Mitigating Hallucinations: Techniques and Tools
This comprehensive guide explains AI hallucinations—when language models generate incorrect or fabricated information—and provides practical techniques to mitigate them. We cover everything from basic prompt engineering strategies to advanced retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) frameworks, fine-tuning approaches, and specialized tools. Learn how to implement fact-checking systems, confidence scoring, and hybrid approaches that combine multiple techniques. Whether you're building AI applications or using AI tools professionally, this guide provides actionable strategies to improve reliability and reduce misleading outputs. Includes step-by-step implementation guidance, tool comparisons, and real-world examples.
Mitigating Hallucinations: Techniques and Tools
AI hallucinations occur when language models generate information that seems plausible but is factually incorrect, misleading, or completely fabricated. As AI systems become more integrated into critical applications—from customer service to medical advice and legal research—mitigating these hallucinations has become essential for building trustworthy AI systems. This comprehensive guide explains what causes hallucinations, provides practical techniques to reduce them, and reviews the tools available for implementation.
Hallucinations aren't necessarily a sign of poor AI design; they're a fundamental characteristic of how current language models work. These models predict the next most likely word based on patterns in their training data, without true understanding or fact-checking capabilities. When the training data contains contradictions, gaps, or biases, or when prompts push the model beyond its knowledge boundaries, hallucinations can occur.
Understanding the Root Causes of AI Hallucinations
Before we can effectively mitigate hallucinations, we need to understand why they happen. Research shows several primary causes:
- Training Data Limitations: Models can only learn from their training data. If this data contains errors, outdated information, or insufficient coverage of certain topics, the model may generate incorrect information confidently
- Statistical Nature of Predictions: Language models generate text by predicting the next most statistically likely token, not by retrieving verified facts. This statistical approach can produce plausible-sounding but incorrect information
- Prompt Ambiguity: Vague or overly broad prompts can lead the model to "fill in gaps" with fabricated information
- Overconfidence in Patterns: Models sometimes detect patterns in their training data that don't reflect reality and apply them too broadly
- Instruction Following Errors: When trying to follow complex instructions, models might generate supporting "facts" to make their responses more complete
Understanding these causes helps us choose the right mitigation strategies. Some techniques address training limitations, others work around statistical prediction issues, and some add verification layers on top of model outputs.
Prompt Engineering: The First Line of Defense
The simplest and most accessible approach to reducing hallucinations is through careful prompt engineering. These techniques require no technical setup and can be implemented immediately in any AI application.
Structured Prompt Templates
Creating structured prompts that guide the model toward more accurate responses can significantly reduce hallucinations. Research from OpenAI shows that certain prompt patterns yield more reliable results:
- Instruction-Context-Question Format: Clearly separate the instruction, provide relevant context, then ask the specific question
- Step-by-Step Reasoning Requests: Asking models to "think step by step" or "show your work" reduces fabrication rates
- Uncertainty Acknowledgment: Teaching models to say "I don't know" when uncertain rather than guessing
For example, instead of asking "Tell me about quantum computing," a better structured prompt would be: "Based on the following verified sources about quantum computing [provide sources], explain the basic principles in simple terms. If any information isn't covered in these sources, acknowledge the gap rather than speculating."
Temperature and Sampling Parameters
Technical parameters like temperature, top-p, and frequency penalty directly impact hallucination rates. Lower temperature settings (0.1-0.3) produce more focused, deterministic outputs with fewer surprises but can be less creative. Higher temperatures (0.7-1.0) increase creativity but also increase hallucination risks.
The key is matching parameter settings to use cases: factual Q&A benefits from low temperature, creative writing can tolerate higher settings. Most commercial AI tools allow adjusting these parameters, though often through advanced settings.
