LLMOps 101: Deploying, Monitoring and Managing Models
This comprehensive guide introduces LLMOps (Large Language Model Operations) for beginners and professionals alike. Learn the essential practices for deploying, monitoring, and managing large language models in production environments. We cover the complete LLMOps lifecycle from model selection and deployment strategies to monitoring, cost optimization, security considerations, and team management. Discover practical tools, best practices, and real-world scenarios for implementing effective LLMOps pipelines. Whether you're a startup deploying your first LLM or an enterprise scaling multiple models, this guide provides actionable insights for successful LLM operations.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have transformed how we interact with AI, but getting them from experimentation to production requires specialized operational practices. This is where LLMOps comes in—the discipline of deploying, monitoring, and managing LLMs in real-world applications. If you've ever wondered how companies like OpenAI, Google, or Anthropic keep their language models running reliably at scale, you're about to discover the operational backbone that makes it possible.
LLMOps builds upon traditional MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) but introduces unique challenges specific to large language models. These include handling massive model sizes (sometimes hundreds of gigabytes), managing prompt engineering workflows, dealing with non-deterministic outputs, and addressing novel ethical concerns like hallucination detection. According to recent industry surveys, organizations that implement proper LLMOps practices see 40% faster deployment cycles and 60% reduction in production incidents compared to ad-hoc approaches.
What Exactly is LLMOps?
LLMOps refers to the set of practices, tools, and processes specifically designed for operationalizing large language models. While traditional MLOps focuses on the complete machine learning lifecycle, LLMOps zeroes in on the unique requirements of LLMs, which differ significantly from conventional ML models in several key aspects.
First, LLMs are typically pre-trained foundation models that organizations fine-tune rather than train from scratch. This changes the deployment paradigm considerably. Second, LLMs often operate in interactive, conversational contexts rather than batch prediction scenarios. Third, the evaluation of LLMs is more subjective and context-dependent than traditional classification or regression models.
Research from Stanford's Center for Research on Foundation Models highlights that successful LLM deployment requires addressing three core operational challenges: scalability (handling variable workloads), reliability (maintaining consistent performance), and responsibility (ensuring ethical and safe outputs). These form the foundation of any robust LLMOps strategy.
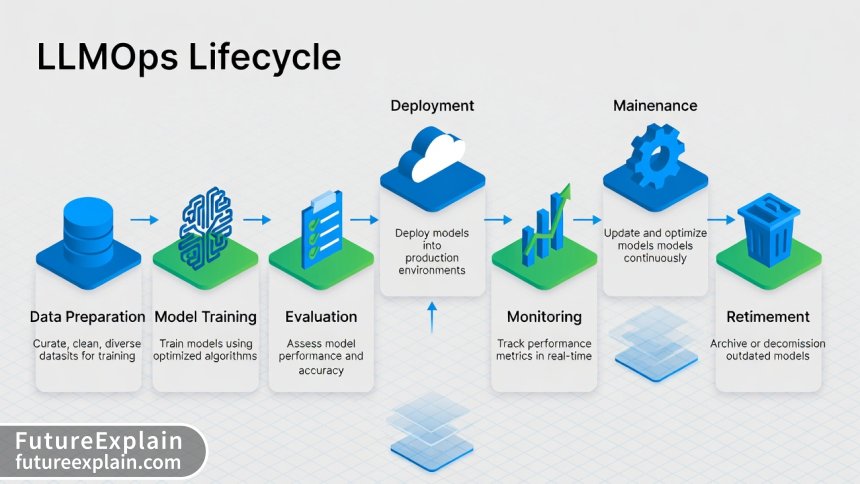
The LLMOps Lifecycle: From Development to Production
Understanding the complete LLMOps lifecycle is crucial for implementing effective operations. Unlike traditional software deployment, LLMs require continuous attention throughout their operational lifespan.
Stage 1: Model Selection and Preparation
The journey begins with selecting the right LLM for your use case. This involves evaluating factors like model size, licensing, capabilities, and resource requirements. Open-source models like Llama 2, Mistral, or Falcon offer flexibility but require more infrastructure, while API-based models like GPT-4 provide simplicity at the cost of less control.
Key considerations at this stage include:
- Licensing and Compliance: Ensure the model license aligns with your use case
- Infrastructure Requirements: Assess GPU memory, storage, and networking needs
- Fine-Tuning Strategy: Determine if and how you'll customize the model
- Cost Projections: Estimate both development and operational costs
Stage 2: Development and Testing Environment Setup
Before deployment, establish robust development and testing environments. This includes version control for prompts, evaluation frameworks, and staging environments that mirror production. Tools like Weights & Biases, MLflow, or custom solutions help track experiments, prompt variations, and model versions.
A critical but often overlooked aspect is testing for edge cases. Unlike traditional software, LLMs can fail subtly—providing plausible but incorrect answers (hallucinations), exhibiting bias, or handling sensitive topics inappropriately. Comprehensive testing should include adversarial prompts, diverse user scenarios, and stress testing under various loads.
