Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Explained Simply
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a revolutionary AI approach that combines the creative power of large language models with external knowledge sources. Unlike traditional AI that relies only on its training data, RAG systems can retrieve up-to-date, specific information from databases, documents, or the internet before generating responses. This guide explains RAG in simple, non-technical terms, showing how it works through clear analogies, real-world examples, and practical applications. You'll learn why RAG reduces AI hallucinations, how businesses use it for accurate customer support, and what makes it different from regular chatbots. Perfect for beginners, this article breaks down complex concepts into easy-to-understand explanations without technical jargon.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Explained Simply
Have you ever asked an AI chatbot a question about current events, only to get a response like "I'm sorry, my knowledge only goes up to 2023"? Or perhaps you've received an answer that sounds plausible but turns out to be completely made up? These limitations of traditional artificial intelligence are exactly what Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) was created to solve.
RAG represents one of the most important breakthroughs in making AI more accurate, reliable, and useful for real-world applications. At its core, RAG is about giving AI systems a way to look things up before they answer—much like how a student might consult reference books before writing an essay, or how you might search the internet to answer a friend's question.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore RAG from the ground up, using simple explanations, practical examples, and clear analogies. Whether you're a business owner considering AI tools, a student learning about technology, or simply curious about how modern AI works, this article will give you a solid understanding of what RAG is and why it matters.
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation? The Simple Definition
Retrieval-Augmented Generation, or RAG, is an AI technique that combines two powerful capabilities:
- Retrieval: The ability to search for and find relevant information from external sources
- Augmented Generation: Using that retrieved information to enhance and inform the AI's response
Think of it this way: A regular AI language model is like a brilliant student who has memorized thousands of textbooks but can't look anything up during an exam. A RAG system, on the other hand, is like that same brilliant student who now has access to a well-organized library and knows exactly how to find the specific information they need.
The term was first introduced by Facebook AI researchers in 2020, but the concept has rapidly evolved and been adopted across the AI industry. Today, RAG powers many of the most advanced AI applications you might encounter, from sophisticated customer support chatbots to intelligent research assistants.
Why RAG Matters: Solving AI's Biggest Limitations
To understand why RAG is such a breakthrough, we need to look at the limitations of traditional large language models (LLMs):
The Knowledge Cutoff Problem
Traditional AI models have a fixed knowledge cutoff date. They can only know what was included in their training data, which might be months or years old. If you ask about events that happened after their training, they either can't answer or might make something up. RAG solves this by allowing the AI to retrieve current information from up-to-date sources.
The Hallucination Problem
AI hallucinations occur when models generate plausible-sounding but incorrect information. This happens because AI doesn't "know" facts in the way humans do—it predicts the most likely next word based on patterns. RAG reduces hallucinations by grounding responses in retrieved factual information.
The Specificity Problem
General AI models aren't trained on your company's specific documents, your personal preferences, or niche technical information. RAG enables AI to access and use specialized knowledge relevant to particular contexts or organizations.
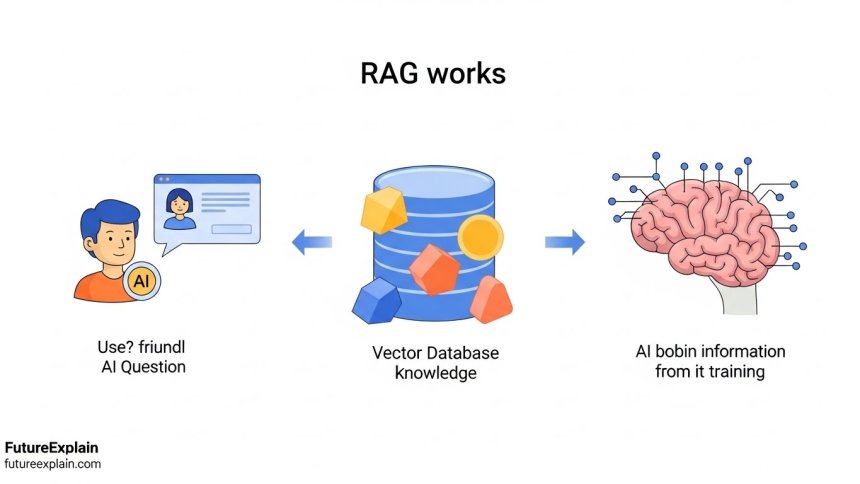
How RAG Works: A Step-by-Step Walkthrough
Let's break down the RAG process into simple steps that anyone can understand. Imagine you're asking an AI about the latest developments in renewable energy:
Step 1: The User Asks a Question
You type: "What are the most promising new solar panel technologies announced in the last six months?"
Step 2: The Question Gets Understood and Prepared for Search
The RAG system analyzes your question to understand what you're really asking for. It identifies key concepts like "solar panel technologies," "promising," and "last six months." It might rephrase or expand the query to improve search results.
