Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) — Advanced Practical Guide
This advanced practical guide to Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) moves beyond basic tutorials to production-ready implementation patterns for 2025. We cover advanced RAG architectures, hybrid search strategies combining vector, keyword, and filtering approaches, and practical deployment considerations including cost optimization and scaling. Learn to implement effective chunking strategies, handle multi-modal documents, optimize retrieval precision, and monitor RAG systems in production. Includes real-world patterns for reducing hallucinations, improving answer quality, and troubleshooting common RAG failures. Whether you're building enterprise chatbots, document assistants, or knowledge management systems, this guide provides the advanced techniques needed for successful RAG deployment.

Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) — Advanced Practical Guide
Retrieval-Augmented Generation has rapidly evolved from an academic concept to a production necessity for building reliable, knowledge-grounded AI applications. While basic RAG tutorials abound, real-world deployment requires navigating complex trade-offs, optimization strategies, and scaling considerations. This advanced guide moves beyond "hello world" examples to provide practical patterns for building production-ready RAG systems in 2025.
RAG fundamentally addresses the core limitation of large language models: their static knowledge cutoff and tendency to hallucinate facts. By retrieving relevant information from external knowledge bases and injecting it into the LLM's context window, RAG systems can provide accurate, up-to-date responses grounded in verifiable sources. However, the simplicity of this concept belies the complexity of implementation. This guide will walk you through advanced patterns, common pitfalls, and optimization strategies that separate proof-of-concepts from production systems.
Understanding the Advanced RAG Architecture
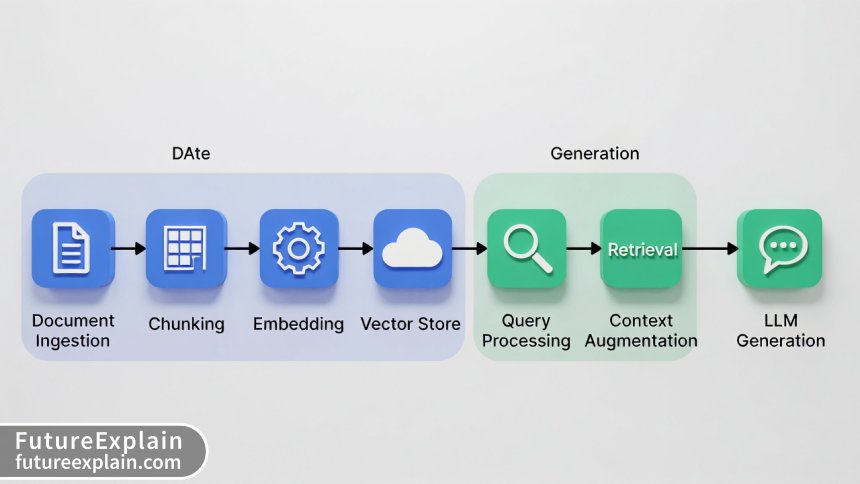
At its core, RAG consists of two main phases: retrieval and generation. The retrieval phase finds relevant documents or document chunks from a knowledge base, while the generation phase uses this retrieved context along with the user's query to produce a coherent answer. However, production systems require more sophisticated architectures.
Beyond Basic RAG: Advanced Patterns
Simple RAG implementations often suffer from several limitations: they retrieve irrelevant documents, miss crucial context due to poor chunking, fail to handle complex queries, and struggle with scaling. Advanced RAG addresses these through several patterns:
- Recursive Retrieval: Instead of single-pass retrieval, this pattern performs multiple retrieval passes, refining the query based on initial results to improve relevance.
- Hybrid Search: Combining vector similarity search with traditional keyword matching and metadata filtering for improved recall.
- Query Expansion and Rewriting: Automatically expanding or rewriting user queries to improve retrieval effectiveness.
- Multi-Hop Reasoning: Breaking complex questions into sub-queries and retrieving information for each step.
- Contextual Compression: Reducing retrieved context to only the most relevant portions before sending to the LLM.
Document Processing Pipeline Design
The quality of your RAG system begins with document processing. Poor preprocessing leads to poor retrieval, regardless of how sophisticated your search algorithms become.