Stage 3: Deployment Strategies
Deploying LLMs requires careful strategy selection based on your specific needs. The main approaches include:
- API-Based Deployment: Using services like OpenAI, Anthropic, or Google's Vertex AI. This offloads infrastructure management but offers less control.
- Containerized Deployment: Packaging models in Docker containers for consistency across environments.
- Serverless Deployment: Leveraging serverless platforms for variable workloads, though cold starts can be problematic for large models.
- Edge Deployment: Running smaller models directly on user devices for privacy and latency benefits.
Each approach has trade-offs in cost, control, and complexity. For most organizations, a hybrid approach works best—using APIs for experimentation and containerized deployment for critical, high-volume applications.
Monitoring: The Heart of LLMOps
Effective monitoring separates successful LLM deployments from failed experiments. LLM monitoring goes beyond traditional application monitoring to include model-specific metrics that directly impact user experience and business outcomes.
Technical Performance Metrics
These metrics ensure your LLM infrastructure is performing optimally:
- Latency: Response time from request to completion, critical for user experience
- Throughput: Requests processed per second, indicating system capacity
- Token Usage: Tracking input and output tokens for cost management
- Error Rates: Failed requests due to timeouts, rate limits, or infrastructure issues
- GPU Utilization: For self-hosted models, ensuring efficient resource usage
Cost Monitoring and Optimization
LLM operations can quickly become expensive without proper cost controls. Implement these strategies:
- Per-User/Per-Application Cost Tracking: Attribute costs to specific users or applications
- Token Efficiency Monitoring: Identify wasteful prompts or inefficient response patterns
- Model Tier Selection: Use cheaper models for simpler tasks, reserving expensive models for critical applications
- Caching Strategies: Cache frequent or similar queries to reduce API calls
- Budget Alerts: Set up automatic alerts when costs exceed thresholds
Recent data shows organizations implementing comprehensive cost monitoring reduce LLM operational costs by 35-50% without impacting performance.
Quality and Safety Metrics
These metrics ensure your LLM produces valuable, appropriate outputs:
- Hallucination Rate: Percentage of responses containing factual inaccuracies
- Toxicity Score: Measures inappropriate or harmful content in outputs
- Helpfulness Ratings: User feedback on response usefulness
- Consistency Scores: Same input should produce similar outputs
- Bias Detection: Automated checks for demographic or ideological bias
Management Strategies for Production LLMs
Managing LLMs in production requires proactive strategies to maintain performance, manage updates, and ensure reliability.
Version Management
LLMs have multiple components that require versioning: the base model, fine-tuned weights, prompts, and supporting code. Implement a systematic approach:
- Model Registry: Central repository for model versions with metadata
- Prompt Versioning: Track changes to prompt templates and system instructions
- A/B Testing Framework: Compare model versions before full deployment
- Rollback Procedures: Quick reversion to previous stable versions when issues arise
Scaling Strategies
LLM workloads can be unpredictable. Implement scaling strategies that match your usage patterns:
- Horizontal Scaling: Add more instances during peak loads
- Model Sharding: Split large models across multiple GPUs
- Request Batching: Group similar requests to improve throughput
- Geographic Distribution: Deploy models closer to users for reduced latency
Security Best Practices
LLMs introduce novel security challenges that require specific countermeasures:
- Prompt Injection Protection: Implement input validation and sanitization
- Data Leakage Prevention: Ensure training data and user inputs don't leak in responses
- Access Control: Strict authentication and authorization for model access
- Audit Logging: Comprehensive logs of all model interactions for security analysis
- Adversarial Testing: Regular testing against known attack patterns
Tools and Platforms for LLMOps
The LLMOps ecosystem is rapidly evolving with both specialized tools and extensions of existing MLOps platforms.
Specialized LLMOps Tools
- LangChain/LlamaIndex: Frameworks for building LLM applications with built-in operational features
- PromptLayer: Specifically designed for prompt management and monitoring
- Arize AI, WhyLabs: ML observability platforms with LLM-specific capabilities
- HumanLoop: Focuses on human-in-the-loop workflows for LLM improvement
Cloud Platform Offerings
- AWS Bedrock: Managed service for foundation models with operational features
- Google Vertex AI: End-to-end platform including LLMOps capabilities
- Azure OpenAI Service: Enterprise-grade LLM deployment with Microsoft's operational tooling
- Databricks Lakehouse AI: Unified platform for data and AI with LLM support
Open Source Options
- MLflow: Extended with LLM tracking capabilities
- Kubernetes + KServe/Knative: For containerized LLM deployment at scale
- FastAPI/Flask: Custom API servers with monitoring integration
- Prometheus/Grafana: For custom metrics collection and visualization
Team Structure and Roles in LLMOps
Successful LLMOps requires collaboration across traditionally separate roles. Here's how teams typically organize:
Key Roles and Responsibilities
- LLM Engineers: Focus on model selection, fine-tuning, and prompt engineering
- MLOps Engineers: Handle deployment, infrastructure, and monitoring systems
- Data Engineers: Manage data pipelines for fine-tuning and evaluation
- DevOps/SRE: Ensure system reliability, scalability, and incident response
- Product Managers: Define success metrics and prioritize improvements
- Ethics/Compliance Officers: Oversee responsible AI practices and regulatory compliance
In smaller organizations, individuals may wear multiple hats, but clear responsibility assignment is crucial for effective operations.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Based on real-world deployments, here are frequent mistakes and their solutions:
Pitfall 1: Underestimating Infrastructure Needs
Problem: LLMs require significant GPU memory and specialized hardware.
