technology powers advanced image generation and sophisticated natural language processing for SEO.
With this foundation, let's explore how these technologies translate into tangible tools for your online business.
Revolutionizing Visuals: AI for Product Images
High-quality visuals are non-negotiable in e-commerce, but professional photography is costly and time-intensive. AI is changing this by assisting in every stage of the visual lifecycle.
AI-Generated Product Photography
Generative AI models, particularly diffusion models and transformers, can create photorealistic images from text descriptions[citation:9]. For a merchant, this means you can type "a minimalist black ceramic mug on a marble tabletop with morning light" and receive a high-fidelity image suitable for your listing.
This is not simple copy-paste. These models are trained on massive datasets of images and their text descriptions, learning intricate patterns of how light reflects, how textures appear, and how objects relate[citation:5]. The "generative" part means they create new, original compositions based on this learned understanding.
How it works in practice: Platforms like Midjourney, DALL-E, or specialized e-commerce tools use this technology. You provide a prompt—a detailed text description. The AI model interprets this prompt, referencing its vast training to synthesize a new image pixel-by-pixel. The best platforms allow for iterative refinement: you can say "make the background lighter" or "add a plant in the corner," and the AI adjusts the image accordingly.
Primary Benefits:
- Cost Reduction: Eliminates the need for photoshoots, studios, photographers, and physical samples for every product variant (e.g., a t-shirt in 10 colors).
- Speed & Scalability: Generate hundreds of lifestyle images or product variations in minutes, crucial for large catalogs or rapid testing.
- Consistency: Maintain a uniform aesthetic (lighting, angle, background) across all product images, which is often challenging in manual photography.
AI-Powered Image Editing and Enhancement
Beyond generation, AI dramatically simplifies editing. Tools can now automatically:
- Remove and Replace Backgrounds: Instantly isolate a product and place it on any background you choose.
- Upscale Resolution: Enlarge small or low-quality images without the blurry pixelation of traditional methods, making older photos usable.
- Correct Color and Lighting: Automatically adjust white balance and exposure to make product colors appear true-to-life.
- Create Model Avatars: Generate diverse human models wearing your apparel, allowing for inclusive representation without organizing a full-scale shoot.
These tools often use a type of deep learning called convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which are specifically designed to process visual data by recognizing features like edges, textures, and shapes[citation:10].
Visuals Produced by AI
The Personalization Engine: AI for Product Recommendations
Personalized recommendations are the single most effective tool for increasing average order value and customer loyalty. Modern systems move far beyond "customers who bought this also bought..."
How Recommendation Algorithms Learn
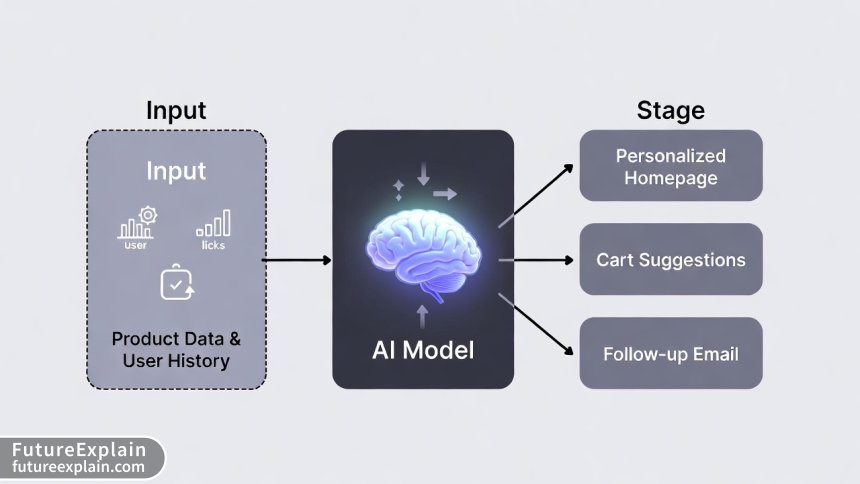
At its heart, a recommendation system is a prediction engine. It uses historical data to predict what a specific user is most likely to want next. This is primarily achieved through machine learning[citation:4].
The system is trained on two main types of data:
- Explicit Data: Clear actions like past purchases, product ratings, and "add to cart" events.
- Implicit Data: Behavioral signals like time spent on a product page, click-through rates on emails, search queries within the store, and scroll depth.
The AI models find complex, non-obvious patterns in this data. For example, it might learn that users who buy specialty coffee beans and click on articles about pour-over techniques are highly likely to be interested in a new brand of gooseneck kettles within the next 30 days—even if they’ve never viewed a kettle before.
