AI in Customer Support: How Chatbots Really Work
A clear, beginner-friendly guide to how AI chatbots work in customer support. Learn types, natural language understanding, workflow design, integration, evaluation and best practices for safe, effective automation.
AI in Customer Support: How Chatbots Really Work
Introduction
Companies of all sizes are exploring chatbots to speed up support, reduce repetitive work and provide 24/7 help. But what exactly is happening when a chatbot answers a customer? This guide explains, step by step, how chatbots work, what they can and cannot do, and how to implement them safely and usefully for customer support.
What this article covers
- Different types of chatbots and where they fit
- Key AI components: Natural Language Understanding and dialogue management
- How chatbots connect to systems and workflows
- Performance measurement and best practices
- Privacy, safety, and when to use humans-in-the-loop
Who this article is for
This is written for small business owners, support managers, students and non-technical readers who want a clear picture of chatbots without technical jargon. If you read no-code vs ai tools: what-should-beginners-choose or plan to use automation from what-is-automation-a-beginners-guide, this guide helps you pick the right chatbot approach.
1. Types of chatbots you may encounter
Not all chatbots use the same technology. Choosing the right type depends on your needs.
- Rule-based chatbots: Follow fixed rules and menu flows. Good for simple FAQs and structured forms.
- Retrieval-based chatbots: Search a knowledge base and return the best-matching answer. Useful for help centers.
- Generative (AI) chatbots: Use language models to generate responses in free text. Useful for flexible conversations but require careful oversight.
- Hybrid chatbots: Combine rules with AI: AI suggests responses, but rules and human review control critical steps.
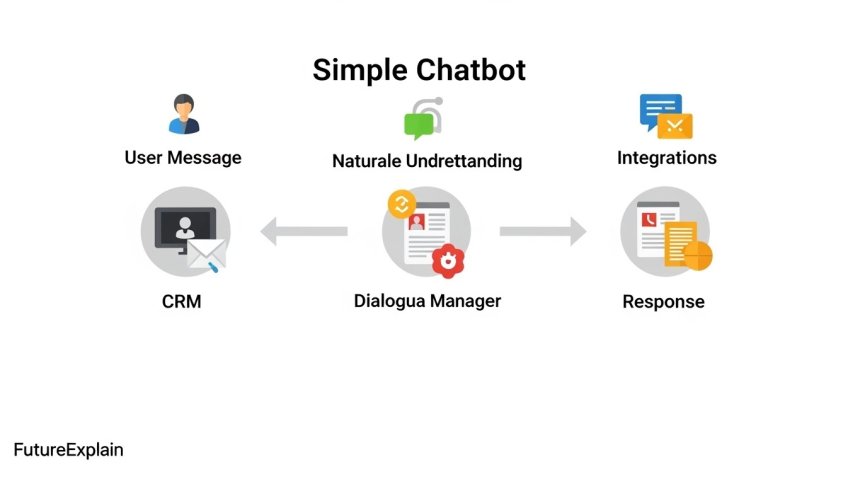
2. Core technology — how a user message becomes a reply
A modern chatbot pipeline typically follows these phases:
2.1 Input processing
User text (or voice converted to text) is first normalized: punctuation removed, case standardized, and common typos corrected. This makes later steps more reliable.
2.2 Natural Language Understanding (NLU)
NLU extracts structured meaning from user text. Two common outputs:
- Intent: The user''s goal (e.g., "reset password", "track order").
- Entities: Specific details in the message (e.g., order number, date).
NLU models are trained on examples. For beginners, many platforms offer prebuilt intent libraries or no-code training tools so you don''t need to build models from scratch. If you want to learn the basics behind NLU, see how-does-machine-learning-work-explained-simply.
2.3 Dialogue management
Dialogue management decides the next action after NLU extracts meaning. Approaches include:
- State machine / rules: A deterministic approach that follows a mapped conversation flow.
- Policy-based: A model (sometimes learned by reinforcement learning) chooses the next step.
- Hybrid: Rules for business-critical decisions and model-based choices for flexible replies.
2.4 Response generation
Finally, the bot composes a reply. This can be:
- Template-based: Fill-in-the-blank replies using entities (safe and predictable).
- Retrieved text: Return an FAQ paragraph.
- Generated text: Use an AI model to create a reply (flexible but needs guardrails).
3. Integrations and data access
A chatbot is useful when it connects to real data and workflows:
- CRMs and ticketing systems: Show order status or open a support ticket.
- Knowledge bases: Search product docs and return correct articles.
- Payment or account systems: Provide invoice or authorization checks (with strong security).
Most platforms connect through APIs. If you prefer no-code, tools like Zapier or Make can link chat platforms to your systems; see no-code vs ai tools for guidance on choosing no-code vs AI-first workflows.
4. Typical chatbot architecture
A simple architecture:
- User (web chat, messaging app)
- Channel adapter (connects to Messenger, WhatsApp, web widget)
- NLU + dialogue manager
- Business logic layer (integrations, database)
- Monitoring, analytics and human escalation
5. When to use a chatbot — common support use cases
- Answering FAQs: Instant answers for common questions.
- Order tracking: Provide status using an order ID.
- Guided troubleshooting: Walk customers through standard diagnostics.
- Ticket creation: Gather details, then create a ticket for human agents.
- Lead qualification: Collect contact details and key needs before handing off to sales.
6. Measuring chatbot success
Key metrics:
- Containment rate: Percentage of conversations resolved by the bot without human handoff.