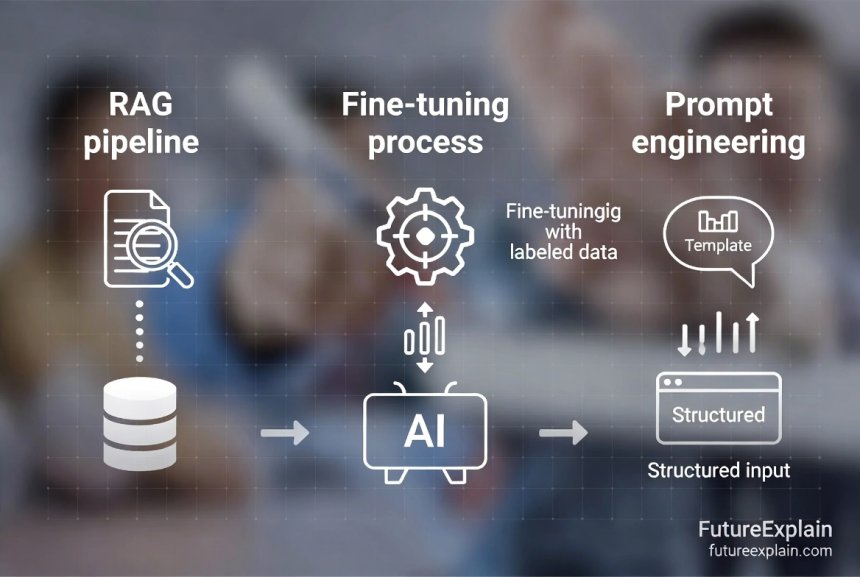
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Grounding AI in Facts
Retrieval-Augmented Generation represents one of the most effective approaches for reducing hallucinations in knowledge-intensive applications. RAG systems work by retrieving relevant information from trusted sources before generating responses, essentially "grounding" the AI in verified facts.
How RAG Systems Work
A typical RAG pipeline involves several steps:
- Document Processing: Source documents are processed and broken into manageable chunks
- Embedding Creation: Each chunk is converted into a numerical representation (embedding) that captures its semantic meaning
- Vector Database Storage: These embeddings are stored in a specialized database that allows efficient similarity searches
- Retrieval at Query Time: When a user asks a question, the system converts it to an embedding and finds the most similar document chunks
- Context Augmentation: Retrieved information is added to the prompt as context before generation
- Response Generation: The language model generates a response based on the retrieved context
This approach dramatically reduces hallucinations because the model has relevant, verified information to work with. Studies show RAG can reduce factual errors by 40-60% in knowledge-heavy domains.
Implementing RAG: Tools and Frameworks
Several tools and frameworks make RAG implementation accessible even for non-experts:
- LangChain: Popular Python framework with built-in RAG components and extensive documentation
- LlamaIndex: Specialized framework for building RAG applications with various data connectors
- Haystack: Open-source framework with pre-built components for search and question answering
- Pinecone/Weaviate: Managed vector databases that simplify the storage and retrieval aspects
For beginners, starting with a managed service like Pinecone combined with LangChain's tutorials provides the gentlest learning curve. The key is beginning with a small, well-defined dataset rather than attempting to index everything at once. Start with a few hundred documents on a specific topic, implement basic retrieval, then expand gradually.
Fine-Tuning: Teaching Models to Be More Careful
While prompt engineering and RAG work with existing models, fine-tuning involves training models on specific data to improve their behavior, including reducing hallucination tendencies.
Supervised Fine-Tuning for Accuracy
This approach involves creating a dataset of high-quality question-answer pairs where answers are meticulously verified and include appropriate uncertainty markers. By training on this curated data, models learn patterns of careful, accurate response generation.
Key considerations for effective fine-tuning include:
- Dataset Quality Over Quantity: A few hundred carefully verified examples often outperform thousands of mediocre ones
- Balanced Uncertainty: Include examples where the correct answer is "I don't have enough information" or "This requires verification"
- Source Attribution: Train models to cite sources when making factual claims
- Contrastive Examples: Include both good and bad examples to help the model distinguish reliable from unreliable responses
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF)
RLHF takes fine-tuning further by incorporating human preferences into training. In this approach:
- Human reviewers rate different model responses
- A reward model learns to predict human preferences
- The main model is optimized to generate responses that receive higher rewards
RLHF has been particularly effective at reducing harmful hallucinations while maintaining model helpfulness. The challenge is that RLHF requires significant human annotation effort and technical expertise to implement.
