AI in Finance: Fraud Detection, Risk, and Automation
This comprehensive guide explores how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the financial sector. Learn how machine learning detects fraudulent transactions in real-time, assess financial risks more accurately, and automates routine banking operations. We explain complex concepts like anomaly detection, credit scoring algorithms, and robotic process automation in simple terms suitable for beginners. Discover practical AI tools for personal finance, small business accounting, and institutional investing. The article also covers important ethical considerations, regulatory challenges, and provides a realistic view of both the capabilities and limitations of AI in finance. Whether you're a consumer, small business owner, or finance professional, this guide helps you understand and navigate the AI transformation happening in financial services today.

Introduction: The Quiet Revolution in Finance
When you check your bank account online, apply for a loan, or make a digital payment, artificial intelligence is likely working behind the scenes to protect your money and streamline the process. The financial industry has become one of the largest adopters of AI technology, transforming everything from fraud prevention to investment strategies. Unlike the flashy chatbots and image generators that dominate headlines, financial AI operates quietly but profoundly, analyzing billions of transactions, assessing risks, and automating processes that once required armies of human analysts.
This transformation isn't just about large banks and hedge funds. Small businesses now use AI-powered accounting software, individuals benefit from smarter budgeting tools, and even regulatory agencies employ machine learning to monitor markets. The impact is so significant that a McKinsey report estimates AI could generate up to $1 trillion in additional value for the global banking industry annually. But what does this mean for you as a consumer, business owner, or someone simply trying to understand this technological shift?
In this comprehensive guide, we'll demystify how AI works in financial contexts. We'll explore three key areas where artificial intelligence is making the biggest impact: fraud detection (protecting your money), risk assessment (making smarter financial decisions), and automation (saving time and reducing errors). We'll explain complex concepts in simple language, provide real-world examples, and offer practical guidance for navigating this changing landscape.
How AI Detects Fraud: From Simple Rules to Intelligent Patterns
Financial fraud has existed as long as money itself, but the digital age has created new opportunities for criminals—and new tools to stop them. Traditional fraud detection systems relied on rules written by human experts: "If a transaction exceeds $1,000 and comes from a foreign country, flag it for review." These rules-based systems worked reasonably well but had significant limitations. They generated many false positives (legitimate transactions flagged as suspicious), couldn't adapt quickly to new fraud patterns, and required constant manual updates.
The Machine Learning Approach
Modern AI systems take a fundamentally different approach. Instead of following explicit rules, they learn patterns from historical data. Here's how it works in practice:
- Training Phase: The system analyzes millions of past transactions, both legitimate and fraudulent. It identifies patterns that human analysts might miss: subtle correlations between transaction time, location, amount, merchant type, and user behavior.
- Feature Engineering: AI systems don't just look at raw data—they create "features" that help identify fraud. For example, instead of just looking at transaction amount, they might calculate "velocity features" like "number of transactions in the last hour" or "distance from previous transaction location."
- Real-Time Scoring: When you make a transaction, the AI system instantly scores it based on hundreds of features. High scores trigger additional verification steps, while low-scoring transactions proceed smoothly.
Types of Fraud Detection AI
Different machine learning approaches excel at different types of fraud detection:
- Supervised Learning: Uses labeled historical data (known fraudulent vs. legitimate transactions) to train models. Effective for established fraud patterns but struggles with completely new attack methods.
- Unsupervised Learning: Looks for anomalies or outliers without predefined labels. Useful for detecting novel fraud schemes that don't match known patterns.
- Semi-Supervised Learning: Combines both approaches, using limited labeled data alongside vast amounts of unlabeled transaction data.