Step 3: Searching the Knowledge Base
Here's where the magic happens. Instead of just generating an answer from its training data, the system searches through connected knowledge sources. These could include:
- Company documents and manuals
- Recent news articles and research papers
- Product databases and specifications
- Internal knowledge bases
- Approved websites and resources
The search isn't like regular Google searching. RAG systems typically use something called "vector search" or "semantic search," which looks for conceptually similar information rather than just keyword matches. This is more like how a librarian might help you find books on a topic even if you don't know the exact titles.
Step 4: Retrieving Relevant Information
The system retrieves the most relevant chunks of information. It might find recent articles about perovskite solar cells, research papers on bifacial panels, and industry reports about solar efficiency breakthroughs.
Step 5: Augmenting the AI's Knowledge
The retrieved information is added to the original question as context. So now, instead of just asking the AI to answer based on its training, the system essentially says: "Here's the user's question, AND here are some relevant, up-to-date documents. Please use both to generate an answer."
Step 6: Generating the Enhanced Response
The AI generates a response that incorporates both its general knowledge about solar technology AND the specific, current information it just retrieved. The result is a more accurate, relevant, and timely answer.
Step 7: Providing Sources (Optional but Helpful)
Many RAG systems can also cite their sources, telling you which documents or data they used to generate specific parts of their answer. This builds trust and allows you to verify the information.
The Technology Behind RAG: Simplified Explanation
While you don't need to understand the technical details to grasp RAG's value, knowing a little about the underlying technology can help you appreciate how it works. Here are the key components in simple terms:
Vector Databases: The AI's Filing System
Vector databases are specialized storage systems that organize information in a way that AI can understand and search efficiently. Instead of storing words as text, they store them as mathematical representations (vectors) that capture the meaning of the content. This allows for "semantic search"—finding information that's conceptually related even if it doesn't contain the exact keywords.
For example, in a vector database, "automobile," "car," and "vehicle" would be stored close together because they have similar meanings, even though they're different words. This is different from traditional databases that might only find exact matches.
Embeddings: Translating Words to Numbers
Embeddings are how AI converts text into those mathematical representations. Think of embeddings as a special code that captures the meaning of words and sentences. The sentence "The cat sat on the mat" and "The feline rested on the rug" would have similar embeddings even though they use different words.
The Retrieval Mechanism: Finding the Right Information
When you ask a question, the RAG system converts your question into an embedding, then searches the vector database for content with similar embeddings. The closest matches (in terms of mathematical similarity) are retrieved as potentially relevant information.
The Language Model: The Creative Brain
This is the part most people think of as "the AI"—systems like GPT-4, Claude, or Llama. The language model takes the retrieved information and the original question, then generates a coherent, natural-sounding response that incorporates both.
Real-World Examples of RAG in Action
RAG isn't just theoretical—it's powering practical applications you might already be using:
Customer Support Chatbots
Imagine a telecom company's support chatbot. A regular AI might give generic answers about internet troubleshooting. A RAG-enhanced chatbot can access the company's specific knowledge base, retrieve information about current outages in your area, check your account details (with permission), and provide personalized troubleshooting steps based on your specific router model.
Legal and Research Assistants
Legal professionals use RAG systems to search through thousands of case files, statutes, and precedents. The AI can retrieve relevant cases and help draft documents that reference specific laws and rulings accurately.
Medical Diagnosis Support
While AI doesn't replace doctors, RAG systems can help medical professionals by retrieving the latest research studies, clinical guidelines, and drug information to support diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Enterprise Knowledge Management
Large companies use RAG to help employees find information across massive internal documentation, past project reports, training materials, and procedural manuals. New employees can ask questions and get answers based on the company's specific knowledge rather than general internet information.
Educational Tools
Educational platforms use RAG to provide students with answers that reference specific textbook sections, lecture notes, and curriculum materials, ensuring alignment with what's being taught.