Confidence Scoring and Uncertainty Quantification
Instead of trying to eliminate all hallucinations, some approaches focus on identifying when hallucinations are likely so applications can handle uncertainty appropriately.
Internal Consistency Checking
This technique involves generating multiple responses to the same prompt and checking for consistency. If responses contradict each other, the system flags potential reliability issues. Tools like:
- Self-Consistency Sampling: Generating multiple reasoning paths and taking the most common answer
- Monte Carlo Dropout: Running inference multiple times with random variations to estimate uncertainty
- Ensemble Methods: Combining predictions from multiple models or model versions
These approaches don't prevent hallucinations but help detect them, allowing applications to request human verification or provide appropriate warnings.
Verification Against Knowledge Bases
Another detection approach involves automatically checking generated content against trusted knowledge bases. This can be implemented through:
- Fact-Checking APIs: Services that verify claims against databases like Wikipedia or specialized knowledge graphs
- Named Entity Verification: Checking that mentioned entities exist and have correct attributes
- Temporal Consistency Checks: Ensuring dates and timelines make logical sense
While comprehensive verification remains computationally expensive, selective checking of key claims can catch many significant hallucinations.

Specialized Tools and Frameworks
Several tools specifically designed for hallucination mitigation have emerged, each with different approaches and trade-offs.
Guardrail Frameworks
Guardrail frameworks add validation layers around AI model outputs. Notable examples include:
- NeMo Guardrails: NVIDIA's framework for adding programmable guardrails that can filter, redirect, or modify model outputs based on configurable rules
- Guardrails AI: Open-source framework for validating LLM outputs using pydantic-style schemas and quality checks
- Microsoft Guidance: Framework for controlling model generation through constrained decoding and output formatting
These frameworks work by intercepting model outputs, applying validation rules, and either passing clean outputs or triggering corrective actions. They're particularly useful for production applications where consistent behavior is critical.
Enterprise-Grade Solutions
For organizations needing comprehensive solutions, several platforms offer integrated hallucination mitigation:
- Cohere's Command R+: Built with enterprise reliability features including source citation and reduced hallucination rates
- Anthropic's Claude: Constitutional AI approach designed to minimize harmful outputs including hallucinations
- Google's Vertex AI Grounding: Features that automatically ground responses in specified sources with attribution
- IBM Watsonx.governance: Tools for monitoring, detecting, and mitigating model issues including hallucinations
These solutions typically combine multiple techniques (RAG, fine-tuning, validation) into integrated platforms but come with higher costs and vendor lock-in considerations.
Hybrid Approaches: Combining Multiple Techniques
The most effective hallucination mitigation often comes from combining multiple approaches. Here are proven combination strategies:
RAG + Confidence Scoring
Implement RAG for factual grounding, then add confidence scoring on the generated responses. If confidence is low, the system can:
- Fall back to just presenting retrieved documents without generation
- Flag the response for human review
- Ask clarifying questions to gather more context
Prompt Engineering + Verification APIs
Use carefully engineered prompts to reduce initial hallucination rates, then run key factual claims through verification services. This balances performance (verifying everything is slow) with reliability.
Fine-Tuning + Guardrails
Fine-tune models to be generally more reliable, then add specific guardrails for critical domains or high-risk outputs. This approach is common in regulated industries like healthcare and finance.
Choosing the Right Approach: Decision Framework
With so many options available, choosing the right hallucination mitigation strategy depends on several factors:
| Use Case | Recommended Primary Approach | Supplemental Techniques | Tools to Consider |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Q&A with internal documents | RAG with vector search | Source attribution, confidence thresholds | LangChain + Pinecone |
| Creative writing assistance | Temperature adjustment + prompt constraints | Style consistency checks | Custom prompt templates |
| Customer support automation | Fine-tuning on verified responses | Fallback to human agent rules | OpenAI fine-tuning or Anthropic |
| Research assistance | RAG + fact-checking APIs | Multiple source verification | LlamaIndex + fact-check services |
| Code generation | Test-driven constraints | Syntax validation, security scanning | GitHub Copilot with custom rules |
The decision should consider:
- Accuracy Requirements: How critical is perfect accuracy? Medical applications need higher standards than creative brainstorming.