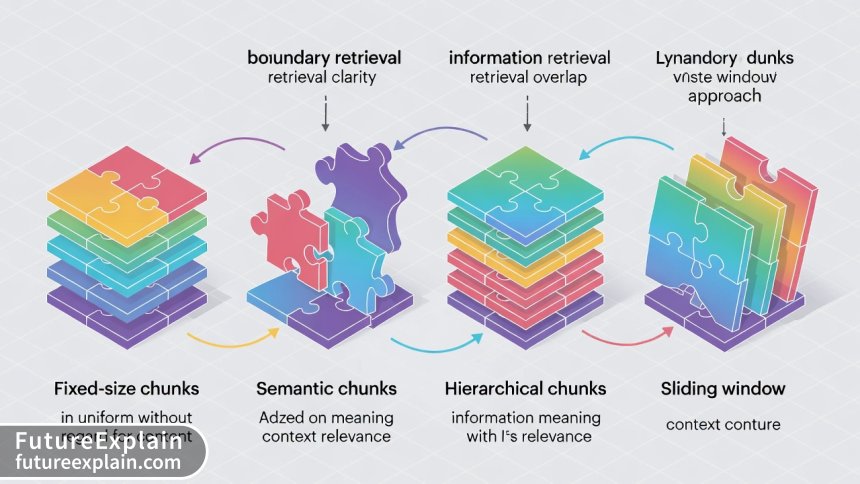
Advanced Chunking Strategies
Fixed-size chunking (e.g., 512 tokens) is common in tutorials but often suboptimal for real documents. Advanced strategies include:
- Semantic Chunking: Using embeddings or semantic analysis to chunk at natural boundaries (paragraphs, sections, topics).
- Hierarchical Chunking: Creating multiple chunk sizes with parent-child relationships for different retrieval scenarios.
- Overlapping Chunks: Implementing sliding windows with configurable overlap to preserve context across boundaries.
- Content-Aware Chunking: Different strategies for different content types (code, tables, prose, lists).
Metadata Engineering
Effective metadata transforms simple document retrieval into intelligent information access. Beyond basic metadata (date, author, source), consider:
- Document type and structure indicators
- Topic classifications and key phrases
- Entity mentions (people, organizations, locations)
- Document quality scores or confidence indicators
- Temporal relevance markers for time-sensitive information
Metadata enables powerful filtering and boosting during retrieval, significantly improving relevance. For example, you might prioritize recent documents for time-sensitive queries or technical documents for engineering questions.
Embedding Models and Vector Stores Selection
Choosing appropriate embedding models and vector databases significantly impacts system performance and accuracy.
Embedding Model Considerations for 2025
While OpenAI's text-embedding-ada-002 remains popular, 2025 brings more specialized options:
- Task-Specific Embeddings: Models fine-tuned for specific domains (legal, medical, technical).
- Multilingual Embeddings: Models that handle multiple languages in a shared embedding space.
- Instruction-Tuned Embeddings: Models that understand embedding instructions for better task alignment.
- Small but Effective Models: Efficient models like GTE-small that balance performance and cost.
When evaluating embedding models, consider not just benchmark performance but also:
- Inference latency and throughput requirements
- Cost per embedding (critical at scale)
- Context window limitations
- Batch processing capabilities
Vector Database Selection Matrix
The vector database landscape has matured significantly. Selection criteria should include:
| Database | Best For | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Pinecone | Managed service, quick startup | Vendor lock-in, cost at scale |
| Weaviate | Hybrid search, GraphQL interface | Self-hosting complexity |
| Qdrant | Performance, Rust-based | Younger ecosystem |
| Chroma | Local development, simplicity | Production scaling challenges |
| Redis with Redisearch | Existing Redis infrastructure | Advanced configuration needed |
| PostgreSQL with pgvector | SQL integration, ACID compliance | Performance at extreme scale |
Hybrid Search Implementation
Pure vector search excels at semantic similarity but can miss exact matches or struggle with specific terminology. Hybrid search combines multiple approaches for optimal results.
Three-Pillar Hybrid Approach
An effective hybrid search implementation typically combines:
- Vector Similarity Search: For semantic understanding and conceptual matching
- Keyword/BMM25 Search: For exact term matching and traditional information retrieval
- Metadata Filtering: For precision based on document attributes
The challenge lies in effectively combining these scores. Common approaches include:
- Weighted Combination: Assigning weights to each score type based on query analysis
- Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF): Combining rankings without requiring score normalization
- Learning to Rank (LTR): Training a model to predict optimal combinations
Query Understanding and Routing
Advanced RAG systems analyze queries to determine the optimal retrieval strategy:
- Factual Queries: May benefit from keyword-heavy approaches
- Conceptual Queries: Prioritize vector similarity
- Complex Multi-Part Queries: May require decomposition and multi-hop retrieval
- Temporal Queries: Heavily weight recency filters
Implementing query classification allows dynamic adjustment of retrieval parameters, significantly improving relevance.
Retrieval Optimization Techniques
Even with perfect document processing and hybrid search, retrieval can be optimized further.