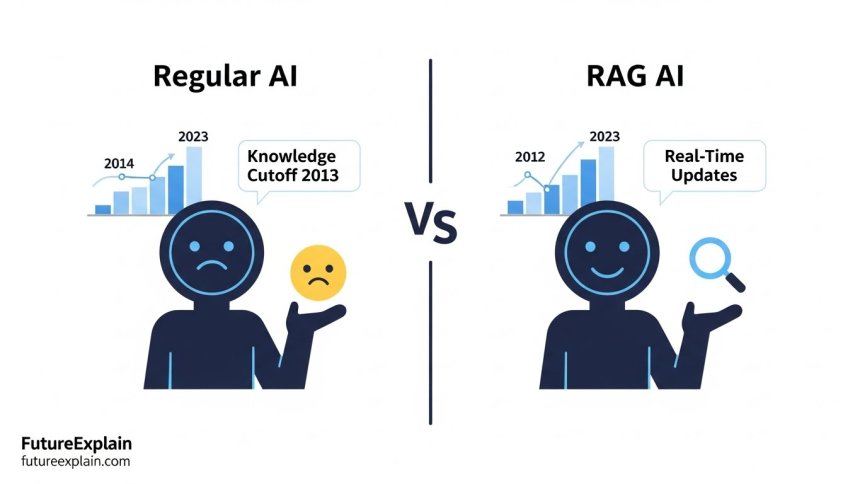
RAG vs. Traditional AI: Key Differences
Understanding how RAG differs from traditional AI approaches helps clarify its unique value:
Knowledge Source
- Traditional AI: Relies solely on pre-trained knowledge (static, fixed at training time)
- RAG: Combines pre-trained knowledge with dynamically retrieved information (current, specific)
Accuracy and Factuality
- Traditional AI: Can generate plausible but incorrect information (hallucinations)
- RAG: Grounds responses in retrieved facts, reducing hallucinations
Timeliness
- Traditional AI: Limited by knowledge cutoff date
- RAG: Can access and use current information
Specificity
- Traditional AI: General knowledge only
- RAG: Can access specialized, proprietary, or context-specific information
Transparency
- Traditional AI: Hard to trace where information came from
- RAG: Can provide source citations and references
Benefits of RAG: Why Organizations Are Adopting It
The advantages of RAG systems explain their rapid adoption across industries:
Improved Accuracy and Reduced Hallucinations
By grounding responses in retrieved facts, RAG systems make fewer factual errors. One study found that RAG could reduce hallucination rates by up to 60% compared to base models for certain types of questions.
Cost-Effectiveness
RAG can be more economical than continuously retraining large models. Instead of expensive retraining cycles to update knowledge, organizations can simply update their knowledge bases. This is particularly valuable for information that changes frequently, like product specifications or regulatory requirements.
Enhanced Trust and Transparency
When RAG systems cite their sources, users can verify information. This builds trust, especially in professional contexts where accuracy matters. A customer support agent (human or AI) who can say "According to our service manual section 4.2..." is more credible than one who gives unsourced advice.
Better Handling of Niche Topics
General AI models struggle with highly specialized topics they weren't extensively trained on. RAG allows organizations to build AI assistants that are experts in their specific domain, whether that's semiconductor manufacturing, medieval literature, or marine biology.
Data Privacy and Control
Organizations can keep sensitive information in their private knowledge bases rather than including it in public AI training data. The RAG system retrieves from these private sources without exposing the raw data in the model itself.
Limitations and Challenges of RAG
While powerful, RAG isn't a perfect solution. Understanding its limitations helps set realistic expectations:
Dependency on Quality Knowledge Bases
The saying "garbage in, garbage out" applies strongly to RAG. If the knowledge base contains outdated, incorrect, or biased information, the RAG system will propagate those issues. Maintaining high-quality, current knowledge bases requires ongoing effort and resources.
Retrieval Accuracy Challenges
Sometimes the system retrieves irrelevant or incomplete information. If the retrieval step fails, even the best language model can't generate an accurate answer. Improving retrieval accuracy remains an active area of research and development.
Context Window Limitations
There's only so much retrieved information an AI can process at once. If too many documents are retrieved, the system might need to prioritize or summarize, potentially losing important details.
Complexity and Implementation Cost
Setting up a RAG system is more complex than using a basic chatbot API. It requires infrastructure for knowledge bases, retrieval mechanisms, and integration between components. While tools are becoming more accessible, there's still a learning curve.
Latency Considerations
The retrieval step adds time to response generation. For simple questions that the base AI could answer correctly, RAG might provide only marginal improvement at the cost of slower responses. Systems need to balance when to use retrieval versus when to rely on the model's internal knowledge.
Common Misconceptions About RAG
Let's clear up some common misunderstandings:
Misconception 1: "RAG makes AI omniscient"
Reality: RAG only knows what's in its accessible knowledge bases. It can't retrieve information that doesn't exist in those sources.
Misconception 2: "RAG eliminates all AI errors"
Reality: RAG reduces but doesn't eliminate errors. Retrieval can fail, sources can be wrong, and the AI can still misinterpret retrieved information.
Misconception 3: "RAG is only for large enterprises"
Reality: While early adopters were large organizations, tools are making RAG accessible to small businesses and even individuals. Services like certain AI platforms now offer RAG capabilities with minimal setup.
Misconception 4: "RAG replaces all other AI approaches"
Reality: RAG complements other techniques. Sometimes simple AI responses are sufficient, and the overhead of RAG isn't justified. Different tools for different jobs.
Getting Started with RAG: Practical Steps for Beginners
If you're interested in exploring RAG for your needs, here's a beginner-friendly approach:
Step 1: Identify Your Use Case
Start with a specific need. Are you trying to:
- Answer customer questions based on your product manuals?