- Latency Tolerance: Some techniques (like extensive verification) add significant processing time.
- Technical Resources: RAG requires more infrastructure than simple prompt engineering.
- Data Availability: Fine-tuning requires quality training data; RAG requires source documents.
- Cost Constraints: Some commercial solutions provide effectiveness but at ongoing subscription costs.
Implementation Best Practices
Regardless of which techniques you choose, certain implementation practices improve outcomes:
Start Simple, Iterate Complex
Begin with the simplest effective approach (often prompt engineering), measure results, then add complexity only where needed. Many teams over-engineer solutions when simpler approaches would suffice for their actual use cases.
Establish Metrics and Monitoring
Define clear metrics for hallucination rates and implement monitoring before and after mitigation efforts. Useful metrics include:
- Factual Accuracy Rate: Percentage of factual claims that verify correctly
- Hallucination Detection Rate: How often the system correctly identifies uncertain outputs
- False Positive Rate: How often correct information is flagged as potentially hallucinated
- User Correction Requests: How often users report or correct information
Maintain Human-in-the-Loop Options
Even with the best automated mitigation, maintain pathways for human verification, especially for high-stakes applications. Design systems to:
- Gracefully defer to human experts when confidence is low
- Make it easy for users to report suspected hallucinations
- Include clear disclaimers about potential inaccuracies where appropriate
The Future of Hallucination Mitigation
Research continues to advance hallucination mitigation techniques. Emerging approaches include:
- Improved Training Methods: Techniques like Constitutional AI that build reliability into training objectives from the beginning
- Better Uncertainty Quantification: Models that can better estimate and communicate their own uncertainty
- Multimodal Verification: Using multiple data types (text, images, structured data) to cross-verify information
- Causal Understanding: Moving beyond statistical patterns to models with some causal reasoning capabilities
While no technique currently eliminates hallucinations completely, the combination of approaches available today can reduce them to manageable levels for most practical applications. The key is understanding your specific requirements and implementing a tailored combination of techniques.
Further Reading
To continue your learning about AI reliability and safety:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Explained Simply - Deep dive into RAG implementation
- Ethical AI Explained: Why Fairness and Bias Matter - Broader context on AI safety
- Prompt Engineering Best Practices for Better Outputs - Advanced prompt techniques
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
1520
Like
1520
 Dislike
15
Dislike
15
 Love
320
Love
320
 Funny
45
Funny
45
 Angry
8
Angry
8
 Sad
12
Sad
12
 Wow
210
Wow
210

















This article bridges the gap between academic research and practical implementation perfectly. As a product manager, I need this level of detail to make informed decisions about our AI roadmap.
The future developments section gives context for where to invest learning time. Focusing on uncertainty quantification and multimodal verification seems like where the field is heading.
We're implementing the named entity verification technique for our news summarization tool. Checking that people, places, and organizations actually exist before publishing summaries.
The section on reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) explained it better than any technical paper I've read. Clear, practical implications rather than just theory.
The ensemble methods mention caught my attention. We're testing response comparison between GPT-4 and Claude for critical queries - if they agree, higher confidence; if they disagree, flag for review.
How do these techniques apply to non-English languages? We're building multilingual support and concerned that RAG/document processing might be harder for languages with less training data.
For non-English languages: Prompt engineering and temperature adjustments work similarly across languages. RAG effectiveness depends on: 1) Quality of embedding models for that language, 2) Availability of documents in that language, 3) Language-specific tokenization challenges. For languages with less support, focus more on prompt engineering and confidence scoring. Also consider multilingual models (like mBERT or XLM-R) that handle multiple languages better. Start with your highest-traffic language first, then expand.