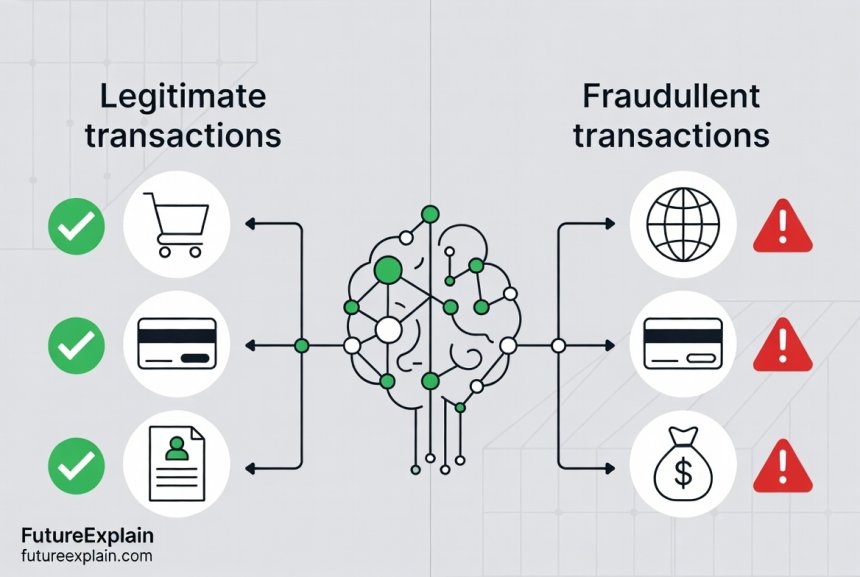
Major payment processors like Visa and MasterCard process over 100,000 transactions per minute during peak times. Their AI systems make fraud decisions in milliseconds, with accuracy rates exceeding 99%. According to industry reports, these systems prevent billions in fraud annually while reducing false positives by 30-50% compared to older rule-based systems.
Practical Impact: Consider Sarah, who travels frequently for work. Under old rules, her overseas transactions would often be declined, requiring frustrating calls to her bank. Modern AI systems recognize her travel patterns (she typically visits the same cities monthly) and device signatures (she uses her phone for most purchases). The system learns that transactions from London on her iPhone during business hours are normal for Sarah, while the same transaction from someone else's device might trigger alerts.
Risk Assessment: From Gut Feel to Data-Driven Decisions
Risk assessment is fundamental to all financial decisions. Should a bank approve a loan? What interest rate should they charge? How much capital should an institution hold in reserve? Traditionally, these decisions relied heavily on human judgment, limited data, and standardized formulas like FICO scores for consumer credit.
AI transforms risk assessment in several key ways:
1. More Comprehensive Data Analysis
Traditional credit scoring uses maybe 15-20 data points. Modern AI systems can analyze thousands of data points from diverse sources:
- Traditional credit history
- Bank account transaction patterns (with user permission)
- Utility and telecom payment history
- Education and employment data
- Public records and social signals (in regulated ways)
- Behavioral data from digital interactions
This doesn't mean AI is spying on your social media posts. Regulated financial institutions must comply with fair lending laws that restrict what data can be used. However, with proper consent and within regulatory boundaries, AI can paint a more complete picture of creditworthiness.
2. Dynamic Risk Assessment
Traditional risk models are static—they're updated quarterly or annually. AI models can update in near real-time as new data becomes available. For example, if someone loses their job, traditional systems might not know for months. An AI system analyzing bank transactions might detect reduced income within weeks and adjust risk assessments accordingly (with appropriate safeguards and notifications).
3. Predictive Power for Unusual Situations
The COVID-19 pandemic revealed limitations of traditional risk models. Historical data from normal economic conditions poorly predicted behavior during government-mandated lockdowns. AI systems that incorporated alternative data (industry shutdown patterns, geographic infection rates, government support programs) performed better at predicting which borrowers would struggle and which would adapt.
Financial Automation: Beyond Simple Recurring Payments
When most people think of financial automation, they imagine scheduled bill payments or automatic savings transfers. Modern AI-powered automation goes much further, handling complex tasks that once required human expertise.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Finance
RPA uses software "robots" to automate repetitive tasks. In finance, this includes:
- Accounts Payable/Receivable: Extracting data from invoices, matching to purchase orders, processing payments
- Reconciliation: Automatically matching bank statements with internal records
- Regulatory Reporting: Gathering data from multiple systems to generate required reports
- Customer Onboarding: Collecting and verifying customer information during account setup
Early RPA systems followed strict rules, but AI-enhanced RPA can handle exceptions and variations. For example, an AI system can learn to process invoices from different vendors even when they use different formats or terminology.
Intelligent Document Processing
Financial services are drowning in paperwork: loan applications, tax documents, contracts, statements. AI systems using natural language processing and computer vision can:
- Extract key information from scanned documents
- Categorize documents by type and purpose
- Identify missing or inconsistent information
- Route documents to appropriate personnel or systems
This technology has become particularly valuable for mortgage processing, where a single application might involve dozens of documents from multiple sources.