- Help employees find information in company documents?
- Create a research assistant for a specific topic?
Clear use cases help determine what knowledge sources you need.
Step 2: Gather and Organize Your Knowledge
Collect the documents, databases, or information sources you want the AI to access. This might include:
- PDF manuals and guides
- FAQ documents
- Product specifications
- Internal process documentation
- Approved reference materials
Step 3: Explore No-Code/Low-Code Tools
You don't need to be a programmer to experiment with RAG. Several platforms offer RAG capabilities through user-friendly interfaces. Look for tools that allow you to upload documents and create AI assistants that can query them.
Step 4: Start Small and Test Thoroughly
Begin with a limited set of documents and test with realistic questions. Pay attention to:
- Accuracy of answers
- Relevance of retrieved information
- Response time
- User experience
Step 5: Iterate and Improve
Based on testing, refine your knowledge base, adjust how questions are processed, and improve the retrieval settings. RAG systems often need tuning to work well for specific use cases.
The Future of RAG: What's Next?
RAG technology continues to evolve rapidly. Here are some trends to watch:
Multimodal RAG
Current RAG primarily works with text, but future systems will retrieve and integrate information from images, audio, video, and structured data. Imagine asking "What's wrong with this machine?" and the AI retrieving similar maintenance cases with photos and diagnostic data.
More Intelligent Retrieval
Future retrieval systems will better understand context, user intent, and the relationships between different pieces of information. They might retrieve not just directly relevant documents but also background information that helps the AI provide more complete answers.
Real-Time Knowledge Integration
While current RAG can access relatively current information, future systems might integrate real-time data streams—stock prices, weather data, social media trends—to provide truly up-to-the-minute answers.
Personalization
RAG systems will become better at understanding individual users' contexts, preferences, and knowledge levels, retrieving and presenting information in the most useful way for each person.
Simplified Implementation
As with most technologies, RAG implementation will become easier and more accessible. More platforms will offer RAG as a standard feature rather than a complex add-on.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Use
As with all powerful technologies, RAG raises important ethical questions:
Source Attribution and Copyright
When RAG systems use copyrighted material, proper attribution and respect for intellectual property rights are essential. Organizations need clear policies about what sources can be used and how.
Bias in Knowledge Bases
If the knowledge bases contain biased information, RAG systems will amplify those biases. Regular audits of knowledge sources for fairness and representativeness are important.
Transparency About Limitations
Users should understand when they're interacting with a RAG system versus a regular AI, and what sources the system is using. Clear disclosure builds appropriate trust.
Data Privacy
When RAG systems access personal or sensitive data, robust privacy protections are essential. This includes secure storage of knowledge bases and careful control over what information can be retrieved.
For more on responsible AI practices, see our guide on ethical AI explained.
Conclusion: RAG as a Bridge Between AI and Human Knowledge
Retrieval-Augmented Generation represents a significant step toward more reliable, accurate, and useful artificial intelligence. By combining the creative language capabilities of large models with the precision of information retrieval, RAG helps address some of AI's most frustrating limitations.
For businesses, RAG offers a practical path to AI assistants that actually know about your specific products, services, and processes. For individuals, it promises AI tools that can provide current, sourced information rather than educated guesses. And for society, it moves us toward AI systems that are more transparent about their knowledge sources and limitations.
As RAG technology continues to mature and become more accessible, we can expect to see it powering increasingly sophisticated applications—from personalized tutors that reference specific curriculum materials to customer service agents that know both general troubleshooting and your specific account history.
The key insight is simple yet powerful: Sometimes the smartest answer isn't what you already know, but knowing where to look for the information you need. RAG gives AI that capability, bridging the gap between artificial intelligence and the vast, ever-growing repository of human knowledge.
Further Reading
If you found this guide helpful, you might also enjoy:
- Embeddings and Vector Databases: A Beginner Guide
- How Does Machine Learning Work? Explained Simply
- AI Myths vs Reality: What AI Can and Cannot Do
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
1842
Like
1842
 Dislike
23
Dislike
23
 Love
456
Love
456
 Funny
89
Funny
89
 Angry
12
Angry
12
 Sad
8
Sad
8
 Wow
312
Wow
312

















Transparency and source citation are now expected features, not nice-to-haves. The article was ahead of its time on this.
My personal project became a startup! The RAG foundation was key to our initial prototype.
The distinction between RAG and search+summarize is clearer now with experience. RAG's integration is indeed more sophisticated.
Vector databases are now mainstream. The explanation here helped me understand why they matter beyond RAG applications.
Our company FAQ RAG system has evolved into a full knowledge management platform. The foundation was crucial.
The comparison to search engines makes more sense now with AI-powered search becoming common. RAG principles are everywhere.