Types of Recommendation Systems
- Collaborative Filtering: This method predicts your interests by collecting preferences from many users ("the wisdom of the crowd"). If User A and User B have similar purchase histories, the system will recommend to User A items that User B liked but User A hasn't seen. It works without needing to know anything about the products themselves.
- Content-Based Filtering: This method recommends items similar to those a user has liked in the past, based on product features (tags, categories, descriptions, image attributes). If you bought a raincoat, it might recommend other waterproof jackets.
- Hybrid Models: The most advanced and effective systems combine collaborative and content-based filtering, along with other signals like context (time of day, device used) and real-time session behavior. This often involves deep learning models that can process all these data types simultaneously for a highly accurate prediction[citation:3].
These hybrid models frequently rely on neural networks that can take in diverse data (user ID, product metadata, timestamps) and learn a unified representation, or embedding, of both users and products in a shared mathematical space. Items located close to a user in this space become the recommendations.
Visuals Produced by AI
Where to Deploy Recommendations
Effective personalization is omnichannel:
- On-Site: "Recommended for you" on the homepage, product pages, and cart page.
- Email & Retargeting Ads: "Back in stock" alerts or "You might have missed" emails featuring personalized products.
- Post-Purchase: Suggesting complementary products in order confirmation emails or on the "thank you" page.
Winning Search Traffic: AI for E-commerce SEO
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) ensures potential customers can find your products. AI assists by automating research, optimizing content, and understanding user intent at scale.
AI-Powered Keyword and Market Research
Tools using natural language processing (NLP)—a branch of AI that helps computers understand human language[citation:1]—can analyze millions of search queries to uncover opportunities.
- They identify long-tail keyword phrases (e.g., "women's waterproof hiking boots wide width") that have lower competition but high purchase intent.
- They cluster topics and questions that real shoppers are asking around your product category, informing your content strategy.
- They analyze competitor listings at scale to reverse-engineer what search engines are rewarding for specific terms.
Automating and Optimizing Product Content
Creating unique, compelling descriptions for thousands of products is a monumental task. AI can help generate, expand, and optimize this content.
Large Language Models (LLMs) like those powering ChatGPT are trained on massive text datasets and can generate human-like text[citation:5]. In e-commerce, they can:
- Draft Product Descriptions: Provide key features and benefits, and the AI can write multiple versions tailored for different tones (technical, luxurious, eco-friendly).
- Create Meta Tags: Automatically generate persuasive page titles and meta descriptions that include target keywords, improving click-through rates from search results.
- Generate Structured Data (Schema Markup): Create the code that helps search engines understand your product's price, availability, and reviews, making you eligible for rich results like product snippets.
A Critical Caveat: Hallucinations. LLMs can sometimes generate plausible-sounding but incorrect or fabricated information—a phenomenon known as "hallucination"[citation:5][citation:6]. AI-generated content must always be reviewed, fact-checked, and edited by a human. It is a powerful drafting assistant, not a replacement for human oversight.
Technical SEO and User Experience Insights
AI can also monitor your site's health and user experience signals, which are increasingly important for search rankings:
- Crawl budget optimization by identifying and prioritizing important pages for search engines to index.
- Analysis of user behavior metrics (like bounce rate and time on page) to pinpoint pages that may be underperforming due to content or UX issues.
Getting Started: A Practical Implementation Roadmap
Adopting AI doesn't require a Ph.D. or a massive budget. A strategic, phased approach is key.
Phase 1: Audit and Identify (Weeks 1-2)
- Pinpoint the Pain Point: Where is the biggest bottleneck or cost? Is it producing images for 500+ SKUs? Is your conversion rate low because recommendations are generic? Is your organic traffic stagnant?
- Audit Your Data: AI feeds on data. Do you have clean, structured product data? Are you tracking user behavior (clicks, views, cart additions)? Start collecting and organizing this data.
Phase 2: Explore and Experiment (Weeks 3-8)
- Start with Point Solutions: Don't try to build a custom AI model. Use existing SaaS platforms.
- For Images: Test a tool like Midjourney or Canva's AI features to generate lifestyle images for a new product line.
- For Recommendations: Most modern e-commerce platforms (Shopify Plus, BigCommerce) have built-in or app-based recommendation engines. Activate it and monitor its performance.
- For SEO: Use a tool like SurferSEO, MarketMuse, or Frase that uses AI to analyze content and suggest optimizations.