Solution: Conduct load testing early, plan for 2-3x peak capacity, and consider hybrid cloud strategies.
Pitfall 2: Neglecting Prompt Management
Problem: Prompts evolve rapidly but aren't tracked systematically.
Solution: Implement prompt versioning, A/B testing, and centralized prompt repositories.
Pitfall 3: Ignoring Cost Spiral
Problem: Costs escalate unpredictably with usage growth.
Solution: Implement usage quotas, automated cost alerts, and efficiency optimizations from day one.
Pitfall 4: Overlooking Security Risks
Problem: LLMs introduce new attack vectors like prompt injection.
Solution: Incorporate security testing into your CI/CD pipeline and implement defense-in-depth strategies.
Implementing Your First LLMOps Pipeline: A Step-by-Step Guide
Let's walk through setting up a basic but robust LLMOps pipeline for a hypothetical customer support chatbot.
Step 1: Define Requirements and Metrics
Start with clear objectives: "Reduce customer support ticket volume by 30% while maintaining customer satisfaction scores above 4.5/5." Define specific metrics: response accuracy, resolution rate, customer satisfaction, and cost per conversation.
Step 2: Choose Your Stack
For our example: GPT-4 API for responses, LangChain for orchestration, FastAPI for serving, Prometheus for metrics, and a simple database for conversation logging. Total estimated cost: $2,000/month for 10,000 conversations.
Step 3: Implement Basic Monitoring
Set up tracking for: response latency (target: under 2 seconds), token usage, error rates, and manual quality sampling (100 conversations reviewed daily).
Step 4: Deploy with Rollback Capability
Use containerized deployment with blue-green deployment strategy. Ensure you can revert to previous version within 5 minutes if issues arise.
Step 5: Establish Feedback Loops
Implement thumbs up/down buttons in the interface, weekly manual review sessions, and automatic escalation to human agents when confidence scores drop below threshold.
Step 6: Iterate and Improve
Based on monitoring data and feedback, continuously refine prompts, adjust confidence thresholds, and optimize costs.
Future Trends in LLMOps
The LLMOps landscape is evolving rapidly. Here are key trends to watch:
- Specialized Hardware: AI accelerators optimized for LLM inference
- AutoML for LLMs: Automated optimization of prompts and fine-tuning parameters
- Federated Learning: Collaborative model improvement without sharing sensitive data
- Real-time Adaptation: Models that adjust behavior based on immediate feedback
- Regulatory Compliance Tools: Automated auditing for AI regulations like the EU AI Act
Getting Started with LLMOps: Practical Next Steps
If you're new to LLMOps, here's a practical progression path:
- Week 1-2: Experiment with API-based models. Track prompts and responses in a simple spreadsheet.
- Week 3-4: Set up basic monitoring for latency and cost. Implement simple logging.
- Month 2: Containerize your application. Implement versioning for prompts.
- Month 3: Add quality metrics and user feedback collection.
- Month 4+: Implement automated testing, advanced monitoring, and optimization cycles.
Remember: LLMOps is an iterative process. Start simple, measure everything, and gradually add sophistication as your needs evolve.
Conclusion
LLMOps represents the essential bridge between LLM experimentation and production value. By implementing systematic approaches to deployment, monitoring, and management, organizations can unlock the full potential of large language models while mitigating risks and controlling costs. The key principles—comprehensive monitoring, proactive management, security-first design, and continuous improvement—apply whether you're deploying your first chatbot or managing hundreds of models across global operations.
As LLMs become increasingly integral to business operations, investing in robust LLMOps practices will differentiate successful implementations from costly experiments. Start with the fundamentals outlined in this guide, adapt them to your specific context, and remember that the most effective LLMOps strategy is one that evolves alongside both the technology and your organizational needs.
Visuals Produced by AI
Further Reading
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
1421
Like
1421
 Dislike
23
Dislike
23
 Love
356
Love
356
 Funny
45
Funny
45
 Angry
12
Angry
12
 Sad
8
Sad
8
 Wow
289
Wow
289
















The team structure discussion validated our recent organizational changes. Good to know we're on the right track!
Great balance between depth and accessibility. Covers the important topics without getting lost in unnecessary technical details.
The cost optimization strategies alone make this article worth reading. We've already implemented several and seen significant savings.
We've bookmarked this article and refer back to it regularly. It's become part of our onboarding for new team members working with LLMs.
Practical, actionable advice throughout. This is exactly what the industry needs as LLMs move from experimentation to production.
The future trends section has given us ideas for our technology roadmap. Always good to think ahead!