AI in Different Financial Sectors
Retail Banking
Your local bank branch or online bank likely uses AI in multiple ways:
- Personalized Product Recommendations: Like Netflix suggests movies, banks suggest relevant financial products based on your transaction patterns and life events (detected through spending changes).
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Handling routine inquiries about balances, transactions, and basic problem resolution.
- Predictive Customer Service: Identifying customers likely to encounter problems (like overdrafts) and proactively offering solutions.
Investment and Wealth Management
The world of investing has been transformed by AI:
- Algorithmic Trading: Executing trades based on market signals faster than any human could. While high-frequency trading gets attention, more interesting are AI systems that identify longer-term opportunities based on diverse data sources.
- Portfolio Management: Robo-advisors like Betterment and Wealthfront use algorithms to create and manage diversified portfolios based on individual risk tolerance and goals.
- Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing news, social media, and earnings calls to gauge market sentiment about specific stocks or sectors.
Insurance
Insurance companies were among the first financial institutions to embrace statistical modeling, and AI represents the next evolution:
- Claims Processing: Automatically assessing damage from photos (for auto or property claims), detecting potential fraud, and accelerating payments for straightforward claims.
- Dynamic Pricing: More sophisticated risk assessment allowing for personalized premiums based on actual behavior (like telematics in auto insurance).
- Risk Prevention: Alerting property owners about risks (like potential water damage from weather patterns) before claims occur.
Ethical Considerations and Regulatory Challenges
The power of AI in finance comes with significant responsibilities and challenges that regulators, institutions, and consumers must navigate.
The "Black Box" Problem
Many advanced AI models, particularly deep learning systems, are difficult to interpret. When a loan application is denied, regulations typically require explaining why. If the AI system can't provide a clear reason beyond "the model said no," it creates legal and ethical problems.
This has led to the development of Explainable AI (XAI) techniques that help interpret complex models. Financial institutions are investing in XAI to meet regulatory requirements and maintain customer trust. For example, some systems now generate plain-language explanations: "Your application was denied due to high debt-to-income ratio and three late payments in the last year."
Bias and Fairness
AI systems learn from historical data, and if that data contains biases, the AI will perpetuate or even amplify them. In lending, this could mean discrimination against certain demographic groups, even if the AI isn't explicitly considering protected characteristics like race or gender.
Financial institutions combat this through:
- Bias Testing: Regularly testing models for disparate impact on protected groups
- Fairness Constraints: Building mathematical constraints into models to ensure equitable outcomes
- Diverse Training Data: Ensuring training data represents diverse populations
- Human Oversight: Maintaining human review for edge cases and appeals
Data Privacy and Security
Financial AI requires vast amounts of sensitive data. Protecting this data involves:
- Encryption: Both for data at rest and in transit
- Federated Learning: Training AI models across decentralized devices without sharing raw data
- Differential Privacy: Adding mathematical noise to data to protect individual privacy while maintaining overall statistical usefulness
- Consent Management: Clear opt-in processes for data usage beyond core services
Practical Guide: Implementing AI in Your Financial Life
For Individuals
You don't need to work at a bank to benefit from financial AI. Here are practical ways to leverage these technologies:
- Budgeting Apps: Tools like Mint, YNAB, or PocketGuard use AI to categorize spending, identify patterns, and suggest optimizations.
- Investment Platforms: Robo-advisors provide low-cost, diversified portfolio management based on your goals and risk tolerance.
- Credit Monitoring: Services that use AI to detect unusual patterns that might indicate identity theft.
- Smart Savings: Apps that analyze your cash flow and automatically transfer small amounts to savings.
For Small Businesses
Small businesses can implement AI financial tools without large IT budgets:
- AI-Powered Accounting: Platforms like QuickBooks Online use machine learning for receipt scanning, expense categorization, and cash flow forecasting.
- Fraud Prevention Services: Affordable services that monitor business accounts for suspicious activity.
- Dynamic Pricing Tools: For e-commerce businesses, tools that optimize pricing based on demand, competition, and customer behavior.
- AI-Driven Lending Platforms: Alternative lenders using AI to assess creditworthiness beyond traditional metrics.
Implementation Checklist
When adopting any AI financial tool, consider:
- Transparency: Does the provider explain how their AI works in understandable terms?
- Control: Can you adjust settings or override decisions?
- Security: What measures protect your financial data?
- Cost vs. Benefit: Does the value justify any fees or subscription costs?