- Run Controlled Tests: For recommendations, run an A/B test showing AI-powered recommendations vs. your old "top sellers" list. For images, test AI-generated photos against traditional photos on a product page and track conversion rate.
Phase 3: Integrate and Scale (Months 3+)
- Based on experiment results, integrate the winning solutions into your core workflows.
- Consider more advanced, connected platforms that offer a suite of AI tools (e.g., a customer data platform with integrated personalization).
- Continuously measure KPIs: Conversion rate, average order value, return on ad spend (for dynamic product ads), and organic traffic growth.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Use
As you implement AI, it's crucial to do so responsibly. The models are only as good as the data they're trained on, and that data can contain human biases[citation:5].
- Bias in Recommendations: If your historical sales data is skewed (e.g., primarily featuring models of one ethnicity), an AI trained on that data may perpetuate that bias by disproportionately recommending those products. Actively curate training data and outputs for diversity and fairness.
- Transparency with AI-Generated Content: Should you disclose if a product image is AI-generated? While not always legally required, transparency can build trust with certain customer segments. Consider clear labels for "digital model" or "AI-generated visual."
- Data Privacy: Personalization relies on user data. Be explicit in your privacy policy about how you use data for recommendations and ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Use privacy-preserving techniques where possible, such as on-device processing or federated learning[citation:8].
- Job Impact & Human-in-the-Loop: AI is a tool for augmentation. It automates repetitive tasks (background removal, drafting descriptions) freeing your team to focus on higher-value creative strategy, complex customer service, and ethical oversight of the AI's outputs.
The Future of AI in E-commerce
The trajectory points towards more integrated, conversational, and immersive experiences.
- AI Shopping Agents: Moving beyond chatbots, future AI agents will act autonomously on behalf of users[citation:9]. A customer could say, "Find me a comfortable sofa under $1,500 that fits my modern living room dimensions and is available within two weeks." The AI agent would search across multiple stores, compare specs, check inventory, and present a shortlist.
- Hyper-Personalized and Generative Stores: Imagine a storefront that dynamically regenerates for each visitor—showing entirely different products, images, and promotions based on that user's unique profile and intent in real-time.
- Voice and Visual Search Dominance: AI will power more accurate searches using spoken language or images snapped from the real world ("find a chair like this one").
- Regulation and Standardization: As AI's role grows, so will regulatory scrutiny aimed at ensuring safety, transparency, and accountability[citation:8]. Proactively adopting ethical guidelines will be a competitive advantage.
Implementing AI in e-commerce is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day competitive necessity. By starting with a clear understanding of the foundational technologies—machine learning for recommendations, generative AI for visuals, and NLP for SEO—you can make informed decisions. Begin with a specific, high-impact problem, experiment with accessible tools, measure the results rigorously, and always maintain a human-centric, ethical approach. The goal is not to replace human creativity and judgment, but to amplify it, creating more efficient operations and more engaging, personalized experiences for every customer.
Further Reading
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
1420
Like
1420
 Dislike
12
Dislike
12
 Love
310
Love
310
 Funny
45
Funny
45
 Angry
8
Angry
8
 Sad
5
Sad
5
 Wow
205
Wow
205



















Just finished a test using an AI tool to generate meta descriptions for 500 old product pages. The time saved was immense, and we've already seen a lift in CTR from search. The ROI was almost immediate.
As a backend developer, I appreciate that the article correctly explained concepts like embeddings and neural networks without dumbing them down. It respects the reader's intelligence.
Clear and actionable. More articles like this, please. The tech world needs less hype and more clear 'how-to' guides.
Implemented the Phase 1 audit after reading this. Realized our biggest pain point wasn't images or SEO, but cart abandonment. Looking into AI tools that personalize the cart page with recommendations now. Thanks for the framework!
The comment thread here is almost as valuable as the article itself! So many practical insights and warnings from people who've tried this.
A question on ethics: if an AI generates a product image, who owns the copyright? The user who wrote the prompt? The company that made the AI? This feels like a legal grey area for commercial use.
Sophie, you've identified one of the most contentious and unresolved legal questions in AI today. Copyright ownership for AI-generated works varies by jurisdiction and platform terms of service. Some countries deny copyright to non-human creators, while others are evaluating the level of human input required. As of early 2025, the safest commercial practice is to: 1) Thoroughly read the Terms of Service of the AI tool you use, 2) Consider tools that explicitly grant commercial license to outputs, and 3) Consult with a legal professional for major campaigns. This area of law is evolving rapidly[citation:8].