Re-Ranking Strategies
Initial retrieval often returns more candidates than needed. Re-ranking refines these results:
- Cross-Encoder Re-rankers: Models like BGE-reranker that evaluate query-document pairs more accurately than embeddings alone
- LLM-based Re-ranking: Using lightweight LLMs to score relevance (more expensive but potentially more accurate)
- Multi-stage Retrieval: Broad retrieval followed by precision-focused re-ranking
When implementing re-ranking, consider the cost-benefit trade-off. Cross-encoders typically add 50-200ms latency but can improve top-1 accuracy by 10-30%. For high-stakes applications, this trade-off is often justified.
Contextual Compression and Relevance Filtering
Retrieved documents often contain irrelevant sections. Contextual compression extracts only the most relevant portions:
- Extractive Compression: Identifying and extracting key sentences or passages
- Abstractive Compression: Summarizing retrieved content (more computationally intensive)
- Selective Inclusion: Including full documents only when confidence is high
This reduces token usage (lower cost, faster inference) and often improves answer quality by reducing noise.
Generation Phase Optimization
The generation phase transforms retrieved context into coherent answers. Optimization here focuses on prompt engineering and LLM selection.
Advanced Prompt Patterns for RAG
Beyond simple "context + question" prompts, effective patterns include:
- Instruction Positioning: Placing instructions before context to improve adherence
- Context Prioritization: Ordering retrieved documents by relevance in the prompt
- Citation Requirements: Explicitly requiring citations to specific sources
- Uncertainty Acknowledgment: Teaching the LLM to acknowledge when context is insufficient
- Format Constraints: Specifying output formats (bullet points, structured data, etc.)
LLM Selection and Configuration
Different LLMs excel at different RAG tasks:
- GPT-4/GPT-4 Turbo: Strong reasoning, good instruction following, higher cost
- Claude 3 Series: Excellent long-context handling, strong compliance
- Open Source Models (Llama 3, Mixtral): Cost-effective, customizable, varying capabilities
- Specialized Models: Domain-specific models for technical, medical, or legal content
Consider implementing model routing based on query complexity, domain, and cost constraints.
Production Deployment Considerations
Moving from prototype to production introduces new challenges around scalability, monitoring, and reliability.
Scalability Patterns
RAG systems scale along multiple dimensions:
- Document Volume: From thousands to millions of documents
- Query Throughput: From occasional to thousands of queries per second
- Update Frequency: From static to real-time document updates
Architectural patterns for scaling include:
- Sharding Strategies: Partitioning vector stores by topic, time, or other dimensions
- Caching Layers: Caching embeddings, retrieval results, and generated responses
- Async Processing Pipelines: For document ingestion and embedding generation
- Load Balancing and Replication: For high availability
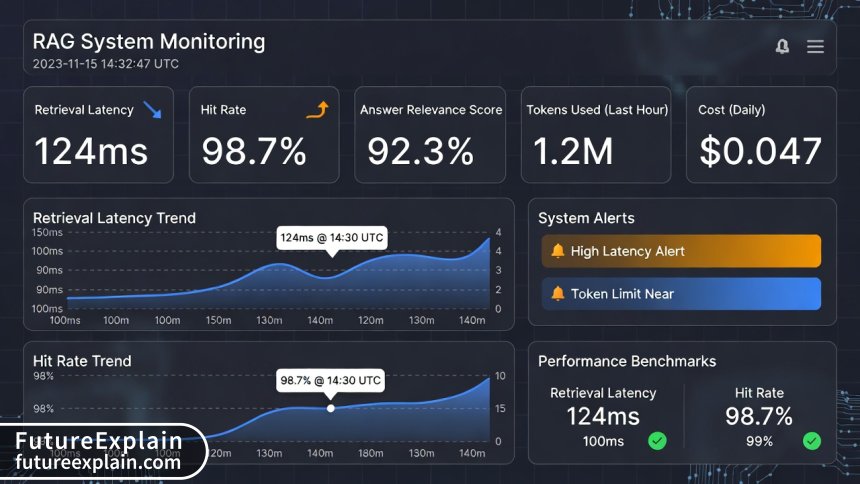
Monitoring and Observability
Production RAG systems require comprehensive monitoring:
- Retrieval Metrics: Hit rate, precision@k, mean reciprocal rank
- Generation Metrics: Answer relevance, faithfulness to sources, hallucination rate
- Performance Metrics: End-to-end latency, token usage, cost per query
- Business Metrics: User satisfaction, task completion rate
Implement structured logging to trace queries through the entire pipeline, enabling debugging and optimization.