- Resolution accuracy: Correctness of answers compared to ground truth.
- Customer satisfaction (CSAT): User ratings after the interaction.
- Fallback rate: How often the bot fails to understand and returns a default message.
- Response time: Latency between user message and bot reply.
7. Design patterns and best practices
Design well to avoid common pitfalls:
- Set clear expectations: Tell users they''re chatting with a bot and what it can do.
- Use quick replies and buttons: Reduce typing and guide the conversation.
- Provide easy escalation: If the bot cannot help, route to a human with context captured.
- Fail gracefully: Use friendly fallback messages and retry options.
- Monitor and iterate: Use logs and human review to improve intents and responses.
8. Safety, privacy, and compliance
When connecting chatbots to customer data, follow these controls:
- Minimize sensitive data: Don''t send unnecessary personal data to third-party AI services.
- Mask or pseudonymize: Replace direct identifiers before sending external requests.
- Data retention: Keep logs only as long as needed and follow local regulations.
- User consent: Inform users about data usage and obtain consent when required.
For a beginner''s guide to using AI responsibly, read how-to-use-ai-responsibly-beginner-safety-guide.
9. Human-in-the-loop: when humans are necessary
Some scenarios require human oversight:
- High-risk decisions (billing changes, refunds)
- Escalations where nuanced judgment is required
- When confidence is low — route to an agent with the transcript
Start with a supervised rollout: let humans review suggested replies before full automation.
10. Implementation paths for beginners
Three realistic approaches:
- No-code platform: Use a chatbot builder with NLU pre-configured. Good to launch fast.
- Platform + integrations: Use a managed chatbot service and connect to your CRM via APIs or a tool like Zapier.
- Custom AI: For large companies with specific needs — build with developer help and robust testing.
If you need help choosing tools, see top-ai-tools-for-beginners-to-boost-productivity and best-automation-tools-for-non-technical-users.
11. Example: a simple chatbot flow
Example flow for order tracking:
- User: "Where is my order #12345?"
- Bot NLU: intent = track_order, entity = order_number: 12345
- Dialogue manager: call order API
- Bot: "Your package is in transit and expected delivery is March 20."
This simple example shows NLU + integration + template reply. Compare it with a human agent workflow and you''ll see where automation saves time.
12. Costs and when they matter
Costs depend on volume and technology:
- Rule-based flows are cheap.
- API calls to advanced language models have per-call costs; monitor usage during a pilot.
- Measure ROI by time saved and reduction in human workload.
For budgeting tips see ai-for-small-businesses-practical-use-cases.
13. Monitoring and continuous improvement
Monitor logs and common failure points. Use A/B tests for different reply styles and track CSAT. Regularly retrain NLU on real chat examples.
14. Integration with contact channels
Chatbots can live inside:
- Your website (web widget)
- Messaging apps (WhatsApp, Messenger)
- Email triage systems
- Voice channels (with speech-to-text)
Each channel has rules and limitations; test on the channel your customers use most.
15. Avoiding common mistakes
- Don''t promise more than the bot can deliver.
- Don''t ignore logs. Low-volume failures can reveal big UX problems.
- Don''t skip security reviews when connecting to payment or account systems.

16. Case study sketches (short)
Example 1: A small ecommerce store used a rule-based bot for tracking + returns and cut basic support volume by 30%. Example 2: A midsize company used hybrid AI for triage, routing complex cases to agents and saw shorter first-response times.
17. How to start today — a 6-step checklist
- Identify the top 3 support tasks by volume.
- Choose a no-code or managed chatbot option for a pilot.
- Prepare sample dialogues and common questions.
- Connect essential systems (orders, accounts) with minimal permissions.
- Run a small pilot with human review on edge cases.
- Measure containment, CSAT, and iterate.
18. Related articles and learning path
To build background knowledge, read:
- what-is-artificial-intelligence-a-complete-beginners-guide
- how-does-machine-learning-work-explained-simply
- no-code-vs-ai-tools-what-should-beginners-choose
- how-to-use-ai-responsibly-beginner-safety-guide
Forward-looking: learn how personalization works in how-ai-personalization-works-netflix-youtube-amazon and consider careers covered in ai-careers-explained-beginner-friendly-career-paths.
19. Final thoughts
Chatbots are practical tools when chosen and implemented with clear goals, monitoring and human oversight. Start small, measure outcomes, and iterate. Use the hybrid approach for critical tasks and ensure privacy controls before connecting any sensitive systems.
Further reading
- ai-in-customer-support-how-chatbots-really-work (this article)
- related resources
For templates, prompts and no-code examples, see top-ai-tools-for-beginners-to-boost-productivity and best-free-ai-tools-you-can-use-without-technical-skills.
Share
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
900
Like
900
 Dislike
8
Dislike
8
 Love
140
Love
140
 Funny
30
Funny
30
 Angry
2
Angry
2
 Sad
1
Sad
1
 Wow
60
Wow
60















Short opinion: Start small and iterate. This article is a great starting point.
Experience: We used shadow mode and found many small UX issues before full launch.
Praise: Very actionable. The 6-step checklist is a keeper.
Question: How do we set confidence thresholds without historical data?
Use conservative thresholds initially and route many low-confidence cases to humans; refine thresholds after observing performance.
Constructive feedback: maybe include a short handoff checklist for agents.
Question: Is it OK to log full transcripts for quality review?
Log transcripts only when needed, and redact personal data. Keep access controls for review purposes.