- Integration: Does it work with your existing financial systems?
The Future of AI in Finance
As AI technology continues to evolve, several trends are likely to shape the financial landscape:
1. Hyper-Personalization
Financial products and advice will become increasingly tailored to individual circumstances, life stages, and even personal values (like ESG investing preferences).
2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Integration
AI will play a crucial role in managing risks and opportunities in blockchain-based financial systems, which lack traditional intermediaries.
3. Regulatory Technology (RegTech)
AI will help financial institutions comply with increasingly complex regulations more efficiently, and help regulators monitor markets more effectively.
4. AI-Human Collaboration
The future isn't about AI replacing financial professionals but augmenting their capabilities. Advisors will use AI to handle data analysis while focusing on relationship-building and complex judgment calls.
5. Embedded Finance
AI-powered financial services will become seamlessly integrated into non-financial platforms—think of shopping apps that offer instant, AI-assessed financing at checkout.
Conclusion: Navigating the AI Financial Revolution
The integration of artificial intelligence into finance represents one of the most significant technological shifts in the industry's history. From protecting our transactions against fraud to making credit more accessible through better risk assessment, AI offers tangible benefits for consumers, businesses, and the overall financial system.
However, this transformation requires thoughtful navigation. As users of financial services, we should educate ourselves about how these systems work, understand their limitations, and advocate for transparency and fairness. As the technology continues to evolve, maintaining a balance between innovation and regulation, efficiency and ethics, automation and human oversight will be crucial.
The future of finance isn't about cold, impersonal algorithms replacing human judgment. It's about combining the pattern recognition power of AI with human wisdom, empathy, and ethical consideration. By understanding these technologies, we can make better financial decisions, protect our assets more effectively, and participate in shaping a financial system that serves everyone more efficiently and fairly.
Further Reading
- AI in Healthcare: Real Use Cases and Limitations - Explore how AI transforms another highly regulated industry with similar ethical considerations.
- AI in Marketing: Simple Explanation for Beginners - Learn how AI personalization works in consumer-facing applications.
- Ethical AI Explained: Why Fairness and Bias Matter - Deep dive into the ethical considerations crucial for financial AI systems.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
423
Like
423
 Dislike
8
Dislike
8
 Love
156
Love
156
 Funny
23
Funny
23
 Angry
12
Angry
12
 Sad
7
Sad
7
 Wow
89
Wow
89
















How does AI handle cross-border transactions and different regulatory environments? The anti-money laundering requirements vary so much between countries.
I'd love to see a follow-up article with case studies of AI implementation failures in finance. Learning from what doesn't work is just as important as understanding successes.
Great suggestion! Case studies of both successes and failures provide valuable lessons. We're planning an article series on real-world AI implementation challenges across different industries, including finance. Failures often teach more than successes about the importance of proper testing, data quality, and change management.
The comparison between supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised learning for fraud detection was the clearest explanation I've read. Most technical articles assume too much prior knowledge. More of this beginner-friendly but comprehensive content please!
The future trends section got me thinking about embedded finance. I've already seen this with buy-now-pay-later options at checkout. If AI makes instant credit decisions, will this lead to more impulsive spending and debt problems?
This is a crucial ethical consideration. Responsible AI implementation should include affordability assessments, spending pattern analysis, and perhaps even "cooling off" periods for certain types of instant credit. Regulators are starting to look at these issues, especially for products targeting vulnerable consumers. Technology should enable financial inclusion, not exploitation.
That's a real concern. I work with a debt counseling non-profit, and we're already seeing clients with multiple BNPL loans they can't manage. AI might make credit too easily accessible without proper affordability checks.
As an educator teaching personal finance, this article gave me great examples to use in class. Students are fascinated by AI but don't always understand its practical applications. The fraud detection explanation will make our banking security unit much more engaging.
Could you elaborate more on AI in insurance? The brief section was interesting, but I'd love to know how AI handles more subjective claims like business interruption or contingent business interruption where the losses aren't as clear-cut as auto damage.
Excellent question about complex insurance claims. For business interruption, AI systems analyze historical claims data, industry benchmarks, financial statements, and even news/social sentiment about the interruption cause. They're particularly useful for detecting potential fraud in subjective claims by identifying patterns that deviate from normal claims. We'll cover AI in insurance more comprehensively in a future article.