Cost Optimization Strategies
RAG costs can escalate quickly with scale. Effective optimization addresses multiple cost centers:
Embedding Cost Management
- Batch Processing: Processing documents in large batches during off-peak hours
- Incremental Updates: Only re-embedding changed portions of documents
- Caching Strategies: Caching embeddings for repeated queries or similar documents
- Model Selection: Choosing cost-effective embedding models without significant quality loss
LLM Inference Cost Reduction
- Context Minimization: Sending only necessary context through careful retrieval and compression
- Model Tier Selection: Using lighter models for simpler queries
- Response Caching: Caching identical or similar responses
- Token Usage Optimization: Monitoring and optimizing prompt construction
Privacy and Security Considerations
RAG systems often handle sensitive information, requiring careful security implementation.
Data Protection Patterns
- On-Premises Deployment: Keeping embeddings and vector stores within controlled infrastructure
- Encryption Strategies: Encrypting data at rest and in transit
- Access Controls: Document-level and field-level access restrictions
- Audit Logging: Comprehensive logging of data access and usage
Compliance Considerations
Different regulations impose different requirements:
- GDPR/Privacy Laws: Right to be forgotten, data minimization
- Industry Regulations: HIPAA for healthcare, FINRA for finance
- Internal Policies: Data retention, usage restrictions
Design systems with compliance in mind from the beginning, as retrofitting can be challenging.
Troubleshooting Common RAG Issues
Even well-designed RAG systems encounter issues. A systematic troubleshooting approach is essential.
Poor Retrieval Quality
When retrieval fails to find relevant documents:
- Check embedding quality on your specific domain
- Evaluate chunking strategy - chunks may be too large/small or at wrong boundaries
- Test query expansion techniques
- Consider hybrid search if using pure vector search
- Examine metadata usage for filtering issues
Hallucinations Despite Retrieved Context
When LLMs ignore or misinterpret retrieved context:
- Test prompt engineering variations (instruction positioning, citation requirements)
- Reduce context length to minimize distraction
- Implement context prioritization (most relevant first)
- Consider different LLMs with better instruction following
- Add verification steps to check answer against sources
Performance Issues
For latency or throughput problems:
- Profile each pipeline component to identify bottlenecks
- Implement caching at multiple levels
- Consider approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) for faster retrieval
- Batch similar operations where possible
- Scale horizontally based on load patterns
Future Trends and Evolution
RAG technology continues to evolve rapidly. Key trends for 2025 and beyond include:
- Multimodal RAG: Retrieving and reasoning across text, images, audio, and video
- Agentic RAG: RAG systems that can plan, iterate, and use tools
- Federated RAG: Retrieving from distributed, privacy-preserving knowledge sources
- Learning RAG Systems: Systems that improve through feedback and usage
- Specialized Hardware Acceleration: Dedicated hardware for vector operations
Conclusion
Building production-ready RAG systems requires moving beyond basic tutorials to address the complex interplay of retrieval quality, generation accuracy, system performance, and operational costs. The patterns and strategies outlined in this guide provide a foundation for implementing effective RAG systems that deliver real business value.
Successful RAG implementation is iterative: start with a simple implementation, measure performance rigorously, identify bottlenecks, and apply targeted optimizations. Focus on the metrics that matter for your specific use case, whether that's answer accuracy, response latency, cost efficiency, or user satisfaction.
As RAG technology continues to mature, staying informed about new models, tools, and patterns will be essential. The field moves quickly, but the fundamental principles of effective information retrieval and contextual generation remain constant.
Visuals Produced by AI
Further Reading
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
15240
Like
15240
 Dislike
85
Dislike
85
 Love
2310
Love
2310
 Funny
420
Funny
420
 Angry
15
Angry
15
 Sad
8
Sad
8
 Wow
647
Wow
647



















Final thought: this article and the discussion it generated have been more valuable than any conference or course on RAG. Practical, battle-tested advice from real implementers. Thank you all!
We implemented the caching strategies mentioned in comments. Three-layer cache: 1) Query embedding (1 hour), 2) Retrieval results (15 min), 3) Generated answers (5 min for common questions). Massive performance improvement.
The monitoring section made us add anomaly detection for retrieval hit rate. Caught a bug where new documents weren't being indexed properly. Monitoring isn't sexy but it's essential.
The article doesn't mention handling contradictory information in sources. We have documents that conflict. How do others handle this in RAG systems?
Nadira, conflicting sources is challenging. Approaches: 1) Source prioritization (trust scores), 2) Recency bias (newer over older), 3) Present multiple perspectives with citations, 4) Detect conflicts and ask clarifying questions. We're writing a dedicated article on this complex topic!
Update on document updates: we implemented the tiered importance approach. Critical policy docs update real-time, reference material updates nightly. Works perfectly and cuts update costs by 70%.
The cost tracking dashboard template idea saved us thousands. We identified inefficient prompts that were sending too much context. Fixed them and cut costs by 35% with no quality loss.